Abstract
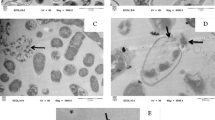
Sodium hypochlorite (NaOCl) is commonly used as a disinfectant; however, its bactericidal mechanism has not yet been clarified. In the present study, the bactericidal mechanism of NaOCl was examined using microscopy and gel electrophoresis techniques with Staphylococcus aureus strain 209P. S. aureus cells treated with 500 and 1000 ppm NaOCl for 5 and 15 min were observed by SEM and TEM. SEM images of the bacterial cells treated with NaOCl showed an irregular surface, with cells being partially invaginated. TEM images of the bacterial cells showed cytoplasmic alterations, accompanied by a partially irregular cellular surface. Under a fluorescence microscope, we clearly observed fluorescence quenching in the 1000 ppm NaOCl-treated cells. Based on these observations, which indicated that NaOCl damaged chromosomal DNA, we next extracted chromosomal DNA from bacterial cells treated with NaOCl and performed agarose gel electrophoresis. Chromosomal DNA was absent in the DNA sample from the bacterial cells treated with 500 ppm NaOCl. From these biochemical results, it was strongly suggested that NaOCl degrades the chromosomal DNA of S. aureus. We consider that the morphological changes in the cytoplasm induced by NaOCl may be related to NaOCl-induced degradation of S. aureus chromosomal DNA.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Koszczol C, Bernardo K, Kronke M, Krut O (2006) Subinhibitory quinupristin/dalfopristin attenuates virulence of Staphylococcus aureus. J Antimicrob Chemother 58:564–574
Tillotson GS, Draghi DC, Sahm DF, Tomfohrde KM, Fabro TD, Critchley IA (2008) Susceptibility of Staphylococcus aureus isolated from skin and wound infections in the United States 2005–07: laboratory-based surveillance study. J Antimicrob Chemother 62:109–115
Abid N, Maalej S, Rouis S (2004) Morphological and physiological changes of Staphylococcus aureus exposed to hypochlorous acid. Microbiology 38:245–250
Rutala WA, Weber DJ (1997) Uses of inorganic hypochlorite (bleach) in health-care facilities. Clin Microbiol Rev 10:597–610
Dychdala GR (1991) Chlorine and chlorine compounds. Disinfect Steriliz Preserv 4:131–151
Yamada S, Sugai M, Komatsuzawa H, Nakashima S, Oshida T, Matsumoto A, Suginaka H (1996) An autolysin ring associated with cell separation of Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol 178:1565–1571
Sugai M, Yamada S, Nakashima S, Komatsuzawa H, Matsumoto A, Oshida T, Suginaka H (1997) Localized perforation of the cell wall by a major autolysin: atl gene products and the onset of penicillin-induced lysis of Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol 179:2958–2962
Yamada S, Matsumoto A (1984) Localization of protein A on the cell surface of Staphylococcus aureus Cowan I and protein A-deficient strains. J Electron Microsc 33:172–174
Robinson JM, Hardman JK, Sloan GL (1979) Relationship between lysostaphin endopeptidase production and cell wall composition in Staphylococcus staphylolyticus. J Bacteriol 137:1158–1164
Trayer HR, Buckley CE (1970) Molecular properties of lysostaphin, a bacteriolytic agent specific for Staphylococcus aureus. J Biol Chem 145:4842–4846
Wyllie AH (1980) Glucocorticoid-induced thymocyte apoptosis is associated with endogenous endonuclease activation. Nature 284:555–556
Abreu AC, Tavares RR, Borges A, Mergulhao F, Simoes M (2013) Current and emergent strategies for disinfection of hospital environments. J Antimicrob Chemother 68:2718–2732
Lydon MJ, Keeler KD, Thomas DB (1980) Vital DNA staining and cell sorting by flow microfluorometry. J Cell Physiol 102:175–181
Gomes BPFA, Ferraz CCR, Vianna ME, Berber VB, Teixeira FB, Souza FJ (2001) In vitro antimicrobial activity of several concentrations of sodium hypochlorite and chlorhexidine gluconate in the elimination of Enterococcus faecalis. Int Endod J 34:424–428
Vianna ME, Gomes BPFA (2004) In vitro evaluation of the antimicrobial activity of chlorhexidine and sodium hypochlorite. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 97:79–84
Barber VB, Gomes BPFA, Sena NT, Vianna ME, Ferraz CCR, Zaia AA, Souza-Filho FJ (2006) Efficacy of various concentrations of NaOCl and instrumentation techniques in reducing Enterococcus faecalis within root canals and dentinal tubules. Int Endod J 39:10–17
Maillard J-Y, Hann AC, Baubet V, Perrin R (1998) Efficacy and mechanisms of action of sodium hypochlorite on Pseudomonas aeruginosa PA01 phage F116. J Appl Microbiol 85:925–932
Estrela C, Estrela CRA, Barbin EL, Spano JCE, Marchesan MA, Pecora JD (2002) Mechanism of action of sodium hypochlorite. Braz Dent J 13:113–117
Fukuzaki S (2006) Mechanisms of actions of sodium hypochlorite in cleaning and disinfection processes. Biocontrol Sci 11:147–157
Mohammadi Z (2008) Sodium hypochlorite in endodontics: an update review. Int Dent J 58:329–341
Fukutsuji K, Yamada S, Harada T (2013) Ultrastructural cell wall characteristics of clinical gentamycin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolates. Med Mol Morphol 46(2):70–76
Hyo Y, Yamada S, Fukutsuji K, Harada T (2013) Thickening of the cell wall in macrolide-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Med Mol Morphol 46(4):217–224
Nakano H, Kurihara K, Okamoto M, Tone S, Shinohara K (1997) Heat-induced apoptosis and p53 in cultured mammalian cells. Int J Radiat Biol 71:519–529
Dwyer DJ, Camacho DM, Kohanski MA, Callura JM, Colins JJ (2012) Antibiotic-induced bacterial cell death exhibits physiological and biochemical hallmarks of apoptosis. Mol Cell 46:561–572
Mcdonnell G, Russell AD (1999) Antiseptics and disinfectants: activity, action, and resistance. Clin Microbiol Rev 12:147–179
Mckenna SM, Davies KJA (1988) The inhibition of bacterial growth by hypochlorous acid. Biochem J. 254:685–692
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by research project Grants, 25-60 and 26-7, from Kawasaki Medical School. We thank Nobuaki Matsuda and Keiko Isoda from the Bioimaging Research Unit (Kawasaki Medical School) for their excellent technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
S Yamada has received technical consulting charges from Panasonic Corporation. The rest of the authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ujimine, S., Tone, S., Saito, M. et al. Intracellular morphological changes in Staphylococcus aureus induced by treatment with sodium hypochlorite. Med Mol Morphol 50, 178–184 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00795-017-0159-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00795-017-0159-6