Abstract
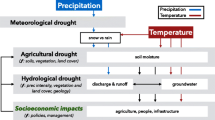
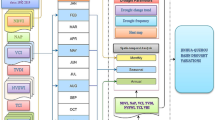
The present study aims to investigate Iran’s agrometeorological drought history and its properties using Multivariate Standardized Drought Index (MSDI). For this purpose, precipitation and soil moisture recorded at 99 synoptic stations in Iran during 1985 to 2018 were selected. Based on MSDI time series, drought properties including duration and severity were calculated and trend analysis was carried on using Trend Free Prewhitening Mann Kendall test. Also, the standard normal homogeneity test was applied to investigate chronological drought change-point detection. From agrometeorological perspective, results showed that longer and more severe droughts are more dominant in southern, southeastern, northeastern, and some western regions of the country. Trend analysis revealed that most study stations have rising frequency and significant drying trend especially in winter at central plateau and western regions. Also, we recognized two main periods 1991–2000 and 2006–2010 that many stations experienced change-point in their MSDI time series, mainly because of climatic and anthropogenic causes. Drought properties assessment shows 6 stations with serious upward trend in drought duration and severity in northeast and western regions. Sens’s Slope statistics in these stations was calculated around 1.5 degree per event for drought severity and 1 month per event for drought duration. It is also observed that the 75th quantile of drought severity for most parts of the country is between 13 and 18 and the 75th quantile for drought duration varies between 8 and 24 months in different regions. The probability analysis revealed that most stations have a ratio around 2–5 times increase in drought occurrence probability after change point, leading to longer and more severe droughts in these stations. The paper indicates a serious situation related to agrometeorological drought occurrence, persistence, and severity in Iran because of many climatic and anthropogenic factors over the last 30 years.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Code availability
The code generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Agrawala S, Barlow M, Cullen H, Lyon B (2001) The drought and humanitarian crisis in central and southwest Asia: a climate perspective. IRI Spec Rep NO 01–11:20. https://doi.org/10.7916/D8NZ8FHQ
Araghi A, Martinez CJ, Adamowski J, Olesen JE (2018) Spatiotemporal variations of aridity in Iran using high-resolution gridded data. Int J Climatol 38:2701–2717. https://doi.org/10.1002/joc.5454
Bari Abarghouei H, Asadi Zarch MA, Dastorani MT et al (2011) The survey of climatic drought trend in Iran. Stoch Environ Res Risk Assess 25:851–863. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00477-011-0491-7
Bazrafshan J (2017) Effect of air temperature on historical trend of long-term droughts in different climates of Iran. Water Resour Manag 31:4683–4698. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-017-1773-8
Bezak N, Mikoš M, Šraj M (2014) Trivariate frequency analyses of peak discharge, hydrograph volume and suspended sediment concentration data using copulas. Water Resour Manag 28:2195–2212. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-014-0606-2
Bhalme HN, Mooley DA (1980) Large-scale droughts/ floods and monsoon circulation. Mon Weather Rev 108:1197–1211. https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0493(1980)108%3c1197:LSDAMC%3e2.0.CO;2
Cook ER, Seager R, Cane MA, Stahle DW (2007) North American drought: reconstructions, causes, and consequences. Earth-Science Rev 81:93–134. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.earscirev.2006.12.002
Dorigo W, Wagner W, Gruber A, et al (2018) ESA soil moisture climate change initiative (Soil_Moisture_cci): Version 03.2 data collection. Cent Environ Data Anal. https://doi.org/10.5285/b810601740bd4848b0d7965e6d83d26c
Dracup JA, Lee KS, Paulson EG (1980) On the definition of droughts. Water Resour Res 16:297–302. https://doi.org/10.1029/WR016i002p00297
Emadodin I, Reinsch T, Taube F (2019) Drought and Desertification in Iran. Hydrology 6:66. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology6030066
Golian S, Mazdiyasni O, AghaKouchak A (2014) Trends in meteorological and agricultural droughts in Iran. Theor Appl Climatol 119:679–688. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-014-1139-6
Guha-Sapir D, Hargitt D, Hoyois P (2003) Thirty years of natural diasasters. 1974–2003 : The Numbers. Centre for Research on the Epidemiology of Disasters. UCL Presses
Guha-Sapir D, Vos F, Below R (2012) Annual disaster statistical review 2011. … Disasters 52
Hao Z, AghaKouchak A (2013) Multivariate Standardized Drought Index: a parametric multi-index model. Adv Water Resour 57:12–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.advwatres.2013.03.009
Heim RR (2002) A review of twentieth-century drought indices used in the United States. Bull Am Meteorol Soc 83:1149–1166. https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0477-83.8.1149
Kao SC, Govindaraju RS (2010) A copula-based joint deficit index for droughts. J Hydrol 380:121–134. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2009.10.029
Kavian A, Azmoodeh A, Solaimani K (2014) Deforestation effects on soil properties, runoff and erosion in northern Iran. Arab J Geosci 7:1941–1950. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-013-0853-1
Keyantash JA, Dracup JA (2004) An aggregate drought index: assessing drought severity based on fluctuations in the hydrologic cycle and surface water storage. Water Resour Res 40https://doi.org/10.1029/2003WR002610
Kulkarni A, Von SH (1995) Monte Carlo experiments on the effect of serial correlation on the Mann-Kendall test of trend. Meteorol Zeitschrift 4:82–85
Kwon M, Kwon H, Han D (2019) Spatio-temporal drought patterns of multiple drought indices based on precipitation and soil moisture: a case study in South Korea. Int J Climatol 39:4669–4687. https://doi.org/10.1002/joc.6094
Ma M, Ren L, Singh VP et al (2014) New variants of the Palmer drought scheme capable of integrated utility. J Hydrol 519:1108–1119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2014.08.041
Madani K (2014) Water management in Iran: what is causing the looming crisis? J Environ Stud Sci 4:315–328. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13412-014-0182-z
Madani K, AghaKouchak A, Mirchi A (2016) Iran’s socio-economic drought: challenges of a water-bankrupt nation. Iran Stud 49:997–1016. https://doi.org/10.1080/00210862.2016.1259286
Maghrebi M, Noori R, Bhattarai R, et al (2020) Iran’s agriculture in the Anthropocene. Earth’s Futur 8https://doi.org/10.1029/2020EF001547
McKee TB, Nolan J, Kleist J (1993) The relationship of drought frequency and duration to time scales. Prepr Eighth Conf Appl Climatol Amer Meteor, Soc 179–184
Mesgaran M, Madani K, Hashemi H, Azadi P (2016) Evaluation of land and precipitation for agriculture in Iran. Standford Iran 2040, Stanford University, December 2016 https://purl.stanford.edu/vf990qz0340
Modarres R (2006) Regional precipitation climates of Iran. J Hydrol (new Zealand) 45:13–27
Modarres R, Sarhadi A, Burn DH (2016) Changes of extreme drought and flood events in Iran. Glob Planet Change 144:67–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gloplacha.2016.07.008
Mohmmadi Samani K, Pordel N, Hosseini V, Shakeri Z (2020) Effect of land-use changes on chemical and physical properties of soil in western Iran (Zagros oak forests). J for Res 31:637–647. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11676-018-0799-y
Nabaei S, Sharafati A, Yaseen ZM, Shahid S (2019) Copula based assessment of meteorological drought characteristics: regional investigation of Iran. Agric for Meteorol 276–277:107611. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agrformet.2019.06.010
Najafi MR, Moazami S (2016) Trends in total precipitation and magnitude-frequency of extreme precipitation in Iran, 1969–2009. Int J Climatol 36:1863–1872. https://doi.org/10.1002/joc.4465
Nasri M, Modarres R (2009) Dry spell trend analysis of Isfahan Province. Iran Int J Climatol 29:1430–1438. https://doi.org/10.1002/joc.1805
Noori R, Maghrebi M, Mirchi A, et al (2021) Anthropogenic depletion of Iran’s aquifers. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2024221118/-/DCSupplemental
Palmer WC (1965) Meteorological drought. U.S. Weather Bur. Res. Pap. No. 45 58
Pohlert T, Pohlert MT, Kendall S (2016) Package ‘trend.’ Title Non-Parametric Trend Tests Chang Detect
Rahmani, A., Golian, S. and Brocca, L. 2016 Multiyear monitoring of soil moisture over Iran through satellite and reanalysis soil moisture products. Int J Appl Earth Obs Geoinf 48:85-95
Sharafati A, Nabaei S, Shahid S (2020) Spatial assessment of meteorological drought features over different climate regions in Iran. Int J Climatol 40:1864–1884. https://doi.org/10.1002/joc.6307
Shiau JT, Modarres R (2009) Copula-based drought severity-duration-frequency analysis in Iran. Meteorol Appl 16:481–489. https://doi.org/10.1002/met.145
Song Y, Park M (2020) Assessment of quantitative standards for mega-drought using data on drought damages. Sustain 12:3598. https://doi.org/10.3390/SU12093598
Tabari H, Talaee PH (2011) Temporal variability of precipitation over Iran: 1966–2005. J Hydrol 396:313–320. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2010.11.034
Van Rooy MP (1965) A Rainfall anomaly index (RAI) independent of time and space. Notos 14:43–48
Wilhite D (2000) Chapter 1 Drought as a natural hazard: concepts and definitions. Drought Mitig Cent Fac Publ
Yevjevich V (1967) An objective approach to definitions and investigations of continental droughts. Hydrol Pap
Yue S, Pilon P, Phinney B, Cavadias G (2002) The influence of autocorrelation on the ability to detect trend in hydrological series. Hydrol Process 16:1807–1829. https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.1095
Zarei AR, Eslamian S (2017) Trend assessment of precipitation and drought index (SPI) using parametric and non-parametric trend analysis methods (case study: Arid regions of southern Iran). Int J Hydrol Sci Technol 7:12–38. https://doi.org/10.1504/IJHST.2017.080957
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
This research has no ethical issue to declare.
Consent to participate
All authors have to participate in writing the article and consent participation.
Consent for publication
We approve that all authors consent of publication in Theoretical and Applied Climatology.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Isfahani, P.M., Soltani, S. & Modarres, R. Assessing agrometeorological drought trends in Iran during 1985–2018. Theor Appl Climatol 150, 251–262 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-022-04159-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-022-04159-5