Abstract
Objective
Analyze the 2-year clinical performance of single-unit titanium-zirconium (TiZr) alloy narrow-diameter (3.3 mm) dental implants with a hydrophilic surface (Straumann® Roxolid®, SLActive®) in patients with controlled type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), measured using the glycated hemoglobin A (HbA1c) concentration test, compared with results in individuals without T2DM.
Material and methods
The studied sample consisted of 28 patients, 14 with T2DM (study group) and 14 without (control group). The plaque index, bleeding on probing, probing depth, clinical attachment level, gingival biotype, and marginal bone loss (MBL) at the site of the implants were assessed. HbA1c levels were assessed in all patients during each checkup.
Results
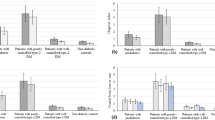
Two years after implant placement and prosthetic restoration no implant failures were reported in either group, resulting in 100% survival and success rates in both groups. No statistically significant differences in MBL were found between the control and study groups (p > 0.05).
Conclusions
Within the limitations of this study, it can be concluded that reduced-diameter TiZr alloy implants with a hydrophilic surface represent a safe and predictable treatment option for patients with well-controlled T2DM. The clinical performance was comparable with that observed in individuals without T2DM in the medium term.
Clinical relevance
The narrow implants placed in patients with T2DM with well-controlled glycemia (HbA1c) showed a marginal bone loss and success and survival rates similar to those of the control group without DM2, in the medium term.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kearney K, Tomlinson D, Smith K, Ajjan R (2017) Hypofibrinolysis in diabetes: a therapeutic target for the reduction of cardiovascular risk. Cardiovasc Diabetol 16:34. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12933-017-0515-9
Blanchaert RH (1998) Implants in the medically challenged patient. Dent Clin N Am 42:35–45
Mellado-Valero A, Ferrer García JC, Herrera Ballester A, Labaig Rueda C (2007) Effects of diabetes on the osseointegration of dental implants. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal 12:E38–E43
He H, Liu R, Desta T, Leone C, Gerstenfeld LC, Graves DT (2004) Diabetes causes decreased osteoclastogenesis, reduced bone formation, and enhanced apoptosis of osteoblastic cells in bacteria stimulated bone loss. Endocrinology 145:447–452. https://doi.org/10.1210/en.2003-1239
Jiao H, Xiao E, Graves DT (2015) Diabetes and its effect on bone and fracture healing. Curr Osteoporos Rep 13:327–335. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11914-015-0286-8
Chrcanovic BR, Albrektsson T, Wennerberg A (2014) Diabetes and oral implant failure: a systematic review. J Dent Res 93:859–867. https://doi.org/10.1177/0022034514538820
Abduljabbar T, Al-Sahaly F, Al-Kathami M, Afzal S, Vohra F (2017) Comparison of periodontal and peri-implant inflammatory parameters among patients with prediabetes, type 2 diabetes mellitus and non-diabetic controls. Acta Odontol Scand 75:319–324. https://doi.org/10.1080/00016357.2017.1303848
Conte A, Ghiraldini B, Casarin RC, Casati MZ, Pimentel SP, Cirano FR, Duarte PM, Ribeiro FV (2015) Impact of type 2 diabetes on the gene expression of bone-related factors at sites receiving dental implants. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg 44:1302–1308. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijom.2015.06.001
Ghiraldini B, Conte A, Casarin RC, Casati MZ, Pimentel SP, Cirano FR, Ribeiro FV (2016) Influence of glycemic control on peri-implant bone healing: 12-month outcomes of local release of bone-related factors and implant stabilization in type 2 diabetics. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res 18:801–809. https://doi.org/10.1111/cid.12339
Mihali SG, Canjau S, Cernescu A, Bortun CM, Wang HL, Bratu E (2018) Effects of a short drilling implant protocol on osteotomy site temperature and drill torque. Implant Dent 27:63–68. https://doi.org/10.1097/ID.0000000000000707
Al Amri MD, Kellesarian SV, Al-Kheraif AA, Malmstrom H, Javed F, Romanos GE (2016) Effect of oral hygiene maintenance on HbA1c levels and peri-implant parameters around immediately-loaded dental implants placed in type-2 diabetic patients: 2 years follow-up. Clin Oral Implants Res 27:1439–1443. https://doi.org/10.1111/clr.12758
Tsai S, Clemente-Casares X, Revelo XS, Winer S, Winer DA (2015) Are obesity-related insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes autoimmune diseases? Diabetes 64:1886–1897. https://doi.org/10.2337/db14-1488
Velloso LA, Eizirik DL, Cnop M (2013) Type 2 diabetes mellitus—an autoimmune disease? Nat Rev Endocrinol 9:750–755. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrendo.2013.131
Donath MY, Shoelson SE (2011) Type 2 diabetes as an inflammatory disease. Nat Rev Immunol 11:98–107. https://doi.org/10.1038/nri2925
O’Leary TJ, Drake RB, Naylor JE (1972) The plaque control record. J Periodontol 43:38. https://doi.org/10.1902/jop.1972.43.1.38
Ainamo J, Bay I (1975) Problems and proposals for recording gingivitis and plaque. Int Dent J 25:229–235
Weinberg MA, Eskow RN (2003) Periodontal terminology revisited. J Periodontol 74:563–565. https://doi.org/10.1902/jop.2003.74.4.563
Kan JY, Rungcharassaeng K, Umezu K, Kois JC (2003) Dimensions of peri-implant mucosa: an evaluation of maxillary anterior single implants in humans. J Periodontol 74:557–562. https://doi.org/10.1902/jop.2003.74.4.557
De Rouck T, Eghbali R, Collys K, De Bruyn H, Cosyn J (2009) The gingival biotype revisited: transparency of the periodontal probe through the gingival margin as a method to discriminate thin from thick gingiva. J Clin Periodontol 36:428–433. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-051X.2009.01398.x
Olsson M, Lindhe J, Marinello CP (1993) On the relationship between crown form and clinical features of the gingiva in adolescents. J Clin Periodontol 20:570–577
Cabrera-Domínguez J, Castellanos-Cosano L, Torres-Lagares D, Machuca-Portillo G (2017) A prospective case-control clinical study of titanium-zirconium alloy implants with a hydrophilic surface in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 32:1135–1144
Esposito M, Grusovin MG, Polyzos IP, Felice P, Worthington HV (2010) Timing of implant placement after tooth extraction: immediate, immediate-delayed or delayed implants? A Cochrane systematic review. Eur J Oral Implantol 3:189–205
Lekholm U, Zarb G (1985) Tissue-integrated prosthesis: osseointegration in clinical dentistry, Quintessence, Chicago
Lindh C, Oliveira GH, Leles CR, do Carmo Matias Freire M, Ribeiro-Rotta RF (2014) Bone quality assessment in routine dental implant treatment among Brazilian and Swedish specialists. Clin Oral Implants Res 25:1004–1009. https://doi.org/10.1111/clr.12221
Pagliani L, Motroni A, Nappo A, Sennerby L (2012) Short communication: use of a diagnostic software to predict bone density and implant stability in preoperative CTs. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res 14:553–557. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1708-8208.2010.00291.x
Association AD (2011) Standards of medical care in diabetes--2011. Diabetes Care 34(Suppl 1):S11–S61. https://doi.org/10.2337/dc11-S011
Buser D, Schenk RK, Steinemann S, Fiorellini JP, Fox CH, Stich H (1991) Influence of surface characteristics on bone integration of titanium implants. A histomorphometric study in miniature pigs. J Biomed Mater Res 25:889–902. https://doi.org/10.1002/jbm.820250708
Fiorellini JP, Chen PK, Nevins M, Nevins ML (2000) A retrospective study of dental implants in diabetic patients. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent 20:366–373
Shurtz-Swirski R, Sela S, Herskovits AT, Shasha SM, Shapiro G, Nasser L, Kristal B (2001) Involvement of peripheral polymorphonuclear leukocytes in oxidative stress and inflammation in type 2 diabetic patients. Diabetes Care 24:104–110
Dowell S, Oates TW, Robinson M (2007) Implant success in people with type 2 diabetes mellitus with varying glycemic control: a pilot study. J Am Dent Assoc 138:355–361 quiz 397-8
Schlegel KA, Prechtl C, Möst T, Seidl C, Lutz R, von Wilmowsky C (2013) Osseointegration of SLActive implants in diabetic pigs. Clin Oral Implants Res 24:128–134. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0501.2011.02380.x
Oates TW, Huynh-Ba G, Vargas A, Alexander P, Feine J (2013) A critical review of diabetes, glycemic control, and dental implant therapy. Clin Oral Implants Res 24:117–127. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0501.2011.02374.x
Nevins ML, Karimbux NY, Weber HP, Giannobile WV, Fiorellini JP (1998) Wound healing around endosseous implants in experimental diabetes. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 13:620–629
Botolin S, McCabe LR (2006) Chronic hyperglycemia modulates osteoblast gene expression through osmotic and non-osmotic pathways. J Cell Biochem 99:411–424. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.20842
McCabe LR (2007) Understanding the pathology and mechanisms of type I diabetic bone loss. J Cell Biochem 102:1343–1357. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.21573
de Paula FJ, Horowitz MC, Rosen CJ (2010) Novel insights into the relationship between diabetes and osteoporosis. Diabetes Metab Res Rev 26:622–630. https://doi.org/10.1002/dmrr.1135
Catalfamo DL, Britten TM, Storch DL, Calderon NL, Sorenson HL, Wallet SM (2013) Hyperglycemia induced and intrinsic alterations in type 2 diabetes-derived osteoclast function. Oral Dis 19:303–312. https://doi.org/10.1111/odi.12002
Sun X, Ren QH, Bai L, Feng Q (2015) Identification of molecular markers related to human alveolar bone cells and pathway analysis in diabetic patients. Genet Mol Res 14:13476–13484. https://doi.org/10.4238/2015.October.28.8
Feldbrin Z, Shargorodsky M (2015) Bone remodelling markers in hypertensive patients with and without diabetes mellitus: link between bone and glucose metabolism. Diabetes Metab Res Rev 31:752–757. https://doi.org/10.1002/dmrr.2668
Amar S, Han X (2003) The impact of periodontal infection on systemic diseases. Med Sci Monit 9:RA291–RA299
Linkevicius T, Apse P, Grybauskas S, Puisys A (2009) The influence of soft tissue thickness on crestal bone changes around implants: a 1-year prospective controlled clinical trial. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 24:712–719
Puisys A, Linkevicius T (2015) The influence of mucosal tissue thickening on crestal bone stability around bone-level implants. A prospective controlled clinical trial. Clin Oral Implants Res 26:123–129. https://doi.org/10.1111/clr.12301
Barter S, Stone P, Brägger U (2012) A pilot study to evaluate the success and survival rate of titanium-zirconium implants in partially edentulous patients: results after 24 months of follow-up. Clin Oral Implants Res 23:873–881. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0501.2011.02231.x
Buser D, Broggini N, Wieland M, Schenk RK, Denzer AJ, Cochran DL, Hoffmann B, Lussi A, Steinemann SG (2004) Enhanced bone apposition to a chemically modified SLA titanium surface. J Dent Res 83:529–533. https://doi.org/10.1177/154405910408300704
Iegami CM, Uehara PN, Sesma N, Pannuti CM, Tortamano Neto P, Mukai MK (2017) Survival rate of titanium-zirconium narrow diameter dental implants versus commercially pure titanium narrow diameter dental implants: a systematic review. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res 19:1015–1022. https://doi.org/10.1111/cid.12527
Al-Nawas B, Domagala P, Fragola G, Freiberger P, Ortiz-Vigón A, Rousseau P, Tondela J (2015) A prospective noninterventional study to evaluate survival and success of reduced diameter implants made from titanium-zirconium alloy. J Oral Implantol 41:e118–e125. https://doi.org/10.1563/aaid-joi-d-13-00149
Hämmerle CH, Brägger U, Bürgin W, Lang NP (1996) The effect of subcrestal placement of the polished surface of ITI implants on marginal soft and hard tissues. Clin Oral Implants Res 7:111–119
de Siqueira RAC, Fontao FNGK, Sartori IAM, Santos PGF, Bernardes SR, Tiossi R (2017) Effect of different implant placement depths on crestal bone levels and soft tissue behavior: a randomized clinical trial. Clin Oral Implants Res 28:1227–1233. https://doi.org/10.1111/clr.12946
Weng D, Nagata MJ, Bell M, Bosco AF, de Melo LG, Richter EJ (2008) Influence of microgap location and configuration on the periimplant bone morphology in submerged implants. An experimental study in dogs. Clin Oral Implants Res 19:1141–1147. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0501.2008.01564.x
Hasuike A, Iguchi S, Suzuki D, Kawano E, Sato S (2017) Systematic review and assessment of systematic reviews examining the effect of periodontal treatment on glycemic control in patients with diabetes. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal 22:E167–E176
Mauri-Obradors E, Estrugo-Devesa A, Jané-Salas E, Viñas M, López-López J (2017) Oral manifestations of diabetes mellitus. A systematic review. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal 22:E586–E594
Pérez-Losada FL, Jané-Salas E, Sabater-Recolons MM, Estrugo-Devesa A, Segura-Egea JJ, López-López J (2016) Correlation between periodontal disease management and metabolic control of type 2 diabetes mellitus. A systematic literature review. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal 21:E440–E446
Olson JW, Shernoff AF, Tarlow JL, Colwell JA, Scheetz JP, Bingham SF (2000) Dental endosseous implant assessments in a type 2 diabetic population: a prospective study. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 15:811–818
van Steenberghe D, Jacobs R, Desnyder M, Maffei G, Quirynen M (2002) The relative impact of local and endogenous patient-related factors on implant failure up to the abutment stage. Clin Oral Implants Res 13:617–622
Gómez-de Diego R, la Rosa MeR M-d, Romero-Pérez MJ, Cutando-Soriano A, López-Valverde-Centeno A (2014) Indications and contraindications of dental implants in medically compromised patients: update. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal 19:e483–e489
Aguilar-Salvatierra A, Calvo-Guirado JL, González-Jaranay M, Moreu G, Delgado-Ruiz RA, Gómez-Moreno G (2016) Peri-implant evaluation of immediately loaded implants placed in esthetic zone in patients with diabetes mellitus type 2: a two-year study. Clin Oral Implants Res 27:156–161. https://doi.org/10.1111/clr.12552
Oates TW, Galloway P, Alexander P, Vargas Green A, Huynh-Ba G, Feine J, McMahan CA (2014) The effects of elevated hemoglobin A(1c) in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus on dental implants: survival and stability at one year. J Am Dent Assoc 145:1218–1226. https://doi.org/10.14219/jada.2014.93
Funding
This study was funded by Institut Straumann AG Peter Merian-Weg 12, CH-4002 Basel (Switzerland) (research grant number IIS 18/10).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional research committee and the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. The research protocol was approved by the Ethics Committee of the Faculty of Dentistry of the University of Seville (Spain).
Informed consent
Written informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cabrera-Domínguez, J.J., Castellanos-Cosano, L., Torres-Lagares, D. et al. Clinical performance of titanium-zirconium implants with a hydrophilic surface in patients with controlled type 2 diabetes mellitus: 2-year results from a prospective case-control clinical study. Clin Oral Invest 24, 2477–2486 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00784-019-03110-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00784-019-03110-9