Abstract
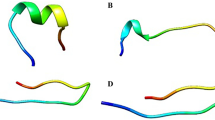
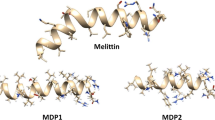
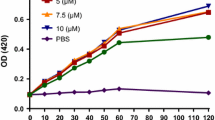
The emergence of multidrug-resistant (MDR) bacteria is a major challenge for antimicrobial chemotherapy. Concerning this issue, antimicrobial peptides (AMPs) have been presented as novel promising antibiotics. Our previous de novo designed melittin-derived peptides (MDP1 and MDP2) indicated their potential as peptide drug leads. Accordingly, this study was aimed to evaluate the kinetics of activity, toxicity, and stability of MDP1 and MDP2 as well as determination of their structures. The killing kinetics of MDP1 and MDP2 demonstrate that all bacterial strains were rapidly killed. MDP1 and MDP2 were ca. 100- and 26.6-fold less hemolytic than melittin and found to be respectively 72.9- and 41.6-fold less cytotoxic than melittin on the HEK293 cell line. MDP1 and MDP2 showed 252- and 132-fold improvement in their therapeutic index in comparison to melittin. MDP1 and MDP2 sustained their activities in the presence of human plasma and were found to be ca. four to eightfold more stable than melittin. Spectropolarimetry analysis of MDP1 and MDP2 indicates that the peptides adopt an alpha-helical structure predominantly. According to the fast killing kinetics, significant therapeutic index, and high stability of MDP1, it could be considered as a drug lead in a mouse model of septicemia infections.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akbari R, Vala MH, Hashemi A, Aghazadeh H, Sabatier J-M, Bagheri KP (2018) Action mechanism of melittin derived antimicrobial peptides, MDP1 and MDP2, de novo designed against multidrug resistant bacteria. Amino Acids 50(9):1231–1243
Akbari R, Vala MH, Pashaei F, Bevalian P, Hashemi A, Bagheri KP (2019) Highly synergistic effects of melittin with conventional antibiotics against multidrug resistant strains of Acinetobacter boummani and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Microb Drug Resistance 25(2):193–202
Andersson DI, Hughes D, Kubicek-Sutherland JZ (2016) Mechanisms and consequences of bacterial resistance to antimicrobial peptides. Drug Resist Updates 26:43–57
Arenas I, Villegas E, Walls O, Barrios H, Rodríguez R, Corzo G (2016) Antimicrobial activity and stability of short and long based arachnid synthetic peptides in the presence of commercial antibiotics. Molecules 21:225
Ashby M, Petkova A, Hilpert K (2014) Cationic antimicrobial peptides as potential new therapeutic agents in neonates and children: a review. Curr Opin Infect Dis 27:258–267
Bacalum M, Radu M (2015) Cationic antimicrobial peptides cytotoxicity on mammalian cells: an analysis using therapeutic index integrative concept. Int J Pept Res Ther 21:47–55
Barashkova AS, Sadykova VS, Salo VA, Zavriev SK, Rogozhin EA (2021) Nigellothionins from black cumin (Nigella sativa L.) seeds demonstrate strong antifungal and cytotoxic activity. Antibiotics 10:166
Barreto-Santamaría A, Curtidor H, Arévalo-Pinzón G, Herrera C, Suárez D, Pérez WH et al (2016) A new synthetic peptide having two target of antibacterial action in E. coli ML35. Front Microbiol 7:2006
Basak S, Singh P, Rajurkar M (2016) Multidrug resistant and extensively drug resistant bacteria: a study. J Pathog 2016:5
Batoni G, Maisetta G, Esin S (2021) Therapeutic potential of antimicrobial peptides in polymicrobial biofilm-associated infections. Int J Mol Sci 22:482
Berthold N, Czihal P, Fritsche S, Sauer U, Schiffer G, Knappe D et al (2013) Novel apidaecin 1b analogs with superior serum stabilities for treatment of infections by gram-negative pathogens. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 57:402–409
Bevalian P, Pashaei F, Akbari R, Bagheri KP (2021) Eradication of vancomycin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus on a mouse model of third-degree burn infection by melittin: an antimicrobial peptide from bee venom. Toxicon 199:49–59
Blondelle SE, Houghten RA (1991) Hemolytic and antimicrobial activities of the twenty-four individual omission analogs of melittin. Biochemistry 30:4671–4678
Bormann N, Koliszak A, Kasper S, Schoen L, Hilpert K, Volkmer R et al (2017) A short artificial antimicrobial peptide shows potential to prevent or treat bone infections. Sci Rep 7:1506
Böttger R, Hoffmann R, Knappe D (2017) Differential stability of therapeutic peptides with different proteolytic cleavage sites in blood, plasma and serum. PLoS ONE 12:e0178943
Brandenburg L-O, Merres J, Albrecht L-J, Varoga D, Pufe T (2012) Antimicrobial peptides: multifunctional drugs for different applications. Polymers 4:539–560
Brunetti J, Falciani C, Roscia G, Pollini S, Bindi S, Scali S et al (2016) In vitro and in vivo efficacy, toxicity, bio-distribution and resistance selection of a novel antibacterial drug candidate. Sci Rep 6:260–277
Buonocore F, Fausto AM, Della Pelle G, Roncevic T, Gerdol M, Picchietti S (2021) Attacins: a promising class of insect antimicrobial peptides. Antibiotics 10:212
Chen CH, Lu TK (2020) Development and challenges of antimicrobial peptides for therapeutic applications. Antibiotics 9:24
Chen Y, Mant CT, Farmer SW, Hancock RE, Vasil ML, Hodges RS (2005) Rational design of α-helical antimicrobial peptides with enhanced activities and specificity/therapeutic index. J Biol Chem 280:12316–12329
Crofts TS, Gasparrini AJ, Dantas G (2017) Next-generation approaches to understand and combat the antibiotic resistome. Nat Rev Microbiol 15:422–434
Dash R, Bhattacharjya S (2021) Thanatin: an emerging host defense antimicrobial peptide with multiple modes of action. Int J Mol Sci 22:1522
Deslouches B, Montelaro RC, Urish KL, Di YP (2020) Engineered cationic antimicrobial peptides (eCAPs) to combat multidrug-resistant bacteria. Pharmaceutics 12:501
Dezfuli HT, Shahbazzadeh D, Eidi A, Bagheri KP, Pakravan N, Amini S, Aghasadeghi MR, Mahdavi M (2014) Induction of IFN-γ cytokine response against hepatitis B surface antigen using melittin. Gastroenterol Hepatol Bed Bench 7(2):108
Easton DM, Nijnik A, Mayer ML, Hancock RE (2009) Potential of immunomodulatory host defense peptides as novel anti-infectives. Trends Biotechnol 27:582–590
Eisapoor SS, Jamili S, Shahbazzadeh D, Ghavam Mostafavi P, Pooshang Bagheri K (2016) A new, high yield, rapid, and cost-effective protocol to deprotection of cysteine-rich conopeptide, omega-conotoxin MVIIA. Chem Biol Drug Des 87(5):687–693
Felício MR, Silva ON, Gonçalves S, Santos NC, Franco OL (2017) Peptides with dual antimicrobial and anticancer activities. Front Chem 5:5
Fennell JF, Shipman WH, Cole LJ (1968) Antibacterial action of melittin, a polypeptide from bee venom. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med 127:707–710
Fink MP (2008) Animal models of sepsis and its complications. Kidney Int 74:991–993
Fjell CD, Hiss JA, Hancock RE, Schneider G (2012) Designing antimicrobial peptides: form follows function. Nat Rev Drug Discov 11:37–51
Gao Y, Wu D, Wang L, Lin C, Ma C, Xi X et al (2017) Targeted modification of a novel amphibian antimicrobial peptide from Phyllomedusa tarsius to enhance its activity against MRSA and microbial biofilm. Front Microbiol 8:628
Gaspar D, Veiga AS, Castanho MA (2013) From antimicrobial to anticancer peptides. A review. Front Microbiol 4:294
Giuliani A, Pirri G, Nicoletto S (2007) Antimicrobial peptides: an overview of a promising class of therapeutics. Open Life Sci 2:1–33
Hancock RE, Sahl H-G (2006) Antimicrobial and host-defense peptides as new anti-infective therapeutic strategies. Nat Biotechnol 24:1551–1557
Huerta-Cantillo J, Navarro-García F (2016) Properties and design of antimicrobial peptides as potential tools against pathogens and malignant cells. Molecules 9:12
Javadpour MM, Juban MM, Lo W-CJ, Bishop SM, Alberty JB, Cowell SM et al (1996) De novo antimicrobial peptides with low mammalian cell toxicity. J Med Chem 39:3107–3113
Jenssen H, Hamill P, Hancock RE (2006) Peptide antimicrobial agents. Clin Microbiol Rev 19:491–511
Kamech ND, Vukičević D, Ladram A, Piesse C, Vasseur J, Bojović V et al (2012) Improving the selectivity of antimicrobial peptides from anuran skin. J Chem Inf Model 52:3341–3351
Khara JS, Priestman M, Uhía I, Hamilton MS, Krishnan N, Wang Y, Ee PLR (2016) Unnatural amino acid analogues of membrane-active helical peptides with anti-mycobacterial activity and improved stability. J Antimicrob Chemother. https://doi.org/10.1093/jac/dkw107
Khozani RS, Shahbazzadeh D, Harzandi N, Feizabadi MM, Bagheri KP (2019) Kinetics study of antimicrobial peptide, melittin, in simultaneous biofilm degradation and killing of potent biofilm producing MDR Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates. Int J Pept Res Ther 25(10):329–338
Knappe D, Henklein P, Hoffmann R, Hilpert K (2010) Easy strategy to protect antimicrobial peptides from fast degradation in serum. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 54:4003–4005
Lee M-T, Sun T-L, Hung W-C, Huang HW (2013) Process of inducing pores in membranes by melittin. Proc Natl Acad Sci 110:14243–14248
Lyu Y, Yang Y, Lyu X, Dong N, Shan A (2016) Antimicrobial activity, improved cell selectivity and mode of action of short PMAP-36-derived peptides against bacteria and Candida. Sci Rep 6:27258
Ma Z, Yang J, Han J, Gao L, Liu H, Lu Z et al (2016) Insights into the antimicrobial activity and cytotoxicity of engineered α-helical peptide amphiphiles. J Med Chem 59:10946–10962
Madanchi H, Akbari S, Shabani AA, Sardari S, Farahani YF, Ghavami G, Kiasari RE (2019) Alignment-based design and synthesis of new antimicrobial Aurein-derived peptides with improved activity against Gram-negative bacteria and evaluation of their toxicity on human cells. Drug Dev Res 80:162–170
Mahmoodzadeh A, Zarrinnahad H, Bagheri KP, Moradi A, Shahbazzadeh D (2015) First report on the isolation of melittin from Iranian honey bee venom and evaluation of its toxicity on gastric cancer AGS cells. J Chin Med Assoc 78:574–583
Mangoni ML, McDermott AM, Zasloff M (2016) Antimicrobial peptides and wound healing: biological and therapeutic considerations. Exp Dermatol 25:167–173
Masuda R, Dazai Y, Mima T, Koide T (2017) Structure–activity relationships and action mechanisms of collagen-like antimicrobial peptides. Pept Sci. https://doi.org/10.1002/bip.22931
Memar B, Jamili S, Shahbazzadeh D, Bagheri KP (2016) The first report on coagulation and phospholipase A2 activities of Persian Gulf lionfish, Pterois russelli, an Iranian venomous fish. Toxicon 113:25–31
Memariani H, Shahbazzadeh D, Ranjbar R, Behdani M, Memariani M, Pooshang Bagheri K (2017) Design and characterization of short hybrid antimicrobial peptides from pEM-2, mastoparan-VT 1, and mastoparan-B. Chem Biol Drug Des 89(3):327–338
Memariani H, Shahbazzadeh D, Sabatier JM, Pooshang BK (2018) Membrane-active peptide PV 3 efficiently eradicates multidrug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa in a mouse model of burn infection. APMIS 126:114–122
Mohamed MF, Abdelkhalek A, Seleem MN (2016) Evaluation of short synthetic antimicrobial peptides for treatment of drug-resistant and intracellular Staphylococcus aureus. Sci Rep 6:29707
Mojsoska B, Zuckermann RN, Jenssen H (2015) Structure-activity relationship study of novel peptoids that mimic the structure of antimicrobial peptides. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 59:4112–4120
Oren Z, Shai Y (1998) Mode of action of linear amphipathic α-helical antimicrobial peptides. Pept Sci 47:451–463
Organization WH (2014) Antimicrobial resistance: global report on surveillance. World Health Organization, Geneva
Pashaei F, Bevalian P, Akbari R, Bagheri KP (2019) Single dose eradication of multiple drug resistant Acinetobacter baumannii in a mouse model of burn infection by melittin antimicrobial peptide. Microb Pathog 127:60–69
Raghuraman H, Chattopadhyay A (2007) Melittin: a membrane-active peptide with diverse functions. Biosci Rep 27:189–223
Sani MA, Separovic F (2016) How membrane-active peptides get into lipid membranes. Acc Chem Res 49:1130–1138
Seo M-D, Won H-S, Kim J-H, Mishig-Ochir T, Lee B-J (2012) Antimicrobial peptides for therapeutic applications: a review. Molecules 17:12276–12286
Shagaghi N, Bhave M, Palombo EA, Clayton AH (2017) Revealing the sequence of interactions of PuroA peptide with Candida albicans cells by live-cell imaging. Sci Rep 7:43542
Smith R, Separovic F, Milne TJ, Whittaker A, Bennett FM, Cornell BA, Makriyannis A (1994) Structure and orientation of the pore-forming peptide melittin, in lipid bilayers. J Mol Biol 24:456–466
Tossi A, Sandri L, Giangaspero A (2000) Amphipathic, α-helical antimicrobial peptides. Pept Sci 55:4–30
Tyagi P, Singh M, Kumari H, Kumari A, Mukhopadhyay K (2015) Bactericidal activity of curcumin I is associated with damaging of bacterial membrane. PLoS ONE 10:e0121313
Ventura CR, Wiedman GR (2021) Substituting azobenzene for proline in melittin to create photomelittin: a light-controlled membrane active peptide. BBA Biomembr. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamem.2021.183759
Wiradharma N, Khoe U, Hauser CA, Seow SV, Zhang S, Yang Y-Y (2011) Synthetic cationic amphiphilic α-helical peptides as antimicrobial agents. Biomaterials 32:2204–2212
Zarghami V, Ghorbani M, Bagheri KP, Shokrgozar MA (2021) Melittin antimicrobial peptide thin layer on bone implant chitosan-antibiotic coatings and their bactericidal properties. Mater Chem Phys 263:124432
Zarghami V, Ghorbani M, Bagheri KP, Shokrgozar MA (2021) Prevention the formation of biofilm on orthopedic implants by melittin thin layer on chitosan/bioactive glass/vancomycin coatings. J Mater Sci Mater Med 32(7):75
Zasloff M (2002) Antimicrobial peptides of multicellular organisms. Nature 415:389–395
Zhang L-j, Gallo RL (2016) Antimicrobial peptides. Curr Biol 26:14–19
Zhang S-K, Song J-w, Gong F, Li S-B, Chang H-Y, Xie H-M et al (2016) Design of an α-helical antimicrobial peptide with improved cell-selective and potent anti-biofilm activity. Sci Rep 6:27394
Funding
This investigation supported by Shahid Beheshti University of medical science and Pasteur Institute of Iran. The peptides were founded by Jean-Marc Sabatier.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
RA contributed to investigation, methodology, visualization, writing—original draft, data curation, formal analysis. MHV contributed to resources, review and editing. J-MS contributed to resources, review and editing. KPB contributed to conceptualization, methodology, data curation, formal analysis, writing—review and editing.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Ethical approval
This study did not involve human participants or animals and thus ethical approval and informed consent were not required.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Akbari, R., Hakemi Vala, M., Sabatier, JM. et al. Fast killing kinetics, significant therapeutic index, and high stability of melittin-derived antimicrobial peptide. Amino Acids 54, 1275–1285 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-022-03180-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-022-03180-2