Summary
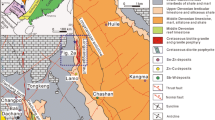
The Dachang Sn-polymetallic ore district is one of the largest tin producing districts in China. Its origin has long been in dispute between magmatic-hydrothermal replacement and submarine exhalative-hydrothermal origin. The Dachang ore district comprises several types of ore deposits, including the Lamo magmatogenic skarn deposit near a granite intrusion, the Changpo-Tongkeng bedded and vein-type sulfide deposit, and the Gaofeng massive sulfide deposit. Sulfide minerals from the Lamo skarn ores show δ34S values in the range between −3 and +4‰ with a mean close to zero, suggesting a major magmatic sulfur source that likely was the intrusive Longxianggai granite. Sulfide minerals from the Gaofeng massive ores show higher δ34S values between +5 and +12‰, whereas sulfide minerals from the Changpo-Tongkeng bedded ores display lighter δ34S values between −7 and −0.2‰. The difference in the sulfur isotope ranges in the two deposits can be interpreted by different degrees of inorganic thermochemcial reduction of marine sulfate using a one-step batch separation fractionation model. Sulfur isotopic compositions from the vein-type ores at Changpo-Tongkeng vary widely from −8 to +4‰, but most of the data cluster around −2.9‰, which is close to that of bedded ores (−3.6‰). The sulfur in vein-type ores might be derived from bedded ores or it represents a mixture of magmatic- and sedimentary-derived sulfur. Pb isotopic compositions of sulfide minerals in the Dachang ore district reveal a difference between massive and bedded ores, with the massive ores displaying more radiogenic Pb isotope ratios. Correlations of 206Pb/204Pb and 207Pb/204Pb or 208Pb/204Pb for the massive and bedded ores are interpreted as two-component mixing of Pb leached from sedimentary host rocks and from deep-seated Precambrian basement rocks composed of metamorphosed volcano-sedimentary rocks. Pb isotopic compositions of sulfide minerals from vein-type ores overlap with those of bedded sulfides. Similar to the sulfur, the lead in vein-type ores might be derived from bedded ores. Skarn ores at Lamo show very limited variations in Pb isotopic compositions, which may reflect a major magmatic-hydrothermal lead source. Helium isotope data of fluid inclusions trapped in sulfides indicate that He in the massive and bedded ores has a different origin than He in fluorite of granite-related veins. The 3He/4He ratios of 1.2–2.9 Ra of fluid inclusions from sulfides at Gaofeng and Changpo-Tongkeng imply a contribution of mantle-derived fluids. Overall our data support a submarine exhalative-hydrothermal origin for the massive and bedded ore types at Dachang.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
P Alfonso RM Prol-Ledesma C Canet JC Melgarejo AE Fallick (2003) ArticleTitleSulfur isotope geochemistry of the submarine hydrothermal coastal vents of Punta Mita, Mexico J Geochim Explor 78–79 301–304 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0375-6742(03)00144-4
PG Burnard R Hu G Turner XW Bi (1999) ArticleTitleMantle, crustal and atmospheric noble gases in Ailaoshan gold deposits, Yunnan Province, China Geochim Cosmochim Acta 63 1595–1604 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0016-7037(99)00108-8
PG Burnard DA Polya (2004) ArticleTitleImportance of mantle-derived fluids during granite associated hydrothermal circulation: He and Ar isotopes of ore minerals from Panasqueira Geochim Cosmochim Acta 68 1607–1615 Occurrence Handle10.1016/j.gca.2003.10.008
MH Cai JW Mao T Liang FX Wu (2004) ArticleTitleHelium and argon isotopic components of fluid inclusions in Dachang tin-polymetallic deposit and their geological implications Mineral Deposits (Beijing) 23 225–231
Cai MH, Mao JW, Liang T (2005) New constraints on the timing and origin of the Dachang tin-polymetallic deposit, Guangxi, China. In: Mao JW, Bierlein FP (eds) Mineral deposits research: meeting the global challenge 2, pp 893–896
H Chen (1988) ArticleTitleEvolution and mineralization of the Late Palaeozoic sedimentary basin in the Danchi area of Guangxi Journal of Chengde Institute of Geology 15 68–78
J Chen (2000) Geochimistry of tin Nanjing University Press Nanjing 320
YC Chen MZ Huang Y Xu (1985) ArticleTitleGeological features and metallogenetic series of the Dachang cassiterite–sulfide–polymetallic belt Acta Geologica Sinica 59 228–240
YC Chen MZ Huang J Xu YZ Hu SH Tang YQ Li LK Meng (1993) Tin deposits of Dachang Geological Publishing House Beijing 361
GE Claypool WT Hosler IR Kaplan H Sakai I Zak (1980) ArticleTitleThe age curves of sulfur and oxygen isotopes in marine sulfate and their mutual interpretation Chem Geol 28 199–260 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0009-2541(80)90047-9
TP Ding ZC Peng H Ni YH Li (1988) Stable isotope studies on several typical mineral deposits in the Nanling region Beijing Science and Technology Publishing House Beijing 21–44
TP Ding SY Jiang DF Wan YH Li (1996) Silicon isotope geochemistry Chinese Geological Publishing House Beijing 125
CS Eldridge N Williams JL Walshe (1993) ArticleTitleSulfur isotope variability in sediment-hosted massive sulfide deposits as determined using the ion microprobe SHRIMP: II. A study of the H.Y.C. deposit at McArthur River, Northern Territory, Australia Econ Geol 88 1–25
DL Fan T Zhang J Ye J Pašava B Kribek P Dobes I Varrin K Zak (2004) ArticleTitleGeochemistry and origin of tin-polymetallic sulfide deposits hosted by the Devonian black shale series near Dachang, Guangxi, China Ore Geol Rev 24 103–120 Occurrence Handle10.1016/j.oregeorev.2003.08.006
Franklin JM, Sangster DM, Lydon JW (1981) Volcanic-associated massive sulfide deposits. Economic Geology 75th Anniversary Volume, pp 485–627
M Fu A Changkakoti HR Krouse J Gray TAP Kwak (1991) ArticleTitleAn oxygen, hydrogen, sulfur, and carbon isotope study of carbonate-replacement (skarn) tin deposits of the Dachang tin field, China Econ Geol 86 1683–1703
M Fu TAP Kwak TP Mernagh (1993) ArticleTitleFluid inclusion studies of zoning in the Dachang tin-polymetallic ore field, People’s Republic of China Econ Geol 88 283–300
W Gehrisch A Maucher (1975) ArticleTitleSulfur isotope and trace element analyses from the Sujitjelma ore deposits, northern Norway Mineral Deposita 10 57–69 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF00207461
F Han RW Hutchinson (1989a) ArticleTitleEvidence for exhalative origin for rocks and ores of the Dachang tin polymetallic field: the ore-bearing formation and hydrothermal exhalative sedimentary rocks Mineral Deposits (Beijing) 8 25–40
F Han RW Hutchinson (1989b) ArticleTitleEvidence for hydrothermal exhalative sedimentary origin of the Dachang tin-polymetallic deposits-geochemistry of rare earth elements and trace elements of the host rocks Mineral Deposits (Beijing) 8 33–42
F Han RW Hutchinson (1990) ArticleTitleEvidence for exhalative origin of the Dachang tin-polymetallic sulfide deposits – their geological and geochemical characteristics Mineral Deposits (Beijing) 9 309–323
F Han RW Hutchinson (1991) ArticleTitleSynthetic studies on the origin of the Dachang tin-polymetallic deposits and their metallogenetic model Bull Chinese Acad Geol Sci 22 61–80
F Han JZ Shen RW Hutchinson (1993) ArticleTitleAdularia: an important indicator mineral of syngenetic origin for stratiform mineralization at the Dachang tin-polymetallic deposit Mineral Deposits (Beijing) 12 330–337
F Han RS Zhao JZ Shen RW Hutchinson SY Jiang HD Chen (1997) Geology and origin of ores in the Dachang tin-polymetallic ore field Geological Publishing House Beijing 213
CA Heinrich (1990) ArticleTitleThe chemistry of hydrothermal tin (tungsten) ore deposits Econ Geol 85 457–481
PM Herzig MD Hannington A Arribas SuffixJr (1998) ArticleTitleSulfur isotopic composition of hydrothermal precipitates from the Lau back-arc: implications for magmatic contributions to seafloor hydrothermal systems Mineral Deposita 33 226–237 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s001260050143
RZ Hu XW Bi G Turner (1999) ArticleTitleHelium and argon isotope geochemistry of ore forming fluids of Ailaoshan gold deposit Science in China (Ser D) 19 321–330
RZ Hu PG Burnard G Turner XW Bi (1998) ArticleTitleHelium and argon isotope systematics in fluid inclusions of Machangqing copper deposit in west Yunnan Province, China Chem Geol 146 55–63 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0009-2541(98)00003-5
D Huston (1999) ArticleTitleStable isotopes and their significance for understanding the genesis of volcanic-hosted massive sulfide deposits: a review Rev Econ Geol 8 157–179
SY Jiang (2001) ArticleTitleBoron isotope geochemistry of hydrothermal ore deposits in China: a preliminary study Phys Chem Earth 26 851–858 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S1464-1895(01)00132-6
SY Jiang F Han JZ Shen MR Palmer (1999) ArticleTitleChemical and Rb–Sr, Sm–Nd isotopic systematics of tourmaline from the Dachang Sn-polymetallic ore deposits, Guangxi Province, P.R. China Chem Geol 157 49–67 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0009-2541(98)00200-9
SY Jiang MR Palmer (1994) ArticleTitleSilicon isotope geochemistry of the Sullivan Pb–Zn deposit, Canada: a preliminary study Econ Geol 89 1623–1629
WC Kelly RO Rye (1979) ArticleTitleGeologic, fluid inclusion, and stable isotope studies of the tin–tungsten deposits of Panasqueira, Portugal Econ Geol 74 1721–1819
TAP Kwak (1987) W–Sn skarn deposits and related metamorphic skarns and granitoids Elservier Amsterdam 451
P Lattanzi M Corazza F Corsini G Tanelli (1989) ArticleTitleSulfide mineralogy in the polymetallic cassiterite deposits of Dachang, P.R. China Mineral Deposita 24 141–147 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF00206318
A Lehurary SE Church RA Koski RM Bouse (1988) ArticleTitlePb isotopes in sulfides from mid-ocean ridge hydrothermal sites Geology 16 362–365 Occurrence Handle10.1130/0091-7613(1988)016<0362:PIISFM>2.3.CO;2
E Marcoux (1998) ArticleTitleLead isotope systematics of the giant massive sulphide deposits in the Iberian Pyrite Belt Mineral Deposita 33 45–58 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s001260050132
H Ohmoto AC Lasaga (1982) ArticleTitleKinetics of reactions between aqueous sulfates and sulfides in hydrothermal systems Geochim Gosmochim Acta 46 1727–1745 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0016-7037(82)90113-2
H Ohmoto M Mizukami SE Drummond CS Eldridge V Pisutha-Arnond TC Lenaugh (1983) ArticleTitleChemical processes of Kuroko formation Econ Geol Mongraph 5 570–604
H Ohmoto RO Rye (1979) Isotopes of sulfur and carbon HL Barnes (Eds) Geochemistry of hydrothermal ore deposits Willey Interscience New York 509–567
J Pan GC Amstutz (1993) ArticleTitleAuthigenetic K-feldspars and their relations to Sn-polymetallic mineralization in the Dachang ore field Chinese J Geochem 12 270–288
J Pan GC Amstutz G Moh (1993) ArticleTitleStratabound anorthites in the Dachang Sn-polymetallic ore field, Guangxi, China Chinese J Geochem 12 261–269 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF02843365
Pašava J, Kř\(\breve{i}\)bek B, Dobeš P, Vavřín I, Žák K, Delian F, Tao Z, Boiron MC (2003) Tin-polymetallic sulfide deposits in the eastern part of the Dachang tin field (South China) and the role of black shales in their origin. Mineral Deposita 38: 39–66
DJ Patterson H Ohmoto M Solomon (1981) ArticleTitleGeological setting and genesis of cassiterite–sulfide mineralization at Renison Bell, western Tasmanian Econ Geol 76 393–438
Z Peng M Watanabe K Hoshino (1997) ArticleTitleOverviews of tin-bearing polymetallic mineralization in the Dachang ore field Res Geol 47 331–341
JM Peter WC Shanks SuffixIII (1992) ArticleTitleSulfur, carbon and oxygen isotope variations in submarine hydrothermal deposits of Guaymas Basin, Gulf of California, USA Geochim Cosmochim Acta 56 2025–2040 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0016-7037(92)90327-F
R Sáez E Pascual M Toscano GR Almodóvar (1999) ArticleTitleThe Iberian type of volcano-sedimentary massive sulphide deposits Mineral Deposita 34 549–570 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s001260050220
DF Sangster (1968) ArticleTitleRelative sulphur isotope abundances of ancient seas and strata-bound sulfide deposits Proc Geol Assoc Canada 19 79–91
K Sato A Sasaki (1980) ArticleTitleLead isotopic feature of the Besshi-type deposits and its bearing on the ore lead evolution Geochem J 14 303–315
JS Seewald WE Seyfried WC Shanks SuffixIII (1994) ArticleTitleVariation in the chemical and stable isotope composition of carbon and sulfur species during organic-rich sediment alteration: an experiment and theoretical study of hydrothermal acitivity at Guaymas Basin, Gulf of California Geochim Cosmochim Acta 58 5065–5082 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0016-7037(94)90232-1
SF Simmons FJ Sawkins DJ Schulutter (1987) ArticleTitleMantle-derived helium in two Peruvian hydrothermal ore deposits Nature 329 429–432 Occurrence Handle10.1038/329429a0
JF Slack (1996) ArticleTitleTourmaline associations with hydrothermal ore deposits Rev Mineral 33 559–643
M Solomon CJ Eastoe JL Walshe GR Green (1988) ArticleTitleMineral deposits and sulfur isotope abundances in the Mount Read volcanics between Que River and Mount Darwin, Tasmania Econ Geol 83 1307–1328
H Strauss (1999) ArticleTitleGeological evolution from isotope proxy signals-sulfur Chem Geol 161 89–101 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0009-2541(99)00082-0
FM Stuart G Turner (1992) ArticleTitleThe abundance and isotopic composition of the noble gases in ancient fluids Chem Geol 101 97–109
FM Stuart G Turner RC Duckworth AE Fallick (1994) ArticleTitleHelium isotopes as tracers of trapped hydrothermal fluids in ocean-floor sulfides Geology 22 823–826 Occurrence Handle10.1130/0091-7613(1994)022<0823:HIATOT>2.3.CO;2
FM Stuart P Burnard RP Taylor RP Taylor G Turner (1995) ArticleTitleResolving mantle and crustal contributions to ancient hydrothermal fluid: He–Ar isotopes in fluid inclusions from Dae Hwa W–Mo mineralization, South Korea Geochim Cosmochim Acta 59 4663–4673 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0016-7037(95)00300-2
FM Stuart RM Ellam R Duckworth (1999) ArticleTitleMetal sources in the Middle Valley massive sulphide deposit, northern Juan de Fuca Ridge: Pb isotope constraints Chem Geol 153 213–225 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0009-2541(98)00148-X
G Tanelli P Lattanzi (1985) ArticleTitleThe cassiterite–polymetallic sulfide deposits of Dachang (Guangxi, People’s Republic of China) Mineral Deposita 20 102–106 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF00204319
RG Taylor (1979) Geology of tin deposits Elsevier Amsterdam 543
Taylor BE, Beaudoin G (2000) Sulphur isotope stratigraphy of the Sullivan Pb–Zn–Ag deposit, B.C.: Evidence for hydrothermal sulphur, and bacterial and thermochemical sulphate reduction. In: Lydon JW, Hoy T, Slack JF, Knapp ME (eds) Geological environment of the Sullivan deposit, British Columbia, Geol Assoc Canada, Mineral Deposits Division, Spec Publ 1: 696–719
W Todt RA Cliff A Hanser AW Hofmann (1996) ArticleTitleEvaluation of a 202Pb–205Pb double spike for high-precision lead isotope analysis Geophys Monogr 95 429–437
F Velasco J Sánchez-Espana AJ Boyce AE Fallick R Sáez GR Almodóvar (1998) ArticleTitleA new sulphur isotopic study of some Iberian Pyrite Belt deposits: evidence of a textural control on sulphur isotope composition Mineral Deposita 34 4–18 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s001260050182
Xu WX (1987) Isotope geochemical study of the Dachang tin-polymetallic ore field. In Proceedings of International Symposium on Geology of Tin Deposits, Geological Publishing House, Beijing, pp 156–164 (in Chinese)
Xu WX, Wu QS, Xun JZ (1984) Isotope geochemistry of the Dachang tin-polymetallic ore field. International Symposium on Geology of Tin Deposits, Beijing (abstract), 96–97
Z Zhang X Li (1981) ArticleTitleStudies on mineralization and composition of Dachang ore field, Guangxi, China Chinese J Geochem 1 74–86
KD Zhao SY Jiang HQ Xiao P Ni (2002) ArticleTitleOrigin of ore-forming fluids of the Dachang Sn-polymetallic ore deposit: Evidence from helium isotopes Chinese Sci Bull 47 1041–1045 Occurrence Handle10.1360/02tb9234
RA Zierenberg RA Koski JL Morton R Bouse WC Shanks SuffixIII (1993) ArticleTitleGenesis of massive sulfide deposits on a sediment-covered spreading center, Escanaba Trough, southern Gorda Ridge Econ Geol 88 2069–2098 Occurrence Handle10.2113/gsecongeo.88.8.2069
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, KD., Jiang, SY., Ni, P. et al. Sulfur, lead and helium isotopic compositions of sulfide minerals from the Dachang Sn-polymetallic ore district in South China: implication for ore genesis. Mineralogy and Petrology 89, 251–273 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00710-006-0148-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00710-006-0148-2