Abstract
Introduction
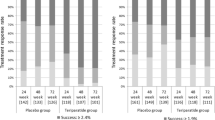
Once-daily teriparatide (D-TPTD) and twice-weekly TPTD (W-TPTD), which are self-administered injections, are generally used in the treatment of severe osteoporosis. This study aimed to reveal the differences in the persistence, safety, and effectiveness of D-TPTD and W-TPTD.
Materials and methods
A total of 102 patients received D-TPTD (n = 51) and W-TPTD (n = 51). The bone mineral densities (BMD) of the lumbar spine, total hip, and femoral neck were measured using dual energy X-ray absorptiometry. The persistence and effectiveness of the two treatments were compared at 12 months.
Results
The persistence in the D-TPTD and W-TPTD groups was 80.4% and 66.7% at 12 months, respectively (p = 0.178). The % changes (Δ) in BMD values from baseline for the lumbar spine in the D-TPTD were significantly higher than those in the W-TPTD (11.2% vs. 6.3%; p < 0.001) at 12 months. The ΔBMD values for the total hip (3.7% vs. 1.3%; p = 0.065) and femoral neck (2.2% vs. 1.6%; p = 0.489) did not differ significantly between the two groups at 12 months. The incidence of new morphological vertebral fractures in the D-TPTD and W-TPTD groups was 7.3% and 8.6%, respectively, at 12 months (p = 1.000).
Conclusions
Lumbar spine BMD (LS-BMD) was significantly increased. Moreover, ΔLS-BMD in the D-TPTD group was higher than that in the W-TPTD group. This study showed that the persistence, ΔTH-BMD, ΔFN-BMD and incidence of vertebral fractures did not differ between the two groups.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability statement
The data is not available due to ethical restrictions.
References
Colón-Emeric CS, Saag KG (2006) Osteoporotic fractures in older adults. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol 20:695–706
Murad MH, Drake MT, Mullan RJ, Mauck KF, Stuart LM, Lane MA, Abu Elnour NO, Erwin PJ, Hazem A, Puhan MA, Li T, Montori VM (2012) Clinical review. comparative effectiveness of drug treatments to prevent fragility fractures: a systematic review and network meta-analysis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 97:1871–1880
Simpson EL, Martyn-St James M, Hamilton J, Wong R, Gittoes N, Selby P, Davis S (2020) Clinical effectiveness of denosumab, raloxifene, romosozumab, and teriparatide for the prevention of osteoporotic fragility fractures: a systematic review and network meta-analysis. Bone 130:115081
Cornelissen D, de Kunder S, Si L, Reginster JY, Evers S, Boonen A, Hiligsmann M, European society for clinical and economic aspect of osteoporosis, osteoarthritis and musculoskeletal diseases (ESCEO) (2020) Interventions to improve adherence to anti-osteoporosis medications: an updated systematic review. Osteoporos Int 31:1645–1669
Keshishian A, Boytsov N, Burge R, Krohn K, Lombard L, Zhang X, Xie L, Baser O (2017) Examining the effect of medication adherence on risk of subsequent fracture among women with a fragility fracture in the U.S. medicare population. J Manag Care Spec Pharm 23:1178–1190
Hiligsmann M, Salas M, Hughes DA, Manias E, Gwadry-Sridhar FH, Linck P, Cowell W (2013) Interventions to improve osteoporosis medication adherence and persistence: a systematic review and literature appraisal by the ISPOR medication adherence & persistence special interest group. Osteoporos Int 24:2907–2918
Siris ES, Selby PL, Saag KG, Borgström F, Herings RM, Silverman SL (2009) Impact of osteoporosis treatment adherence on fracture rates in North America and Europe. Am J Med 122:S3-13
Krueger KP, Berger BA, Felkey B (2005) Medication adherence and persistence: a comprehensive review. Adv Ther 22:313–356
Yu S, Burge RT, Foster SA, Gelwicks S, Meadows ES (2012) The impact of teriparatide adherence and persistence on fracture outcomes. Osteoporos Int 23:1103–1113
Rajzbaum G, Grados F, Evans D, Liu-Leage S, Petto H, Augendre-Ferrante B (2014) Treatment persistence and changes in fracture risk, back pain, and quality of life amongst patients treated with teriparatide in routine clinical care in France: results from the European forsteo observational study. Joint Bone Spine 81:69–75
Chan DC, Chang CH, Lim LC, Brnabic AJM, Tsauo JY, Burge R, Hsiao FY, Jin L, Gürbüz S, Yang RS (2016) Association between teriparatide treatment persistence and adherence, and fracture incidence in Taiwan: analysis using the national health insurance research database. Osteoporos Int 27:2855–2865
Usui T, Funagoshi M, Seto K, Ide K, Tanaka S, Kawakami K (2018) Persistence of and switches from teriparatide treatment among women and men with osteoporosis in the real world: a claims database analysis. Arch Osteoporos 13:54
Marcus R, Wang O, Satterwhite J, Mitlak B (2003) The skeletal response to teriparatide is largely independent of age, initial bone mineral density, and prevalent vertebral fractures in postmenopausal women with osteoporosis. J Bone Miner Res 18:18–23
McClung MR, San Martin J, Miller PD, Civitelli R, Bandeira F, Omizo M, Donley DW, Dalsky GP, Eriksen EF (2005) Opposite bone remodeling effects of teriparatide and alendronate in increasing bone mass. Arch Intern Med 165:1762–1768
Miyauchi A, Matsumoto T, Sugimoto T, Tsujimoto M, Warner MR, Nakamura T (2010) Effects of teriparatide on bone mineral density and bone turnover markers in Japanese subjects with osteoporosis at high risk of fracture in a 24-month clinical study: 12-month, randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind and 12-month open-label phases. Bone 47:493–502
Soen S, Fujiwara S, Takayanagi R, Kajimoto K, Tsujimoto M, Kimura S, Sato M, Krege JH, Enomoto H (2017) Real-world effectiveness of daily teriparatide in Japanese patients with osteoporosis at high risk for fracture: final results from the 24-month Japan fracture observational study (JFOS). Curr Med Res Opin 33:2049–2056
Nakamura T, Sugimoto T, Nakano T, Kishimoto H, Ito M, Fukunaga M, Hagino H, Sone T, Yoshikawa H, Nishizawa Y, Fujita T, Shiraki M (2012) Randomized teriparatide [human parathyroid hormone (PTH) 1–34] once-weekly efficacy research (TOWER) trial for examining the reduction in new vertebral fractures in subjects with primary osteoporosis and high fracture risk. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 97:3097–3106
Sugimoto T, Shiraki M, Fukunaga M, Kishimoto H, Hagino H, Sone T, Nakano T, Ito M, Yoshikawa H, Minamida T, Tsuruya Y, Nakamura T (2019) Study of twice-weekly injections of teriparatide by comparing efficacy with once-weekly injections in osteoporosis patients: the TWICE study. Osteoporos Int 30:2321–2331
Nakamura T, Fukunaga M, Nakano T, Kishimoto H, Ito M, Hagino H, Sone T, Taguchi A, Tanaka S, Ohashi M, Ota Y, Shiraki M (2017) Efficacy and safety of once-yearly zoledronic acid in Japanese patients with primary osteoporosis: two-year results from a randomized placebo-controlled double-blind study (ZOledroNate treatment in efficacy to osteoporosis; ZONE study). Osteoporos Int 28:389–398
Burge R, Sato M, Sugihara T (2016) Real-world clinical and economic outcomes for daily teriparatide patients in Japan. J Bone Miner Metab 34:692–702
Reyes C, Tebe C, Martinez-Laguna D, Ali MS, Soria-Castro A, Carbonell C, Prieto-Alhambra D (2017) One and two-year persistence with different anti-osteoporosis medications: a retrospective cohort study. Osteoporos Int 28:2997–3004
Fujita R, Endo T, Takahata M, Haraya K, Suzuki H, Oda I, Kanayama M, Asano T, Shigenobu K, Iwata A, Yamada K, Takeuchi H, Ohura H, Yoneoka D, Iwasaki N (2022) Real-world persistence of twice-weekly teriparatide and factors associated with the discontinuation in patients with osteoporosis. J Bone Miner Metab 40:782–789
Mochizuki T, Yano K, Ikari K, Kawakami K, Hiroshima R, Koenuma N, Ishibashi M, Shirahata T (2016) Hip structure analysis by DXA of teriparatide treatment: A 24-month follow-up clinical study. J Orthop 13:414–418
Yamamoto T, Hasegawa T, Sasaki M, Hongo H, Tsuboi K, Shimizu T, Ota M, Haraguchi M, Takahata M, Oda K, Luiz de Freitas PH, Takakura A, Takao-Kawabata R, Isogai Y, Amizuka N (2016) Frequency of teriparatide administration affects the histological pattern of bone formation in young adult male mice. Endocrinology 157:2604–2620
Neer RM, Arnaud CD, Zanchetta JR, Prince R, Gaich GA, Reginster JY, Hodsman AB, Eriksen EF, Ish-Shalom S, Genant HK, Wang O, Mitlak BH (2001) Effect of parathyroid hormone (1–34) on fractures and bone mineral density in postmenopausal women with osteoporosis. N Engl J Med 344:1434–1441
Prevrhal S, Krege JH, Chen P, Genant H, Black DM (2009) Teriparatide vertebral fracture risk reduction determined by quantitative and qualitative radiographic assessment. Curr Med Res Opin 25:921–928
Waqas K, Chen J, Koromani F, Trajanoska K, van der Eerden BC, Uitterlinden AG, Rivadeneira F, Zillikens MC (2020) Skin autofluorescence, a noninvasive biomarker for advanced glycation end-products, is associated with prevalent vertebral and major osteoporotic fractures: the Rotterdam study. J Bone Miner Res 35:1904–1913
Kida Y, Saito M, Shinohara A, Soshi S, Marumo K (2019) Non-invasive skin autofluorescence, blood and urine assays of the advanced glycation end product (AGE) pentosidine as an indirect indicator of AGE content in human bone. BMC Musculoskelet Disord 20:627
Shiraki M, Kuroda T, Tanaka S, Saito M, Fukunaga M, Nakamura T (2008) Nonenzymatic collagen cross-links induced by glycoxidation (pentosidine) predicts vertebral fractures. J Bone Miner Metab 26:93–100
Shiraki M, Kashiwabara S, Imai T, Tanaka S, Saito M (2019) The association of urinary pentosidine levels with the prevalence of osteoporotic fractures in postmenopausal women. J Bone Miner Metab 37:1067–1074
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the patients who participated in this study. The authors also thank the medical staff and the clinical research center.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
T. Mochizuki received honoraria for lectures from AbbVie, Astellas, Bristol-Myers, Chugai, Daiichi Sankyo, Eisai, Eli Lilly, Janssen, Mochida, and Pfizer. Yano received honoraria for lectures from AbbVie, Astellas, Ayumi, Bristol-Meyers, Eisai, Hisamitsu, Mochida, and Takeda. K. Ikari received honoraria for lectures from AbbVie, Astellas, Bristol-Myers, Chugai, Eisai, Eli Lilly, Janssen, Takeda, Tanabe-Mitsubishi, and UCB. The other authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest. The sponsors were not involved in the study design; collection, analysis, and interpretation of data; writing of the article; and/or decision to submit the results for publication.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
About this article
Cite this article
Mochizuki, T., Yano, K., Ikari, K. et al. Comparison of different parameters between daily and twice-weekly teriparatide in postmenopausal women with severe osteoporosis. J Bone Miner Metab 41, 220–226 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00774-022-01398-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00774-022-01398-4