Abstract
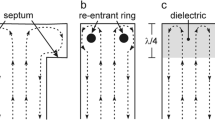
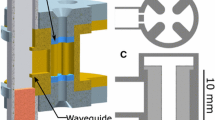
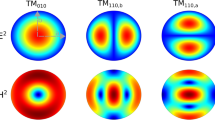
The dielectric tube resonator (DTR) for electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy is introduced. It is defined as a metallic cylindrical TE011 microwave cavity that contains a dielectric tube centered on the axis of the cylinder. Contour plots of dimensions of the metallic cylinder to achieve resonance at 9.5 GHz are shown for quartz, sapphire, and rutile tubes as a function of wall thickness and average radius. These contour plots were developed using analytical equations and confirmed by finite-element modeling. They can be used in two ways: design of the metallic cylinder for use at 9.5 GHz that incorporates a readily available tube such as a sapphire tube intended for NMR and design of a custom procured tube for optimized performance for specific sample-size constraints. The charts extend to the limiting condition where the dielectric fills the tube. However, the structure at this limit is not a dielectric resonator due to the metal wall and does not radiate. In addition, the uniform field (UF) DTR is introduced. Development of the UF resonator starting with a DTR is shown. The diameter of the tube remains constant along the cavity axis, and the diameter of the cylindrical metallic enclosure increases at the ends of the cavity to satisfy the uniform field condition. This structure has advantages over the previously developed UF TE011 resonators: higher resonator efficiency parameter Λ, convenient overall size when using sapphire tubes, and higher quality data for small samples. The DTR and UF DTR structures fill the gap between free space and dielectric resonator limits in a continuous manner.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
R.C. Rempel, C.E. Ward, R.T. Sullivan, M.W. St. Clair, H.E. Weaver, “Gyromagnetic resonance method and apparatus,” U.S. Pat. 3,122,703 (1964)
J.S. Hyde, G.R. Eaton, S.S. Eaton, Concepts Magn Reson. Part A Bridg. Educ. Res. 28A, 85–86 (2006)
L.G. Stoodley, J. Electron Control. 14, 531–546 (1963)
J.S. Hyde, J. Chem. Phys. 43, 806–1818 (1965)
J.S. Hyde, “Microwave cavity resonator”, U.S. Pat. 3,250,985 (1966)
W.M. Walsh Jr., L.W. Rupp Jr., Rev. Sci. Insrum. 57, 2078–2279 (1986)
R.W. Dykstra, G.W. Markham, J. Magn. Reson. 69, 350–355 (1986)
A. Sienkiewicz, K. Qu, Rev. Sci. Instrum. 65, 68–74 (1994)
M. Jaworski, A. Sienkiewicz, C.P. Scholes, J. Magn. Reson. 1969–1992(124), 87–96 (1997)
I.N. Geifman, I.S. Golovina, V.I. Kofman, R.E. Zusmanov, Ferroelectrics 234, 81 (1999)
A. Sienkiewicz, M. Jaworski, B.G. Smith, P.G. Fajer, C.P. Scholes, J. Magn. Reson. 143, 144–152 (2000)
Y.E. Nesmelov, J.T. Surek, D.D. Thomas, J. Magn. Reson. 153, 7–14 (2001)
A. Blank, E. Stavitski, H. Levanon, F. Gubaydullin, Rev. Sci. Instrum. 74, 2853–2859 (2003)
S.M. Mattar, A.H. Emwas, Chem. Phys. Lett. 368, 724–731 (2003)
I.N. Geifman, I.S. Golovina, Concepts Magn. Reson. 26B, 46 (2005)
A. Sienkiewicz, B. Vileno, S. Garaj, M. Jaworski, L. Forró, J. Magn. Reson. 177, 261–273 (2005)
I.S. Golovina, I.N. Geifman, A. Belous, J. Magn. Reson. 195, 52–59 (2008)
R.R. Mett, J.W. Sidabras, I.S. Golovina, J.S. Hyde, Rev. Sci. Instrum. 79, 094702 (2008)
S.M. Mattar, S.Y. Elnaggar, J. Magn. Reson. 209, 174–182 (2011)
A. Raitsimring, A. Astashkin, J.H. Enemark, A. Blank, Y. Twig, Y. Song, T.J. Meade, Appl. Magn. Reson. 42, 441–452 (2012)
S.Y. Elnaggar, R. Tervo, S.M. Mattar, J. Magn. Reson. 238, 1–7 (2014)
S.Y. Elnaggar, R. Tervo, S.M. Mattar, J. Magn. Reson. 242, 57–66 (2014)
S.Y. Elnaggar, R. Tervo, S.M. Mattar, J. Magn. Reson. 245, 50–57 (2014)
S.Y. Elnaggar, R.J. Tervo, S.M. Mattar, J. Appl. Phys. 118, 194901 (2015)
H.Y. Yee, I.E.E.E. Trans, Microwave Theory Tech. 13, 256 (1965)
D.M. Pozar, Microwave Engineering, 4th edn. (Addison-Wesley, New York, 1990), secs. 7.5, 7.8
M.W. Pospieszalski, I.E.E.E. Trans, Microwave Theory Tech. 27, 233 (1979)
F.J. Rosenbaum, Rev. Sci. Instrum. 35, 1550–1554 (1964)
J.S. Hyde, “EPR spectrometer resonant cavity”, U.S. Pat. 3,878,454 (1975)
J.S. Hyde, in Handbook of Microwave Technology, vol. 2, ed. by T.K. Ishii (Academic Press, New York, 1995), pp. 365–402
J.S. Hyde, W. Froncisz, in Advanced EPR: Applications in Biology and Biochemistry, ed. by A.J. Hoff (Elsevier, Amsterdam, 1989), pp. 277–306
G. Feher, Bell Syst. Tech. J. 36, 450–483 (1956)
W. Froncisz, J.S. Hyde, J. Magn. Reson. 47, 515–521 (1982)
R.R. Mett, W. Froncisz, J.S. Hyde, Rev. Sci. Instrum. 72, 4188–4200 (2001)
J.R. Anderson, R.R. Mett, J.S. Hyde, Rev. Sci. Instrum. 73, 3027–3037 (2002)
J.S. Hyde, R.R. Mett, J.R. Anderson, Rev. Sci. Instrum. 73, 4003–4009 (2002)
J.S. Hyde, R.R. Mett, W. Froncisz, J.R. Anderson, “Cavity resonator for electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy having axially uniform field”, U.S. Patent 6,828,789 (2004)
R.R. Mett, J.W. Sidabras, J.S. Hyde, Appl. Magn. Reson. 31, 571–587 (2007)
S. Ramo, J.R. Whinnery, T. Van Duzer, Fields and Waves in Communication Electronics (Wiley, New York, 1965), sec. 8.04
J.D. Jackson, Classical Electrodynamics, 2nd edn. (Wiley, New York, 1975), sec. 8.3
A.R. Von Hippel, Dielectric Materials and Applications (Artech House, Boston, 1954)
M.E. Tobar, J. Krupka, E.N. Ivanov, R.A. Woode, J. Appl. Phys. 83, 1604–1609 (1998)
W.J. Ellison, J. Phys. Chem. Ref. Data 36(1), 1–18 (2007)
J.W. Sidabras, R.R. Mett, J.S. Hyde, J. Magn. Reson. 172, 333–341 (2005)
J.S. Hyde, J.W. Sidabras, R.R. Mett, Resonators for multifrequency EPR of spin labels [chapter 5.2], in Multifrequency Electron Paramagnetic Resonance, Theory and Applications, ed. by S. Misra (Wiley, Berlin, 2011), pp. 244–270
Saint-Gobain Crystals. EFG Sapphire Tubes. Milford, NH: n.p. (2006)
J.S. Hyde, J. Chem. Phys. 43, 1806 (1965)
R.R. Mett, J.S. Hyde, Rev. Sci. Instrum. 76, 014702 (2005)
R.R. Mett, J.R. Anderson, J.W. Sidabras, J.S. Hyde, Rev. Sci. Instrum. 76, 094702 (2005)
R.R. Mett, J.W. Sidabras, J.S. Hyde, Appl. Magn. Reson. 35, 285–318 (2008)
J.S. Hyde, J. Gajdzinski, Rev. Sci. Instrum. 59, 1352 (1988)
J.W. Sidabras, T. Sarna, R.R. Mett, J.S. Hyde, J. Magn. Reson. 282, 129–135 (2017)
L. Mainali, J.W. Sidabras, T.G. Camenisch, J.J. Ratke, M. Raguz, J.S. Hyde, W.K. Subczynski, App. Magn. Reson. 45, 1343–1358 (2014)
Acknowledgements
Research reported in this publication was supported by the National Institute of Biomedical Imaging and Bioengineering of the National Institutes of Health under Award Number P41EB001980. The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the National Institutes of Health.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hyde, J.S., Mett, R.R. EPR Uniform Field Signal Enhancement by Dielectric Tubes in Cavities. Appl Magn Reson 48, 1185–1204 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00723-017-0935-4
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00723-017-0935-4