Abstract
Objectives
The aim of this systematic review was to assess the efficacy and safety of topical non-steroidal immunomodulators (TNSIs) for oral lichen planus (OLP) treatment.
Materials and methods
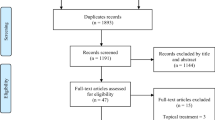
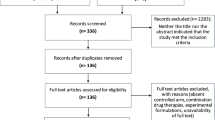
A search strategy designed for this purpose retrieved 1156 references. After analysis of titles and abstracts, 75 studies were selected for full-text analysis. Only randomized controlled clinical trials were selected, resulting in 28 studies included for qualitative and quantitative analysis.
Results
The meta-analysis showed similar benefits in clinical response and symptom resolution between tacrolimus 0.1% and pimecrolimus 1% in comparison to topical steroids (TS). Pimecrolimus showed superior efficacy of clinical response but not for symptom resolution compared to placebo. Tacrolimus and pimecrolimus showed better performance preventing symptom relapse, while pimecrolimus also prevented clinical relapse better than TS. Cyclosporine was superior to placebo; however, TS showed better efficacy of clinical response. Thalidomide and retinoid were assessed in only one trial each, and both showed similar efficacy to TS. Rapamycin also presented similar clinical response to TS; however, the later showed greater reduction of symptoms. Mycophenolate mofetil 2% mucoadhesive was no better than placebo. No serious adverse effects have been reported. Cyclosporine showed a higher frequency and variety of adverse effects.
Conclusions
Topical tacrolimus and pimecrolimus are safe and effective alternatives for OLP treatment.
Clinical relevance
TS are usually the first choice for OLP treatment. Because some oral lesions may have a low response to treatment with TS, more topical therapeutic options, such as TNSIs, should be considered before systemic steroids are used.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ismail SB, Kumar SKS, Zain RB (2007) Oral lichen planus and lichenoid reactions: etiopathogenesis, diagnosis, management and malignant transformation. J Oral Sci 49(2):89–106. https://doi.org/10.2334/josnusd.49.89
Scully C, Carrozzo M (2008) Oral mucosal disease: lichen planus. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg 46(1):15–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bjoms.2007.07.199
Farhi D, Dupin N (2010) Pathophysiology, etiologic factors, and clinical management of oral lichen planus, part I: facts and controversies. Clin Dermatol 28(1):100–108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clindermatol.2009.03.004
Payeras MR, Cherubini K, Figueiredo MA, Salum FG (2013) Oral lichen planus: focus on etiopathogenesis. Arch Oral Biol 58:1057–1069. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.archoralbio.2013.04.004
Eisen D, Carrozzo M, Bagan Sebastian J-V, Thongprasom K (2005) Number V oral lichen planus: clinical features and management. Oral Dis 11(6):338–349. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1601-0825.2005.01142.x
Parashar P (2011) Oral lichen planus. Otolaryngol Clin North Am 44(1):89–107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.otc.2010.09.004
Shirasuna K (2014) Oral lichen planus: malignant potential and diagnosis. Oral Sci Int 11:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1348-8643(13)00030-X
Alrashdan MS, Cirillo N, Mccullough M (2016) Oral lichen planus: a literature review and update. Arch Dermatol Res 308:539–551. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00403-016-1667-2
Sugerman PB, Savage NW, Walsh LJ, Zhao ZZ, Zhou XJ, Khan A, Seymour GJ, Bigby M (2002) The pathogenesis of oral lichen planus. Crit Rev Oral Biol Med 13:350–365. https://doi.org/10.1177/154411130201300405
Gorouhi F, Davari P, Fazel N (2014) Cutaneous and mucosal lichen planus: a comprehensive review of clinical subtypes, risk factors, diagnosis, and prognosis. Sci World J 2014:1–22. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/742826
Yang H, Wu Y, Ma H, Jiang L, Zeng X, Dan H, Zhou Y, Chen Q (2016) Possible alternative therapies for oral lichen planus cases refractory to steroid therapies. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol 121:496–509. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oooo.2016.02.002
De Panfilis G, Manara GC, Allegra F (1981) Remarks on early versus late lichen planus. Arch Dermatol Res 270:163–166. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00408227
Scully C, el-Kom M (1985) Lichen planus: review and update on pathogenesis. J Oral Pathol 14:431–458. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0714.1985.tb00516.x
Vallejo MJ, Huerta G, Cerero R, Seoane JM (2001) Anxiety and depression as risk factors for oral lichen planus. Dermatology 203:303–307. https://doi.org/10.1159/000051777
Koray M, Dulger O, Ak G et al (2003) The evaluation of anxiety and salivary cortisol levels in patients with oral lichen planus. Oral Dis 9:298–301. https://doi.org/10.1034/j.1601-0825.2003.00960.x
Mignogna MD, Lo Russo L, Fedele S (2005) Gingival involvement of oral lichen planus in a series of 700 patients. J Clin Periodonto 32:1029–1033. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-051X.2004.00761.x
van der Meij EH, Mast H, van der Waal I (2007) The possible premalignant character of oral lichen planus and oral lichenoid lesions: a prospective five-year follow-up study of 192 patients. Oral Oncol 43:742–748. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oraloncology.2006.09.006
Cheng Y-SL, Gould A, Kurago Z, Fantasia J, Muller S (2016) Diagnosis of oral lichen planus: a position paper of the American Academy of Oral and Maxillofacial Pathology. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol 122:332–354. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oooo.2016.05.004
Crincoli V, Di Bisceglie MB, Scivetti M, Lucchese A, Tecco S, Festa F (2011) Oral lichen planus: update on etiopathogenesis, diagnosis and treatment. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol 33:11–20. https://doi.org/10.3109/08923973.2010.498014
Al-Hashimi I, Schifter M, Lockhart PB et al (2007) Oral lichen planus and oral lichenoid lesions: diagnostic and therapeutic considerations. Oral Surgery, Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 103 Suppl:S25.e1–S25.12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tripleo.2006.11.001
Carbone M, Conrotto D, Carrozzo M, Broccoletti R, Gandolfo S, Scully C (1999) Topical corticosteroids in association with miconazole and chlorhexidine in the long-term management of atrophic-erosive oral lichen planus: a placebo-controlled and comparative study between clobetasol and fluocinonide. Oral Dis 5(1):44–49. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1601-0825.1999.tb00063.x
Lodi G, Scully C, Carrozzo M, Griffiths M, Sugerman PB, Thongprasom K (2005) Current controversies in oral lichen planus: report of an international consensus meeting. Part 1. Viral infections and etiopathogenesis. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 100(1):40–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tripleo.2004.06.077
Thongprasom K, Prapinjumrune C, Carrozzo M (2013) Novel therapies for oral lichen planus. J Oral Pathol Med 42:721–727. https://doi.org/10.1111/jop.12083
Wu Y, Zhou G, Zeng H (2010) A randomized double-blind, positive-control trial of topical thalidomide in erosive oral lichen planus. YMOE 110:188–195. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tripleo.2010.03.034
Ezzatt OM, Helmy IM (2019) Topical pimecrolimus versus betamethasone for oral lichen planus: a randomized clinical trial. Clin Oral Investig 23:947–956. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00784-018-2519-6
Samimi M, Le Gouge A, Boralevi F et al (2020) Topical rapamycin versus betamethasone dipropionate ointment for treating oral erosive lichen planus: a randomized, double-blind, controlled study. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol 34(10):2384–2391. https://doi.org/10.1111/jdv.16324
Al-hashimi I, Lockhart PB, Wray D et al (2007) Oral lichen planus and oral lichenoid lesions: diagnostic and therapeutic considerations. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 103 Suppl:S25.e1–S25.12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tripleo.2006.11.001
Bagan J, Compilato D, Paderni C et al (2012) Topical therapies for oral lichen planus management and their efficacy: a narrative review. Curr Pharm Des 18:5470–5480. https://doi.org/10.2174/138161212803307617
Samycia M, Lin AN (2012) Efficacy of topical calcineurin inhibitors in lichen planus. J Cutan Med Surg 16:221–229. https://doi.org/10.1177/120347541201600403
Sobaniec S, Bernaczyk P, Pietruski J, Cholewa M, Skurska A, Doli E (2013) Clinical assessment of the efficacy of photodynamic therapy in the treatment of oral lichen planus. Lasers Med Sci 28(1):311–316. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10103-012-1153-9
Conrotto D, Carrozzo M, Ubertalli AV et al (2006) Dramatic increase of tacrolimus plasma concentration during topical treatment for oral graft-versus-host disease. Transplantation 82:1113–1115. https://doi.org/10.4317/medoral.20968
Mattsson U, Magnusson B, Jontell M (2010) Squamous cell carcinoma in a patient with oral lichen planus treated with topical application of tacrolimus. YMOE 110:e1925. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tripleo.2010.02.030
Hodgson TA, Sahni N, Kaliakatsou F, Buchanan JAG, Porter SR (2003) Long-term efficacy and safety of topical tacrolimus in the management of ulcerative/erosive oral lichen planus. Eur J Dermatol 13:466–470
Donovan JCH, Hayes RC, Burgess K, Leong IT, Rosen CF (2005) Refractory erosive oral lichen planus associated with hepatitis C: response to topical tacrolimus ointment. J Cutan Med Surg 9(2):43–46. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10227-005-0038-y
Shichinohe R, Shibaki A, Nishie W, Tateishi Y, Shimizu H (2006) Successful treatment of severe recalcitrant erosive oral lichen planus with topical tacrolimus. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol 20(1):66–68. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1468-3083.2005.01338.x
Swift JC, Rees TD, Plemons JM, Hallmon WW, Wright JC (2005) The effectiveness of 1% pimecrolimus cream in the treatment of oral erosive lichen planus. J Periodontol 76(4):627–635. https://doi.org/10.1902/jop.2005.76.4.627
Volz T, Caroli U, Lu H (2008) Pimecrolimus cream 1% in erosive oral lichen planus—a prospective randomized double-blind vehicle-controlled study. Br J Dermatol 159(4):936–941. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2133.2008.08726.x
Passeron T, Lacour J-P, Fontas E, Ortonne J-P (2007) Treatment of oral erosive lichen planus with 1% pimecrolimus cream: a double-blind, randomized, prospective trial with measurement of pimecrolimus levels in the blood. Arch Dermatol 143:472–476. https://doi.org/10.1001/archderm.143.4.472
Mccaughey C, Machan M, Bennett R, Zone JJ, Hull CM (2011) Pimecrolimus 1% cream for oral erosive lichen planus: a study with a 6-week open-label extension to assess efficacy and safety. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol 25(9):1061–1067. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1468-3083.2010.03923.x
Conrotto D, Carbone M, Carrozzo M, Arduino P, Broccoletti R, Pentenero M, Gandolfo S (2006) Ciclosporin vs. clobetasol in the topical management of atrophic and erosive oral lichen planus: a double-blind, randomized controlled trial. Br J Dermatol 154:139–145. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2133.2005.06920.x
Millard EHD, Langendijk PNJ, Nieboer C (1994) Cyclosporin A in an adhesive base for treatment of recalcitrant oral lichen planus. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol 78(4):437–444. https://doi.org/10.1016/0030-4220(94)90034-5
Franks ME, Macpherson GR, Figg WD (2004) Thalidomide. Lancet 363(9423):1802–1811. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(04)16308-3
Matthews SJ, Mccoy C (2003) Thalidomide: a review of approved and investigational uses. Clin Ther 25(2):342–395. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0149-2918(03)80085-1
Elad S, Epstein JB, Von Bu I, Drucker S, Tzach R, Yarom N (2011) Topical immunomodulators for management of oral mucosal conditions, a systematic review; part II: miscellaneous agents. Expert Opin Emerg Drugs 16(1):183–202. https://doi.org/10.1517/14728214.2011.528390
Petruzzi M, Lucchese A, Lajolo C, Campus G, Lauritano D, Serpico R (2013) Topical retinoids in oral lichen planus treatment: an overview. Dermatology 226:61–67. https://doi.org/10.1159/000346750
Soria A, Agbo-Godeau S, Taieb A, Frances C (2009) Treatment of refractory oral erosive lichen planus with topical rapamycin: 7 cases. Dermatology 218:22–25. https://doi.org/10.1159/000172830
Frieling U, Bonsmann G, Schwarz T, Luger TA, Beissert S (2003) Treatment of severe lichen planus with mycophenolate mofetil. J Am Acad Dermatol 49:1063–1066. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0190-9622(03)02111-X
Iaccarino L, Rampudda M, Canova M, Libera S, Sarzi-Puttini P, Doria A (2007) Mycophenolate mofetil: what is its place in the treatment of autoimmune rheumatic diseases? Autoimmun Rev 6:190–195. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.autrev.2006.11.001
Mutasim DF (2004) Management of autoimmune bullous diseases: pharmacology and therapeutics. J Am Acad Dermatol 51:859–880. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaad.2004.02.013
Sivaraman S, Santham K, Nelson A, Laliytha B, Azhalvel P, Deepak JH (2016) A randomized triple-blind clinical trial to compare the effectiveness of topical triamcinolone acetonate (0.1%), clobetasol propionate (0.05%), and tacrolimus orabase (0.03%) in the management of oral lichen planus. J Pharm Bioallied Sci 8(Suppl 1):S86–S89. https://doi.org/10.4103/0975-7406.191976
Singh AR, Rai A, Aftab M, Jain S, Singh M (2017) Efficacy of steroidal vs non-steroidal agents in oral lichen planus: a randomised, open-label study. J Laryngol Otol 131:69–76. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0022215116009658
Hettiarachchi PVKS, Hettiarachchi RM, Jayasinghe RD, Sitheeque M (2017) Comparison of topical tacrolimus and clobetasol in the management of symptomatic oral lichen planus: a double-blinded, randomized clinical trial in Sri Lanka. J Investig Clin Dent 8:1–6. https://doi.org/10.1111/jicd.12237
Vohra S, Singal A, Sharma SB (2016) Clinical and serological efficacy of topical calcineurin inhibitors in oral lichen planus: a prospective randomized controlled trial. Int J Dermatol 55:101–105. https://doi.org/10.1111/ijd.12887
Arduino PG, Carbone M, Della Ferrera F, Elia A, Conrotto D, Gambino A, Comba A, Calogiuri PL, Broccoletti R (2014) Pimecrolimus vs. tacrolimus for the topical treatment of unresponsive oral erosive lichen planus: a 8 week randomized double-blind controlled study. J Eur Acad Dermatology Venereol 28:475–482. https://doi.org/10.1111/jdv.12128
Sonthalia S, Singal A (2012) Comparative efficacy of tacrolimus 0.1% ointment and clobetasol propionate 0.05% ointment in oral lichen planus: a randomized double-blind trial. Int J Dermatol 51:1371–1378. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-4632.2012.05459.x
Siponen M, Huuskonen L, Kallio-Pulkkinen S, Nieminen P, Salo T (2017) Topical tacrolimus, triamcinolone acetonide, and placebo in oral lichen planus: a pilot randomized controlled trial. Oral Dis 23:660–668. https://doi.org/10.1111/odi.12653
Corrocher G, Di Lorenzo G, Martinelli N et al (2008) Comparative effect of tacrolimus 0.1% ointment and clobetasol 0.05% ointment in patients with oral lichen planus. J Clin Periodontol 35:244–249. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-051X.2007.01191.x
Azizi A, Lawaf S (2007) The comparison of efficacy of adcortyl ointment and topical tacrolimus in treatment of erosive oral lichen planus. J Dent Res Dent Clin Dent Prospects 1:99–102. https://doi.org/10.5681/joddd.2007.017
Laeijendecker R, Tank B, Dekker SK, Neumann HAM (2006) A comparison of treatment of oral lichen planus with topical tacrolimus and triamcinolone acetonide ointment. Acta Derm Venereol 86:227–229. https://doi.org/10.2340/00015555-0070
Radfar L, Wild RC, Suresh L (2008) A comparative treatment study of topical tacrolimus and clobetasol in oral lichen planus. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol 105:187–193. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tripleo.2007.07.029
Riaz HMA, Shakeel A, Shaheen MA, Jaa K (2017) Efficacy of pimecrolimus cream and triamcinolone acetonide paste in the treatment of symptomatic oral lichen planus. Med Forum Mon 28:76–80
Arunkumar S, Kalappanavar AN, Annigeri RG, Kalappa SG (2014) Relative efficacy of pimecrolimus cream and triamcinolone acetonide paste in the treatment of symptomatic oral lichen planus. Indian J Dent Res 6(1):14–19. https://doi.org/10.4103/0975-962X.151692
Gorouhi F, Solhpour A, Beitollahi JM, Afshar S, Davari P, Hashemi P, Nassiri Kashani M, Firooz A (2007) Randomized trial of pimecrolimus cream versus triamcinolone acetonide paste in the treatment of oral lichen planus. J Am Acad Dermatol 57(5):806–813. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaad.2007.06.022
Pakfetrat A, Delavarian Z, Falaki F, Khorashadizadeh M, Saba M (2015) The effect of pimecrolimus cream 1% compared with triamcinolone acetonide paste in treatment of atrophic-erosive oral lichen planus. Iran J Otorhinolaryngol 27:119–126
Thongprasom K, Chaimusig M, Korkij W, Sererat T, Luangjarmekorn L, Rojwattanasirivej S (2007) A randomized-controlled trial to compare topical cyclosporin with triamcinolone acetonide for the treatment of oral lichen planus. J Oral Pathol Med 36:142–146. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0714.2007.00510.x
Yoke PC, Tin GB, Kim MJ, Rajaseharan A, Ahmed S, Thongprasom K, Chaimusik M, Suresh S, Machin D, Bee WH, Seldrup J (2006) A randomized controlled trial to compare steroid with cyclosporine for the topical treatment of oral lichen planus. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 102:47–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tripleo.2005.09.006
Sieg P, Von Domarus H, Von Zitzewitz V, Iven H, Farber L (1995) Topical cyclosporin in oral lichen planus: a controlled, randomized, prospective trial. Br J Dermatol 132:790–794. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2133.1995.tb00728.x
Eisen D, Ellis CN, Duell EA, Griffiths CE, Voorhees JJ (1990) Effect of topical cyclosporine rinse on oral lichen planus. A double-blind analysis. N Engl J Med 323:290–294. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJM199008023230502
Samiee N, Taghavi Zenuz A, Mehdipour M, Shokri J (2020) Treatment of oral lichen planus with mucoadhesive mycophenolate mofetil patch: a randomized clinical trial. Clin Exp Dent Res 6(5):506–511. https://doi.org/10.1002/cre2.302
García-Pola MJ, González-Álvarez L, Garcia-Martin JM (2017) Tratamiento del liquen plano oral. Revisión sistemática y protocolo de actuación. Med Clin (Barc) 149:351–362. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.medcli.2017.06.024
Mutafchieva MZ, Draganova-Filipova MN, Zagorchev PI, Tomov GT (2018) Oral lichen planus—known and unknown: a review. Folia Med (Plovdiv) 60:528–535. https://doi.org/10.2478/folmed-2018-0017
Bombeccari GP, Guzzi G, Tettamanti M, Giannì AB, Baj A, Pallotti F, Spadari F (2011) Oral lichen planus and malignant transformation: a longitudinal cohort study. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 112:328–334. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tripleo.2011.04.009
Fitzpatrick SG, Hirsch SA, Gordon SC (2014) The malignant transformation of oral lichen planus and oral lichenoid lesions: a systematic review. J Am Dent Assoc 145:45–56. https://doi.org/10.14219/jada.2013.10
Warnakulasuriya S, Johnson NW, Van Der Waal I (2007) Nomenclature and classification of potentially malignant disorders of the oral mucosa. J Oral Pathol Med 36:575–580. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0714.2007.00582.x
Moscarella E, Di Brizzi EV, Casari A (2020) Italian expert consensus paper on the management of patients with actinic keratoses. Dermatol Ther 33:e13992. https://doi.org/10.1111/dth.13992
Hada M, Mondul AM, Weinsteins SJ, Albanes D (2020) Serum retinol and risk of overall and site-specific cancer in the ATBC study. Am J Epidemiol 189:532–542. https://doi.org/10.1093/aje/kwz226
Xie L, Song Y, Lin T, Guo H, Wang B, Tang G, Liu C, Huang W, Yang Y, Ling W, Zhang Y, Li J, Huo Y, Wang X, Zhang H, Qin X, Xu X (2019) Association of plasma retinol levels with incident cancer risk in Chinese hypertensive adults: a nested case–control study. Brit J Nutrition 122:293–300. https://doi.org/10.1017/S000711451900120X
Burke MT, Isbel N, Barraclough KA, Jung J-W, Wells JW, Staatz CE (2015) Genetics and nonmelanoma skin cancer in kidney transplant recipients. Pharmacogenomics 16:161–172. https://doi.org/10.2217/pgs.14.156
Lichtenberg S, Rahamimov R, Green H, Fox BD, Mor E, Gafter U, Chagnac A, Rozen-Zvi B (2017) The incidence of post-transplant cancer among kidney transplant recipients is associated with the level of tacrolimus exposure during the first year after transplantation. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 73:819–826. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00228-017-2234-2
Cai SCS, Li W, Tian EAL, Allen JC, Tey HL (2016) Topical calcineurin inhibitors in eczema and cancer association: a cohort study. J Dermatolog Treat 27:531–537. https://doi.org/10.3109/09546634.2016.1163317
Code availability
International Prospective Register of Systematic Reviews (PROSPERO), registration number: CRD42019123579
Funding
We are thankful to CAPES (Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior) and CNPQ (Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico) for financial support (scholarship grants).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. ELS and TBL are responsible for data collection. ELS, TBL, and FV are responsible for data analysis. All authors contributed to the writing of the manuscript, read, and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
No ethics approval was needed because data were retrieved from previously published studies in which informed consent was obtained by the primary investigators.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Supplemental Fig. 1
Risk of bias summary of each study included in the systematic review and meta-analysis (TIF 1308 kb)
ESM 2
(DOCX 12 kb)
ESM 3
(DOCX 28 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
da Silva, E.L., de Lima, T.B., Rados, P.V. et al. Efficacy of topical non-steroidal immunomodulators in the treatment of oral lichen planus: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Oral Invest 25, 5149–5169 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00784-021-04072-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00784-021-04072-7