Abstract
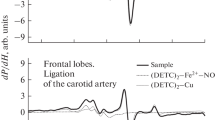
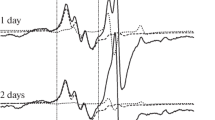
A comparative experimental analysis of intensity of nitric oxide (NO) production and the copper content in the tissues of hippocampus of male Wistar rats after modeling of hemorrhagic stroke and brain injury was conducted using EPR spectroscopy. Modeling of hemorrhagic stroke was carried out by microinjection of 500 nl of autologous blood into the brain to a depth of 5.0 mm (hippocampus) on the left side. Brain injury was performed by removing a piece of nerve tissue from 5.0 mm depth on the left side of hippocampus. It was registered a significant decrease in the NO content in hippocampus by 36 ± 17% on the 3rd day after modeling of hemorrhagic stroke together with decrease by an average of 24 ± 14% of the copper content. There were no significant changes in the NO level in hippocampus found neither on the 3rd day nor on the 7th day after brain injury modeling. There was also no change in copper content. Thus, it was experimentally demonstrated that modeling of brain injury, in contrast to hypoxia induced by hemorrhagic stroke, was not accompanied with significant changes in NO production in hippocampus of rat.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
H.A. Beydoun, C. Butt, M.A. Beydoun, S. Hossain, S.M. Eid, A.B. Zonderman, Cross-sectional study of major procedure codes among hospitalized patients with traumatic brain injury by level of injury severity in the 2004 to 2014 Nationwide Inpatient Sample. Medicine (Baltimore) 100(6), e24438 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1097/MD.0000000000024438
S.T. Dawodu, Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) Definition, Epidemiology, Pathophysiology (Medscape, New York, 2015)
M. Galgano, G. Toshkezi, X. Qiu, T. Russell, L. Chin, L.-R. Zhao, Traumatic brain injury: current treatment strategies and future endeavors. Cell Transpl. 26(7), 1118–1130 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1177/0963689717714102
J.P. Bolanos, A. Almeida, Roles of nitric oxide in brain hypoxia-ischemia. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1411, 415–436 (1999)
H.M. Bramlett, W.D. Dietrich, Pathophysiology of cerebral ischemia and brain trauma: similarities and differences. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 24(2), 133–150 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1097/01.WCB.0000111614.19196.04
J. Serrano, A.P. Fernández, R. Martínez-Murillo, D. Alonso, J. Rodrigo, E. Salas, M. Mourelle, A. Martínez, The nitric oxide donor LA 419 decreases ischemic brain damage. Int. J. Mol. Med. 19(2), 229–236 (2007). https://doi.org/10.3892/ijmm.19.2.229
P. Pacher, J.S. Beckman, L. Liaudet, Nitric oxide and peroxynitrite in health and disease. Physiol. Rev 87, 315–427 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1152/physrev.00029.2006
V. Calabrese, C. Mancuso, M. Calvani, E. Rizzarelli, D.A. Butterfield, A.M.G. Stella, Nitric oxide in the central nervous system: neuroprotection versus neurotoxicity. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 8, 767–775 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1038/nrn2214
Kh.L. Gainutdinov, S.A. Gavrilova, V.S. Iyudin, A.V. Golubeva, M.P. Davydova, G.G. Jafarova, V.V. Andrianov, V.B. Koshelev, EPR study of the intensity of the nitric oxide production in rat brain after ischemic stroke. Appl. Magn. Reson. 40, 267–278 (2011)
P.S. Garry, M. Ezra, M.J. Rowland, J. Westbrook, K.T. Pattinson, The role of the nitric oxide pathway in brain injury and its treatment from bench to bedside. Exp. Neurol. 263, 235–243 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.expneurol.2014.10.017
M.I. Remizova, N.I. Kochetygov, K.A. Gerbout, V.L. Lakomkin, A.A. Timoshin, E.N. Burgova, A.F. Vanin, Effect of dinitrosyl iron complexes with glutathione on hemorrhagic shock followed by saline treatment. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 662(1–3), 40–46 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2011.04.046
M.A. Salykina, E.G. Sorokina, I.A. Krasilnikova, V.P. Reutov, V.G. Pinelis, Effects of selective inhibitors of neuronal and inducible NO-synthase on ATP content and survival of cultured rat cerebellar neurons during hyperstimulation of glutamate receptors. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med 155(1), 40–43 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-013-2075-7
M. Godinez-Rubi, A.E. Rojas-Mayorquin, D. Ortuno-Sahagun, Nitric oxide donors as neuroprotective agents after an ischemic stroke-related inflammatory reaction. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2013, 1 (2013)
E.B. Manukhina, H.F. Downey, R.T. Mallet, Role of nitric oxide in cardiovascular adaptation to intermittent hypoxia. Exp. Biol. Med. 231, 343–365 (2006)
V.P. Reutov, V.E. Okhotin, A.V. Shuklin, E.G. Sorokina, N.S. Kosicin, V.N. Gurin, Nitric oxide and the cycle in the myocardium: molecular, biochemical and physiological aspects. Uspehi fiziologicheskih nauk 38, 39–58 (2007). (In Russ.)
L. Artinian, L. Zhongm, H. Yangm, V. Rehderm, Nitric oxide as intracellular modulator: internal production of NO increases neuronal excitability via modulation of several ionic conductances. Eur. J. Neurosci. 36, 3333–3343 (2012)
P.M. Balaban, M.V. Roshchin, AKh. Timoshenko, Kh.L. Gainutdinov, TKh. Bogodvid, L.N. Muranova, A.B. Zuzina, T.A. Korshunova, Nitric oxide is necessary for labilization of a consolidated context memory during reconsolidation in terrestrial snails. Eur. J. Neurosci. 40, 2963–2970 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1111/ejn.12642
A.F. Vanin, Dinitrosyl iron complexes with thiol-containing ligands as a “working form” of endogenous nitric oxide. Nitric Oxide 54, 15–29 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.niox.2016.01.006
A.F. Vanin, A. Huisman, E.E. Van Faassen, Iron dithiocarbamate as spin trap for nitric oxide detection: methods in enzymology. Pitfalls Successes 359, 27–42 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0076-6879(02)59169-2
J.R. Steinert, T. Chernova, I.D. Forsythe, Nitric oxide signaling in brain function, dysfunction, and dementia. Neuroscientist 16, 435–452 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1177/1073858410366481
K. Maiese, The dynamics of cellular injury: transformation into neuronal and vascular protection. Histol. Histopathol. 16(2), 633–644 (2001). https://doi.org/10.14670/HH-16.633
Z.-N. Guo, A. Shao, L.-S. Tong, W. Sun, J. Liu, Y. Yang, The role of nitric oxide and sympathetic control in cerebral autoregulation in the setting of subarachnoid hemorrhage and traumatic brain injury. Mol. Neurobiol. 53(6), 3606–3615 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-015-9308-x
G.A. Donnan, M. Fisher, M. Macieod, S.M. Davis, Stroke. Lancet 371, 1612–1623 (2008)
Z.Q. Chen, R.T. Mou, D.X. Feng, Z. Wang, G. Chen, The role of nitric oxide in stroke. Med. Gas Res. 7(3), 194–203 (2017). https://doi.org/10.4103/2045-9912.215750
V.P. Reutov, N.V. Samosudova, E.G. Sorokina, A model of glutamate neurotoxicity and mechanisms of the development of the typical pathological process. Biophysics 64(2), 233–250 (2019)
N.A. Terpolilli, M.A. Moskowitz, N. Plesnila, Nitric oxide: considerations for the treatment of ischemic stroke. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 32, 1332–1346 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/jcbfm.2012.12
L. Banci, I. Bertini, S. Ciofi-Baffoni, T. Kozyreva, K. Zovo, P. Palumaa, Affinity gradients drive copper to cellular destinations. Nature 465, 645–648 (2010)
R.A. Festa, D.J. Thiele, Copper: an essential metal in biology. Curr. Biol. 21(21), R877–R883 (2011)
T. Fukai, M. Ushio-Fukai, Superoxide dismutases: role in redox signaling, vascular function, and diseases. Antioxid. Redox Signal 15(6), 1583–1606 (2011)
N. Hogg, Detection of nitric oxide by electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 49, 122–129 (2010)
E.E. van Faassen, M.P. Koeners, J.A. Joles, A.F. Vanin, Detection of basal NO production in rat tissues using iron–dithiocarbamate complexes. Nitric Oxide 18, 279–286 (2008)
Y. Stukach, Stem cells migration to the brain through cranial nerves endings. EuroBiotech J. 1(1), 99–100 (2017)
T. Bogodvid, S. Pashkevich, M. Dosina, A. Zamaro, Y. Tokalchik, G. Yafarova, V. Andrianov, A. Denisov, D. Loiko, K. Gainutdinov, V. Kulchitsky, Effect of intranasal administration of mesenchymal stem cells on the approximate motor activity of rats after simulation of ischemic stroke. Eur. J. Clin. Invest. 49(Suppl 1), 161 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1111/eci.13109
Y. Shanko, A. Zamaro, Y. Takalchik, S. Koulchitsky, S. Pashkevich, E. Panahova, V. Navitskaya, M. Dosina, A. Denisov, S. Bushuk, V. Kulchitsky, Mechanisms of neural network structures recovery in brain trauma. Biomed. J. Sci. Tech. Res. (2018). https://doi.org/10.26717/BJSTR.2018.07.001567
G. Paxinos, C. Watson, The Rat Brain in Stereotaxic Coordinates, 4th edn. (Academic Press, San Diego, 1998)
C. Csonka, T. Pali, P. Bencsik, A. Gorbe, P. Ferdinandy, T. Csont, Measurement of NO in biological samples. Br. J. Pharmacol. 172, 1620–1632 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1111/bph.12832
S.V. Yurtaeva, V.N. Efimov, G.G. Yafarova, A.A. Eremeev, V.S. Iyudin, A.A. Rodionov, Kh.L. Gainutdinov, I.V. Yatsyk, EPR detection of iron storage in rat tissues after simulated microgravity model. Appl. Magn. Res. 47(6), 555–565 (2016)
V.D. Mikoyan, L.N. Kubrina, V.A. Serezhenkov, R.A. Stukan, A.F. Vanin, Complexes of Fe2+ with diethyldithiocarbamate or N-methyl-D-glucamine dithiocarbamate as traps of nitric oxide in animal tissues. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1336, 225–234 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0304-4165(97)00032-9
A.I. Ismailova, O.I. Gnezdilov, L.N. Muranova, A.A. Obynochny, V.V. Andrianov, Kh.L. Gainutdinov, A.G. Nasyrova, R.R. Nigmatullina, F.F. Rahmatullina, A.L. Zefirov, ESR study of the nitric oxide production in tissues of animals under the external influence on the functioning of the cardiovascular and nervous systems. Appl. Magn. Reson 28, 421–430 (2005)
V.V. Andrianov, S.G. Pashkevich, G.G. Yafarova, A.A. Denisov, V.S. Iyudin, TKh. Bogodvid, M.O. Dosina, V.A. Kulchitsky, Kh.L. Gainutdinov, Changes of nitric oxide content in the rat hippocampus, heart and liver in acute phase of ischemia. Appl. Magn. Reson. 47(9), 965–976 (2016)
Kh.L. Gainutdinov, V.V. Andrianov, V.S. Iyudin, S.V. Yurtaeva, G.G. Jafarova, R.I. Faisullina, F.G. Sitdikov, EPR study of nitric oxide production in rat tissues under hypokinesia. Biophysics 58, 203–205 (2013)
M.A. Jakubowska, J. Pyka, D. Michalczyk-Wetula, K. Baczyński, M. Cieśla, A. Susz, P.E. Ferdek, B.K. Płonka, L. Fiedor, P.M. Płonka, Electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy reveals alterations in the redox state of endogenous copper and iron complexes in photodynamic stress-induced ischemic mouse liver. Redox Biol. 34, 566 (2020)
Y. Suzuki, S. Fujii, T. Tominaga, T. Yoshimoto, T. Yoshimura, H. Kamada, The origin of an EPR signal observed in dithiocarbamate-loaded tissues Copper(II)-dithiocarbamate complexes account for the narrow hyperfine lines. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1335(3), 242–245 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1016/s0304-4165(97)00027-5
Y. Shanko, V. Navitskaya, A. Zamaro, S. Krivenko, S. Koulchitsky, V. Kulchitsky, Application of stem cells perineural migration in patients with stroke. J. Neurol. Stroke 9(2), 111–112 (2019). https://doi.org/10.15406/jnsk.2019.09.00358
Y. Shanko, V.V. Navitskaya, A. Zamaro, S. Krivenko, M. Zafranskaya, S. Pashkevich, S. Koulchitsky, Y.S. Takalchik, A. Denisov, V. Kulchitsky, Prospects of perineural administration of autologous mesenchymal stem cells of adipose tissue in patients with cerebral infarction. Biomed J. Sci. Tech. Res. 10(1), 1–3 (2018). https://doi.org/10.26717/BJSTR.2018.10.001884
M.L. Hoff, A. Fabrizius, N.U. Czech-Damal, L.P. Folkow, T. Burmester, Transcriptome analysis identifies key metabolic changes in the hooded seal (Cystophora cristata) brain in response to hypoxia and reoxygenation. PLoS ONE 12(1), e0169366 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0169366
E.B. Manukhina, I.Y. Malyshev, B.V. Smirin, S.Y. Mashina, V.A. Saltykova, A.F. Vanin, Production and storage of nitric oxide in adaptation to hypoxia. Nitric Oxide 3, 393–401 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1006/niox.1999.0244
K.P. Doyle, R.P. Simon, M.P. Stenzel-Poore, Mechanisms of ischemic brain damage. Neurophrmacology 55, 310–318 (2008)
L.X. Liu, Y.J. Yang, Y.J. Jia, A model of hypoxic-ischemic brain damage in the neonatal rats. Bull. Hunan Med. Univ. 28(2), 133–136 (2003)
M. Ziaja, J. Pyka, A. Machowska, A. Maslanka, P.M. Plonka, Nitric oxide spin-trapping and NADPH-diaphorase activity in mature rat brain after injury. J. Neurotrauma. 24(12), 1845–1854 (2007)
G. Inesi, Molecular features of copper binding proteins involved in copper homeostasis. IUBMB Life 69(4), 211–217 (2017)
A.G. Dalecki, M. Haeili, S. Shah, A. Speer, M. Niederweis, O. Kutsch, F. Wolschendorf, Disulfiram and copper ions kill Mycobacterium tuberculosis in a synergistic manner. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 59(8), 4835–4844 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1128/AAC.00692-15
V.V. Andrianov, G.G. Yafarova, S.G. Pashkevich, Y.P. Tokalchik, M.O. Dosina, A.S. Zamaro, TKh. Bogodvid, V.S. Iyudin, L.V. Bazan, A.A. Denisov, V.A. Kulchitsky, Kh.L. Gainutdinov, Changes of the nitric oxide and copper content in the olfactory bulbs of rats brain after modeling of brain stroke and intranasal administration of mesenchymal stem cells. Appl. Magn. Res. 51(4), 375–387 (2020)
O.G. Deryagin, S.A. Gavrilova, Kh.L. Gainutdinov, A.V. Golubeva, V.V. Andrianov, G.G. Yafarova, S.V. Buravkov, V.B. Koshelev, Molecular bases of brain preconditioning. Front. Neurosci. 11, 427 (2017). https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2017.00427
M.H.K. Ansari, P. Karimi, N. Shakib, S.M. Beyrami, The neuroprotective effect of sodium nitrite on ischemic stroke-induced mitochondrial dysfunction via down regulation of intrinsic apoptosis pathway. Crescent J. Medic. Biol. Sci. 5(1), 50–56 (2018)
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Abdulla Chihab and Dinara Silantyeva for help in preparation of this publication.
Funding
Ischemia modeling was carried out at the Brain Center, Institute of Physiology of the National Academy of Sciences of Belarus (Minsk, Belarus) and supported by the Belarusian Republican Foundation for Fundamental Research (Project # B18P-227). Measurement of EPR spectra of samples was carried out in Zavoisky Physical-Technical Institute, KazSC RAS within the framework of a state assignment Federal Research Center of KazSC RAS. The storage of samples and processing of results was carried out at Kazan Federal University (Kazan, Russia) in the framework of fulfilling the state assignment No. 0671-2020-0059.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Andrianov, V.V., Kulchitsky, V.A., Yafarova, G.G. et al. Comparative Study of the Intensity of Nitric Oxide Production and Copper Content in Hippocampus of Rats After Modeling of Hemorrhagic Stroke and Brain Injury. Appl Magn Reson 52, 1657–1669 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00723-021-01423-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00723-021-01423-1