Abstract
Purpose
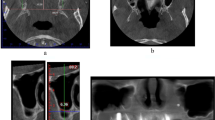
Evaluation of the inner aspect of the maxillary sinus is important for the success of a sinus lift procedure. The most common surgical complication is perforation of the Schneiderian membrane, which is thought to occur because of the presence of maxillary sinus septa. Therefore, we retrospectively investigated the incidence and morphology of maxillary sinus septa using multiplanar reformatted computed tomographic (CT) images from dentate Japanese patients.
Methods
A total of 276 patients and 552 maxillary sinus segments were evaluated. The maxillary sinus septa were divided into four locations: forefront, anterior, middle, and posterior. The heights of the septa were measured at three sites from the deepest point of the sinus floor: lateral, mid-point, and medial.
Results
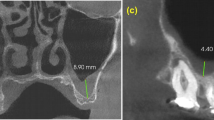
Sinus septa were identified in 191 of 552 (34.6%) maxillary sinus segments obtained from 111 of 276 (40.2%) patients. One unilateral septum was most commonly detected, and the sinus septa were most often located in the middle of the maxillary sinus. The average height of the identified septa was 8.69 ± 4.68 mm (mean ± standard deviation).
Conclusion
Multiplanar reformatted CT images can identify maxillary sinus septa in any plane. The height of maxillary sinus septa in the dentate maxillae was higher than detected in previous studies. Appropriate treatment planning using CT images should be considered to prevent surgical complications.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tatum H, Jr. (1986) Maxillary and sinus implant reconstructions. Dent Clin N Am 30 (2):207–229
Boyne PJ, James RA (1980) Grafting of the maxillary sinus floor with autogenous marrow and bone. Journal of oral surgery (American Dental Association : 1965) 38(8):613–616
Ardekian L, Oved-Peleg E, Mactei EE, Peled M (2006) The clinical significance of sinus membrane perforation during augmentation of the maxillary sinus. Journal of oral and maxillofacial surgery : official journal of the American Association of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeons 64(2):277–282. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joms.2005.10.031
Chanavaz M (1990) Maxillary sinus: anatomy, physiology, surgery, and bone grafting related to implantology--eleven years of surgical experience (1979-1990). The Journal of oral implantology 16(3):199–209
van den Bergh JP, ten Bruggenkate CM, Disch FJ, Tuinzing DB (2000) Anatomical aspects of sinus floor elevations. Clin Oral Implants Res 11(3):256–265
Koymen R, Gocmen-Mas N, Karacayli U, Ortakoglu K, Ozen T, Yazici AC (2009) Anatomic evaluation of maxillary sinus septa: surgery and radiology. Clinical anatomy (New York, NY) 22(5):563–570. https://doi.org/10.1002/ca.20813
Pommer B, Ulm C, Lorenzoni M, Palmer R, Watzek G, Zechner W (2012) Prevalence, location and morphology of maxillary sinus septa: systematic review and meta-analysis. J Clin Periodontol 39(8):769–773. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-051X.2012.01897.x
Krennmair G, Ulm CW, Lugmayr H, Solar P (1999) The incidence, location, and height of maxillary sinus septa in the edentulous and dentate maxilla. Journal of oral and maxillofacial surgery : official journal of the American Association of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeons 57(6):667–671; discussion 671-662
Maestre-Ferrin L, Galan-Gil S, Rubio-Serrano M, Penarrocha-Diago M, Penarrocha-Oltra D (2010) Maxillary sinus septa: a systematic review. Medicina oral, patologia oral y cirugia bucal 15(2):e383–e386
Vinter I, Krmpotic-Nemanic J, Hat J, Jalsovec D (1993) [Does the alveolar process of the maxilla always disappear after tooth loss?]. Laryngorhinootologie 72 (12):605–607. doi:https://doi.org/10.1055/s-2007-997963
Naitoh M, Suenaga Y, Kondo S, Gotoh K, Ariji E (2009) Assessment of maxillary sinus septa using cone-beam computed tomography: etiological consideration. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res 11 Suppl 1:e52–58. doi:https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1708-8208.2009.00194.x, e58
Lee WJ, Lee SJ, Kim HS (2010) Analysis of location and prevalence of maxillary sinus septa. Journal of periodontal & implant science 40(2):56–60. https://doi.org/10.5051/jpis.2010.40.2.56
Park YB, Jeon HS, Shim JS, Lee KW, Moon HS (2011) Analysis of the anatomy of the maxillary sinus septum using 3-dimensional computed tomography. Journal of oral and maxillofacial surgery : official journal of the American Association of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeons 69(4):1070–1078. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joms.2010.07.020
Underwood AS (1910) An inquiry into the anatomy and pathology of the maxillary sinus. J Anat Physiol 44 (Pt 4:354–369
Jun BC, Song SW, Park CS, Lee DH, Cho KJ, Cho JH (2005) The analysis of maxillary sinus aeration according to aging process; volume assessment by 3-dimensional reconstruction by high-resolutional CT scanning. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 132(3):429–434. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.otohns.2004.11.012
Krennmair G, Ulm C, Lugmayr H (1997) Maxillary sinus septa: incidence, morphology and clinical implications. J Craniomaxillofac Surg 25(5):261–265
Cakur B, Sumbullu MA, Durna D (2013) Relationship among Schneiderian membrane, Underwood’s septa, and the maxillary sinus inferior border. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res 15(1):83–87. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1708-8208.2011.00336.x
Rancitelli D, Borgonovo AE, Cicciu M, Re D, Rizza F, Frigo AC, Maiorana C (2015) Maxillary sinus septa and anatomic correlation with the Schneiderian membrane. J Craniofac Surg 26(4):1394–1398. https://doi.org/10.1097/scs.0000000000001725
Ata-Ali J, Diago-Vilalta JV, Melo M, Bagan L, Soldini MC, Di-Nardo C, Ata-Ali F, Manes-Ferrer JF (2017) What is the frequency of anatomical variations and pathological findings in maxillary sinuses among patients subjected to maxillofacial cone beam computed tomography? A systematic review. Medicina oral. patologia oral y cirugia bucal 22(4):e400–e409
Lozano-Carrascal N, Salomo-Coll O, Gehrke SA, Calvo-Guirado JL, Hernandez-Alfaro F, Gargallo-Albiol J (2017) Radiological evaluation of maxillary sinus anatomy: a cross-sectional study of 300 patients. Annals of anatomy = Anatomischer Anzeiger : official organ of the Anatomische Gesellschaft 214:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aanat.2017.06.002
Acknowledgments
We thank Wakiko Tani from the Center for Radiology and Radiation Oncology at our hospital for their expert analytic advice. We thank Angie Smaranda, M (Dent), from Edanz Group (www.edanzediting.com/ac) for editing a draft of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Takeda, D., Hasegawa, T., Saito, I. et al. A radiologic evaluation of the incidence and morphology of maxillary sinus septa in Japanese dentate maxillae. Oral Maxillofac Surg 23, 233–237 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10006-019-00773-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10006-019-00773-2