Abstract
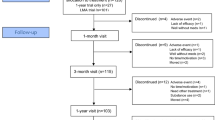
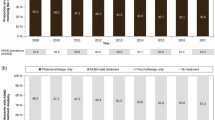
Although ADHD comorbidity has been widely studied, some issues remain unsolved. This multicenter observational study aims to examine comorbid psychiatric disorders in a clinical sample of newly diagnosed, treatment naïve children and adolescents with and without ADHD and, to compare treatment efficacy based on the type of comorbidity. We performed an analysis of the medical records of patients identified from the Regional ADHD Registry database, enrolled in 18 ADHD centers in the 2011–2016 period. 1919 of 2861 subjects evaluated (67%) met the diagnostic criteria for ADHD: 650 (34%) had only ADHD, while 1269 (66%) had at least one comorbid psychiatric disorder (learning disorders, 56%; sleep disorders, 23%; oppositional defiant disorder, 20%; anxiety disorders, 12%). Patients with ADHD of combined type and with severe impairment (CGI-S ≥5) were more likely to present comorbidity. 382 of 724 (53%) followed up patients improved after 1 year of treatment. ADHD with comorbidity showed greater improvement when treated with combined interventions or methylphenidate alone. Specifically, combined treatment showed significant superiority for ADHD with learning disorders (ES 0.66) and ODD (ES 0.98), lower for ADHD with sleep or anxiety disorders. Training intervention alone showed only medium efficacy (ES 0.50) for ADHD and learning disorders. This study was the first describing comorbidity patterns of ADHD in Italy, confirming, in a multicenter clinical setting, that ADHD is more often a complex disorder. Findings highlight important diagnostic, therapeutic, and service organization aspects that should be broadly extended to ensure an appropriate and homogenous ADHD management.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
American Psychiatric Association (2013) Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders, 5th edn. American Psychiatric Publishing, Arlington
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (2013) Mental health surveillance among children—United States, 2005–2011. MMWR 62:1–35
Barkley RA, Russell A (2014) Attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder: A handbook for diagnosis and treatment. Guilford Publications, New York
Feinstein A (1970) The pre-therapeutic classification of co-morbidity in chronic disease. J Chron Dis 23:455–468
Caron C, Rutter M (1991) Comorbidity in child psychopathology: concepts, issues and research strategies. J Child Psychol Psychiatry 32:1063–1080
Angold A, Costello EJ, Erkanli A (1999) Comorbidity. Child Psychol Psychiatry 40(1):57–87
Blanco C, Wall MM, He JP (2015) The space of common psychiatric disorders in adolescents: comorbidity structure and individual latent liabilities. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 54(1):45–52
Gillberg C, Carlström G, Rasmussen P (1983) Hyperkinetic disorders in seven-year-old children with perceptual, motor and attentional deficits. J Child Psychol Psychiatry 24(2):233–246
Brown T (2000) Attention-Deficit Disorders and Comorbidities in children, adolescent and adults. American Psychiatric Press, Washington
Biederman J, Monuteaux MC, Kendrick E, Klein KL, Faraone SV (2005) The CBCL as a screen for psychiatric comorbidity in paediatric patients with ADHD. Arch Dis Child 90:1010–1015
Gillberg C, Gillberg IC, Rasmussen P et al (2004) Coexisting disorders in ADHD: implications for diagnosis and intervention. Eur Child Adolesc Psychiatry 13(Suppl 1):I80–I92
Jensen PS, Martin D, Cantwell DP (1997) Comorbidity in ADHD: implication for research, practice and DSM V. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 36(8):1065–1079
Jensen PS, Hinshaw SP, Kraemer HC et al (2001) ADHD comorbidity findings from the MTA study: comparing comorbid subgroups. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 40:147–158
Kadesjö B, Gillberg C (2001) The comorbidity of ADHD in the general population of Swedish school-age children. J Child Psychol Psychiatry 42:487–492
Spencer TJ, Biederman J, Mick E (2007) Attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder: diagnosis, lifespan, comorbidities, and neurobiology. Ambul Pediatr 7(suppl 1):73–81
Verkuijl N, Perkins M, Fazel M (2015) Childhood attention-deficit Hyperactivity disorder. Br Med J 350:h2168
Elia J, Ambrosini P, Berrettini W (2008) ADHD characteristics: I. Concurrent comorbidity patterns in children and adolescents. Child Adolesc Psychiatry Ment Health 2:15
Larson K, Russ SA, Kahn RS, Halfon N (2011) Patterns of Comorbidity, Functioning, and Service Use for US children with ADHD, 2007. Pediatrics 127(3):462–470
Wilens TE, Biederman J, Spencer TJ (2002) Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder across the lifespan. Annu Rev Med 53:113–131
Yoshimasu K, Barbaresi WJ, Colligan RC, Voigt RG, Killian JM, Weaver AL, Katusic SK (2012) Childhood ADHD is strongly associated with a broad range of psychiatric disorders during adolescence: a population-based birth cohort study. J Child Psychol Psychiatry 53(10):1036–1043
Biederman J, Faraone SV (2005) Attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder. Lancet 366(9481):237–248
Jensen CM, Steinhausen HC (2015) Comorbid mental disorders in children and adolescents with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder in a large nationwide study. Atten Defic Hyperact Disord 7:27–38
Kadesjö B, Gillberg C (1999) Developmental coordination disorder in Swedish 7-year-old children. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 38:820–828
DuPaul GJ, Gormley MJ, Laracy SD (2013) Comorbidity of LD and ADHD: implications of DSM-5 for assessment and treatment. J Learn Disabil 46(1):43–51
Becker SP, Luebbe AM, Langberg JM (2012) Co-occurring mental health problems and peer functioning among youth with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: a review and recommendations for future research. Clin Child Fam Psychol Rev 15:279–302
Cortese S (2015) Sleep and ADHD: what we know and what we do not know. Sleep Med 16:5–6
Healy JM (2010) Different learners: identifying, preventing, and treating your child’s learning problems. Simon and Schuster, New York
Thapar A, Cooper M, Eyre O, Langley K (2013) What have we learnt about the causes of ADHD? J Child Psychol Psyc 54:3–16
Gagliano A, Germanò E, Calamoneri F (2007) Specific learning diabilities and ADHD: characteristic of association. Giornale Neuropsichiatr Evolutiva 27:216–228
Luoni C, Balottin U, Zaccagnino M, Brembilla L, Livetti G, Termine C (2013) Reading difficulties and attention deficit-hyperactivity behaviours: evidence of an early association in a non clinical sample. J Res Read 38:73–90
Ben-Ari Y (2008) Neuro-archaelogy: pre-symptomatic architecture and signature of neurological disorders. Trends Neurosci 31(12):626–636
Pettersson E, Anckarsäter H, Gillberg C, Lichtenstein P (2013) Different neurodevelopmental symptoms have a common genetic etiology. J Child Psychol Psychiatry 54(12):1356–1365
Pennington BF (2006) From single to multiple deficit models of developmental disorders. Cognition 101:385–413
Mick E, Biederman J, Jetton J, Faraone SV (2000) Sleep disturbance associated with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder: the impact of psychiatric comorbidity and pharmacotherapy. J Child Adolesc Psychopharmacol 10(3):223–231
Kirov R, Brand S (2014) Sleep problems and their effect in ADHD. Expert Rev Neurother 14:287–299
Accardo JA, Marcus CL, Leonard MB, Shults J, Meltzer LJ, Elia J (2012) Association between psychiatric comorbidities and sleep disturbances in children with attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder. J Dev Behav Pediatr 33(2):97–105
Banaschewski T, Neale BM, Rothenberger A, Roessner V (2007) Comorbidity of tic disorder and ADHD: conceptual and methodological consideration. Eur Child Adol Psychiatry 16(1):5–14
Connor DF (2015) Pharmacological management of pediatric patients with comorbid attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder oppositional defiant disorder. Pediatric Drugs 17:361–371
Canadian Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder Resource Alliance (CADDRA) (2011) Canadian ADHD practice guidelines, 3rd edn. CADDRA, Toronto
Freitag CM, Hänig S, Schneider A, Seitz C, Palmason H, Retz W, Meyer J (2012) Biological and psychosocial environmental risk factors influence symptom severity and psychiatric comorbidity in children with ADHD. J Neural Transm 119(1):81–94
Canino G, Shrout PE, Rubio-Stipec M et al (2004) The DSM-IV rates of child and adolescent disorders in Puerto Rico: Prevalence, correlates, service use and the effects of impairment. Arch Gen Psychiatry 61(1):85–93
Newcorn JH, Halperin JM, Jensen PS et al (2001) Symptom profiles in children with ADHD: effects of comorbidity and gender. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 40:137–146
Didoni A, Sequi M, Panei P, Bonati M, Lombardy ADHD Registry Group (2011) One-year prospective follow-up of pharmacological treatment in children with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 67:1061–1067
Panei P, Arcieri R, Vella S, Bonati M, Martini N, Zuddas A (2004) Italian attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder registry. Pediatrics 114(2):514
Gazzetta Ufficiale Della Repubblica Italiana, No. 230; 3 ottobre 2003. http://www.gazzettaufficiale.it/atto/serie_generale/caricaDettaglioAtto/originario?atto.dataPubblicazioneGazzetta=2003-10-03&atto.codiceRedazionale=03A10942&elenco30giorni=false. Accessed March 27, 2017
Bonati M, Reale L, Zanetti M, Lombardy ADHD Group (2015) A Regional ADHD Center-Based Network Project for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Children and Adolescents With ADHD. J Atten Disord. doi:10.1177/1087054715599573
Bonati M, Reale L (2013) Reducing overdiagnosis and disease mongering in ADHD in Lombardy. Br Med J 347:f7474
Zanetti M, Cartabia M, Didoni A, Fortinguerra F, Reale L, Bonati M (2016) The impact of a model based clinical regional registry for attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). Health Informatics J. doi:10.1177/1460458216635835
Wechsler D (1991) Wechsler intelligence scale for children, WISC-III, 3rd edn. Psychological Corporation, New York
Wechsler D (2002) WPPSI-III administration and scoring manual. Psychological Corporation, San Antonio
Wechsler D (2003) Wechsler Intelligence Scale for Children, 4th edn. Psychological Corporation, San Antonio
Kaufman J, Birmaher B, Brent D, Rao U, Flynn C, Moreci P, Williamson D, Ryan N (1997) Schedule for affective disorders and schizophrenia for school-age children-present and lifetime version (K-SADS-PL): initial reliability and validity data. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 36(7):980–988
Achenbach TM, Eofbrock C (1983) Manual for the child behaviour checklist. University of Vermont, Burlington
Conners CK, Sitarenios G, Parker JD, Epstein JN (1998) The revised Conners’ Parent Rating Scale (CPRS-R): factor structure, reliability, and criterion validity. J Abnorm Child Psychol 26:257–268
Goyette CH, Conners CK, Ulrich RF (1978) Normative data on revised Conners’ parent and teacher rating scales. J Abnorm Child Psychol 6:221–236
Guy W (1996) ECDEU assessment manual for psychopharmacology: publication ADM 76-338. US Department of Health, Education and Welfare, Washington, pp 218–222
National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (2008) Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. CG72; 2008. http://guidance.nice.org.uk/CG72. Accessed March 27, 2017
SINPIA (2002) Linee-guida per la diagnosi e la terapia farmacologica del Disturbo da Deficit Attentivo con Iperattività (ADHD) in età evolutiva. http://www.iss.it/binary/wpop/cont/SINPIA_L.g.ADHD.1116940207.pdf. Accessed March 27, 2017
Sharpe D (2015) Your Chi-Square test is statistically significant: Now What? Practical assessment. Res Eval 20:1–10
Cohen J (1969) Statistical power analysis for the behavioral sciences. Academic Press, Cambridge
Amiri S, Shafiee-Kandjani AR, Fakhari A et al (2013) Psychiatric Comorbidities in ADHD Children: An Iranian Study among Primary School Students. Arch Iran Med 16(9):513–517
Bakare MO (2012) Attention deficit hyperactivity symptoms and disorder (ADHD) among African children: a review of epidemiology and co-morbidities. Afr J Psychiatry (Johannesbg) 15(5):358–361
Bauermeister JJ, Shrout PE, Ramirez R (2007) ADHD correlates, co-morbidity, and impairment in community and treated samples of children and adolescent. J Abnorm Child Psychol 35(6):883–898
Daviss WB (2008) A review of comorbid depression in pediatric ADHD: etiology, phenomenology, and treatment. J Child Adolesc Psychopharmacol 18:565–571
Farbstein I, Mansbach-Kleinfeld I, Auerbach JG, Ponizovsky AM, Apter A (2014) The Israel Survey of Mental health among adolescent: prevalence of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, comorbidity, methylphenidate use and help seeking patterns. Isr Med Assoc J 16(9):568–573
Maric M, Prins PJ, Ollendick TH (2015) Moderators and mediators of youth treatment outcomes. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Collisson BA, Graham SA, Preston JL, Rose MS, McDonald S, Tough S (2016) Risk and protective factors for late talking: an epidemiologic investigation. J Pediatr 172:168–174
Jurado D, Alarcón RD, Martínez-Ortega JM, Mendieta-Marichal Y, Gutiérrez-Rojas L, Gurpegui M (2017) Factors associated with psychological distress or common mental disorders in migrant populations across the world. Rev Psiquiatr Salud Ment 10(1):45–58
Kessler RC, Berglund P, Demler O, Jin R, Merikangas KR, Walters EE (2005) Lifetime prevalence and age-of-onset distributions of DSM-IV disorders in the national comorbidity survey replication. Arch Gen Psychiatry 62:593–602
Lehti V, Chudal R, Suominen A, Gissler M, Sourander A (2016) Association between immigrant background and ADHD: a nationwide population-based case-control study. J Child Psychol Psychiatry 57(8):967–975
Zenglein Y, Schwenck C, Westerwald E, Schmidt C, Beuth S, Meyer J, Palmason H, Seitz C, Hänig S, Freitag CM (2016) Empirically Determined, Psychopathological Subtypes in Children With ADHD. J Atten Disord 20:96–107
Frigerio A, Rucci P, Goodman R et al (2009) Prevalence and correlates of mental disorders among adolescents in Italy: The PrISMA study. Eur Child Adolesc Psychiatry 18(4):217–226
Polanczyk GV, Salum GA, Sugaya LS, Caye A, Rohde LA (2015) Annual Research Review: a meta-analysis of the worldwide prevalence of mental disorders in children and adolescent. J Child Psychol Psychiatry 56(3):345–365
Park S, Kim BN, Cho SC, Kim JW, Shin MS, Yoo HJ (2015) Prevalence, correlates, and comorbidities of DSM-IV psychiatric disorders in children in Seoul, Korea. Asia Pac J Public Health 27:1942–1951
Barkley RA, Brown TE (2008) Unrecognized attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder in adults presenting with other psychiatric disorders. CNS Spectr 13(11):977–984
Essau CA, Gabbidon J (2013) Epidemiology, comorbidity and mental health service utilization. Blackwell Publishing, The Wiley-Blackwell handbook of the treatment of childhood and adolescent anxiety. doi:10.1111/b.9780470667354.2013.00003.x
Jarret MA, Ollendick TH (2008) A conceptual review of the comorbidity of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder and anxiety: implication for further research and practice. Clin Psychol Rev 28(7):1266–1280
Fischer M, Barkley RA, Smallish L, Fletcher K (2002) Young adult follow-up of hyperactive children: self-reported psychiatric disorders, comorbidity, and the role of childhood conduct problems and teen CD. J Abnorm Child Psychol 30(5):463–475
Lundervold AJ, Hinshaw SP, Sørensen L, Posserud MB (2016) Co-occurring symptoms of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) in a population-based sample of adolescents screened for depression. BMC Psychiatry 16:46
Lee MJ, Yang KC, Shyu YC, Yuan SS, Yang CJ, Lee SY, Lee TL, Wang LJ (2016) Attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder, its treatment with medication and the probability of developing a depressive disorder: a nationwide population-based study in Taiwan. J Affect Disord 189:110–117
Masi G, Millepiedi S, Mucci M, Bertini N, Pfanner C, Arcangeli F (2006) Comorbidity of obsessive-compulsive disorder and attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder in referred children and adolescents. Compr Psychiatry 47(1):42–47
Faraone SV, Biederman J, Mennin D, Wozniak J, Spencer T (1997) Attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder with bipolar disorder: a familial subtype? J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 36:1378–1387
Merikangas KR, Calkins ME, Burstein M et al (2015) Comorbidity of physical and mental disorders in the neurodevelopmental genomics cohort study. Pediatrics 135:e927–e938
SINPIA (2015) L’assistenza ai minori con disturbi neuropsichici in lombardia. Prevenzione, diagnosi, cura e riabilitazione nella rete dei servizi di Neuropsichiatria dell’Infanzia e dell’Adolescenza. http://goo.gl/egJ0EN. Accessed March 27, 2017
Clavenna A, Cartabia M, Sequi M et al (2013) Burden of psychiatric disorders in the pediatric population. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 23(2):98–106
van Ewijk H, Noordermeer SD, Heslenfeld DJ et al (2016) The influence of comorbid oppositional defiant disorder on white matter microstructure in attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Eur Child Adolesc Psychiatry 25:701–710
March JS, Swanson JM, Arnold LE et al (2000) Anxiety as a predictor and outcome variable in the multimodal treatment study of children with ADHD (MTA). J Abnorm Child Psychol 28(6):527–541
MTA Cooperative Group (1999) A 14-month randomized clinical trial of treatment strategies for attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Arch Gen Psychiatry 56(12):1073–1086
Busner J, Targum SD (2007) The clinical global impressions scale: applying a research tool in clinical practice. Psychiatry (Edgmont) 4:28–37
Evans SW, Owens JS, Bunford N (2014) Evidence-based psychosocial treatments for children and adolescents with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. J Clin Child Adolesc Psychol 43:527–551
Pelham WE, Fabiano GA (2008) Evidence-based psychosocial treatments for attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. J Clin Child Adolesc Psychol 37(1):184–214
Thapar A, Cooper M (2016) Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. Lancet 387:1240–1250
Button KS, Ioannidis JP, Mokrysz C et al (2013) Power failure: why small sample size undermines the reliability of neuroscience. Nat Rev Neurosci 14:365–376
Becker SP, Langberg JM, Evans SW (2015) Sleep problems predict comorbid externalizing behaviors and depression in young adolescents with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Eur Child Adolesc Psychiatry 24(8):897–907
Gipson TT, Lance EI, Albury RA, Gentner MB, Leppert ML (2015) Disparities in identification of comorbid diagnoses in children with ADHD. Clin Pediatr (Phila) 54:376–381
Melchior M, Pryor L, van der Waerden J (2015) Commonalities and specificities between attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder and autism-spectrum disorders: can epidemiology contribute? Eur Child Adolesc Psychiatry 24(8):855–858
Acknowledgements
Grateful acknowledgement is made to Chiara Pandolfini for manuscript language editing. Lombardy ADHD Group: Stefano Conte, Valeria Renzetti, Laura Salvoni (Bergamo); Massimo Molteni, Antonio Salandi, Sara Trabattoni (Bosisio Parini, LC); Paola Effedri, Elena Filippini, Elisabetta Pedercini, Edda Zanetti (Brescia); Nadia Fteita (Como); Daniele Arisi, Roberta Mapelli (Cremona); Simona Frassica, Simonetta Oriani, Christian Trevisan (Garbagnate Milanese, MI); Susanna Acquistapace, Ottaviano Martinelli, Davide Villani (Lecco); Emanuela Binaghi, Andrea Deriu, Ernesta Ricotta (Legnano, MI); Arianna Borchia, Paola Morosini (Lodi); Maddalena Breviglieri, Giuseppe Capovilla, Roberto Segala (Mantova); Claudio Bissoli, Maurizio Bonati, Maria Paola Canevini, Massimo Cartabia, Maria Antonella Costantino, Isabella Cropanese, Emiddio Fornaro, Silvia Merati, Alberto Ottolini, Laura Reale, Monica Saccani, Roberto Vaccari, Vera Valenti, Alessandra Valentino, Michele Zanetti (Milano); Umberto Balottin, Matteo Chiappedi, Elena Vlacos (Pavia); Corrado Meraviglia, Maria Grazia Palmieri, Gianpaolo Ruffoni (Sondrio); Francesco Rinaldi, Federica Soardi (Vallecamonica–Sebino, BS); Chiara Luoni, Francesca Pavone, Giorgio Rossi, Cristiano Termine (Varese).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Consortia
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Funding
The study is part of the “Sharing diagnostic-therapeutic approaches for ADHD in Lombardy” project partially funded by the Healtcare Directorate of the Lombardy Region (D.G. sanità n.3798, 8/05/2014). The views expressed are those of the authors and not necessarily those of Regional Healthcare Directorate. The funder had no input in the conduct of the study; the collection, analysis, or interpretation of the data; or the preparation, review, or approval of the manuscript.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Reale, L., Bartoli, B., Cartabia, M. et al. Comorbidity prevalence and treatment outcome in children and adolescents with ADHD. Eur Child Adolesc Psychiatry 26, 1443–1457 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00787-017-1005-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00787-017-1005-z