Abstract
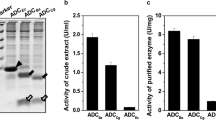
Bacterial l-aspartate α-decarboxylase (PanD) specifically catalyzes the decarboxylation of l-aspartic acid to β-alanine. It is translated as an inactive pro-protein, then processed by self-cleavage to form two small subunits with catalytic activity. There is a significant difference in the efficiency of this process among the reported PanDs, while the structural basis remains unclear. More PanDs with known sequences and characterized properties are needed to shed light on the molecular basis of the self-cleavage process. In this study, PanD genes from 33 selected origins were synthesized and expressed; using purified recombinant enzymes, their self-processing properties were characterized and classified. Three classes of PanDs were acquired based on their self-cleavage efficiency. Combined with the phylogenetic analysis and structure comparison, sited-directed mutagenesis was performed to investigate the effects of four mutants on self-processing. In comparison with the wild-type (96.4%), the self-cleavage efficiencies of mutants V23E, I26C, T27A, and E56S were decreased to 90.5, 83.6, 74.4 and 81.2%, respectively. The results indicated that residues of V23, I26, T27 and E56 were critical to the self-cleavage processing of PanDs. This work provided further understanding to the self-cleavage processing of PanDs, which may contribute to protein engineering of the enzyme.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albert A et al (1998) Crystal structure of aspartate decarboxylase at 2.2 angstrom resolution provides evidence for an ester in protein self-processing. Nat Struct Biol 5:289–293. https://doi.org/10.1038/nsb0498-289
Arnott ZLP, Nozaki S, Monteiro DCF, Morgan HE, Pearson AR, Niki H, Webb ME (2017) The mechanism of regulation of pantothenate biosynthesis by the PanD–PanZ·AcCoA complex reveals an additional mode of action for the antimetabolite N-pentyl pantothenamide (N5-Pan). Biochemistry 56:4931–4939. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.biochem.7b00509
Begley TP, Kinsland C, Strauss E (2001) The biosynthesis of coenzyme A in bacteria. Vitam Horm Adv Res Appl 61(61):157–171
Cronan JE (1980) Beta-alanine synthesis in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol 141:1291–1297
Cui W, Shi Z, Fang Y, Zhou L, Ding N, Zhou Z (2014) Significance of Arg3, Arg54, and Tyr58 of l-aspartate alpha-decarboxylase from Corynebacterium glutamicum in the process of self-cleavage. Biotechnol Lett 36:121–126. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-013-1337-9
Datsenko KA, Wanner BL (2000) One-step inactivation of chromosomal genes in Escherichia coli K-12 using PCR products. Proc Natl Acad Sci 97:6640–6645
Dusch N, Puhler A, Kalinowski J (1999) Expression of the Corynebacterium glutamicum panD gene encoding l-aspartate-alpha-decarboxylase leads to pantothenate overproduction in Escherichia coli. Appl Environ Microbiol 65:1530–1539
Ekstrom JL, Tolbert WD, Xiong H, Pegg AE, Ealick SE (2001) Structure of a human S-adenosylmethionine decarboxylase self-processing ester intermediate and mechanism of putrescine stimulation of processing as revealed by the H243A mutant. Biochemistry 40:9495–9504. https://doi.org/10.1021/bi010736o
Gelfman CM, Copeland WC, Robertus JD (1991) Site-directed alteration of 4 active-site residues of a pyruvoyl-dependent histidine-decarboxylase. Biochemistry 30:1057–1062. https://doi.org/10.1021/bi00218a025
Gliessman JR, Kremer TA, Sangani AA, Jones-Burrage SE, McKinlay JB (2017) Pantothenate auxotrophy in Zymomonas mobilis ZM4 is due to a lack of aspartate decarboxylase activity. FEMS Microbiol Lett. https://doi.org/10.1093/femsle/fnx136
Hayflick SJ (2014) Defective pantothenate metabolism and neurodegeneration. Biochem Soc Trans 42:1063–1068. https://doi.org/10.1042/bst20140008
Huynh QK, Snell EE (1986) Histidine decarboxylase of Lactobacillus 30a. Hydroxylamine cleavage of the-seryl-seryl-bond at the activation site of prohistidine decarboxylase. J Biol Chem 261:1521–1524
Jackowski S, Rock CO (1981) Regulation of coenzyme A biosynthesis. J Bacteriol 148:926–932
McCloskey DE et al (2009) New insights into the design of inhibitors of human S-adenosylmethionine decarboxylase: studies of adenine C8 substitution in structural analogues of S-adenosylmethionine. J Med Chem 52:1388–1407. https://doi.org/10.1021/jm801126a
Monteiro DCF et al (2015) The structure of the PanD/PanZ protein complex reveals negative feedback regulation of pantothenate biosynthesis by coenzyme A. Chem Biol 22:492–503. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chembiol.2015.03.017
Nozaki S, Webb ME, Niki H (2012) An activator for pyruvoyl-dependent l-aspartate alpha-decarboxylase is conserved in a small group of the gamma-proteobacteria including Escherichia coli. Microbiologyopen 1:298–310. https://doi.org/10.1002/mbo3.34
Paulus H (2000) Protein splicing and related forms of protein autoprocessing. Annu Rev Biochem 69:447–496. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.biochem.69.1.447
Pei W et al (2017) Molecular engineering of l-aspartate-α-decarboxylase for improved activity and catalytic stability. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 101:6015–6021. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-017-8337-y
Ramjee MK, Genschel U, Abell C, Smith AG (1997) Escherichia coli l-aspartate-alpha-decarboxylase: preprotein processing and observation of reaction intermediates by electrospray mass spectrometry. Biochem J 323:661–669
Schagger H (2006) tricine–sds-page. Nat Protoc (Electron Ed) 1:16
Schmitzberger F et al (2003) Structural constraints on protein self-processing in l-aspartate-alpha-decarboxylase. EMBO J 22:6193–6204. https://doi.org/10.1093/emboj/cdg575
Scott DE, Ciulli A, Abell C (2007) Coenzyme biosynthesis: enzyme mechanism, structure and inhibition. Nat Prod Rep 24:1009–1026. https://doi.org/10.1039/b703108b
Sharma R, Florea M, Nau WM, Swaminathan K (2012) Validation of drug-Like inhibitors against Mycobacterium tuberculosis l-aspartate alpha-decarboxylase using nuclear magnetic resonance (H-1 NMR). PLoS One. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0045947
Smith RC (1988) The structure and molecular characterization of l-aspartate-alpha-decarbozylase from Escherichia coli. Doctoral Dissertation of Massachusetts institute of technology, Cambridge
Stuecker TN, Hodge KM, Escalante-Semerena JC (2012) The missing link in coenzyme A biosynthesis: PanM (formerly YhhK), a yeast GCN5 acetyltransferase homologue triggers aspartate decarboxylase (PanD) maturation in Salmonella enterica. Mol Microbiol 84:608–619. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2958.2012.08046.x
Stuecker TN, Bramhacharya S, Hodge-Hanson KM, Suen G, Escalante-Semerena JC (2015) Phylogenetic and amino acid conservation analyses of bacterial l-aspartate-alpha-decarboxylase and of its zymogen-maturation protein reveal a putative interaction domain. BMC Res Notes 8:354. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13104-015-1314-6
Tamura K, Peterson D, Peterson N, Stecher G, Nei M, Kumar S (2011) MEGA5: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol Biol Evol 28:2731–2739. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msr121
Tolbert WD, Ekstrom JL, Mathews II, Secrist JA, Kapoor P, Pegg AE, Ealick SE (2001) The structural basis for substrate specificity and inhibition of human S-adenosylmethionine decarboxylase. Biochemistry 40:9484–9494. https://doi.org/10.1021/bi010735w
Tolbert WD, Graham DE, White RH, Ealick SE (2003) Pyruvoyl-dependent arginine decarboxylase from Methanococcus jannaschii: crystal structures of the self-cleaved and S53A proenzyme forms. Structure 11:285–294. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0969-2126(03)00026-1
Van PP, Snell EE (1990) Pyruvoyl-dependent enzymes. Annu Rev Biochem 59:29–59. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.bi.59.070190.000333
Webb ME, Smith AG, Abell C (2004) Biosynthesis of pantothenate. Nat Prod Rep 21:695–721. https://doi.org/10.1039/b316419p
Williamson JM, Brown GM (1979) Purification and properties of l-aspartate-alpha-decarboxylase, an enzyme that catalyzes the formation of beta-alanine in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem 254:8074–8082
Zuman P, Salem N, Kulla E (2009) What do we know about determination of amino acids with orthophthalaldehyde? Electroanalysis 21:645–649. https://doi.org/10.1002/elan.200804426
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the National Science and Technology Major Project (2016YFD0401404), the National Natural Foundation of China (31571817) and national first-class discipline program of Light Industry Technology and Engineering (LITE2018-22).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Handling Editor: C. Schiene-Fischer.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mo, Q., Li, Y., Wang, J. et al. Identification of mutations restricting autocatalytic activation of bacterial l-aspartate α-decarboxylase. Amino Acids 50, 1433–1440 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-018-2620-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-018-2620-9