Abstract
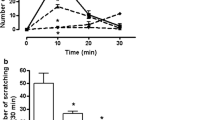
Itch and pain are two irritating sensations sharing a lot in common. Considering the antinociceptive effects of blockade of endocannabinoid degrading enzymes in pain states, we attempted to reduce scratching behavior by endocannabinoid modulation, i.e. by inhibiting fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH), monoacylglycerol lipase (MAGL), or cellular uptake of endocannabinoids. Scratching behavior was induced by intradermal injection of serotonin to Balb/c mice. URB597 (10 mg/kg, i.p.), a FAAH inhibitor, JZL184 (16 mg/kg, i.p.), a MAGL inhibitor, and AM404 (10 mg/kg, i.p.), an endocannabinoid transport inhibitor, were given to evaluate the effects of endocannabinoid modulation on scratching responses. Then, the CB1 receptor antagonist, AM251 (1 mg/kg, i.p.), and the CB2 receptor antagonist, SR144528 (1 mg/kg, i.p.), were administered to determine whether cannabinoid receptors mediate these effects. URB597 and JZL184, but not AM404, attenuated serotonin-induced scratches. The inhibitory effect of URB597 was reversed by SR144528, but cannabinoid receptor antagonists had no other effects on modulation by the inhibitors. We propose that augmenting the endocannabinoid tonus by inhibition of degradative enzymes, FAAH and MAGL, but not cellular uptake, may be a novel target for the development of antipruritic agents.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- 2-AG:
-
2-Arachidonylglycerol
- AEA:
-
Anandamide (N-arachidonylethanolamide)
- CB:
-
Cannabinoid
- FAAH:
-
Fatty acid amide hydrolase
- MAGL:
-
Monoacylglycerol lipase
- TRPV-1:
-
Tansient receptor potential vanilloid type-1
References
Cevikbas F, Steinhoff M, Ikoma A (2011) Role of spinal neurotransmitter receptors in ıtch: new ınsights into therapies and drug development. CNS Neurosci Ther 17(6):742–749. doi:10.1111/J.1755-5949.2010.00201.X
Davidson S, Giesler GJ (2010) The multiple pathways for itch and their interactions with pain. Trends Neurosci 33(12):550–558. doi:10.1016/J.Tins.09.002
Di Marzo V (2008) Targeting the endocannabinoid system: to enhance or reduce? Nat Rev Drug Discov 7(5):438–455. doi:10.1038/Nrd2553
Dogrul A, Seyrek M, Yalcin B, Ulugol A (2012) Involvement of descending serotonergic and noradrenergic pathways in CB1 receptor-mediated antinociception. Prog Neuro-Psychoph 38(1):97–105. doi:10.1016/J.Pnpbp.01.007
Graf M, Kantor S, Anheuer ZE, Modos EA, Bagdy G (2003) m-CPP-induced self-grooming is mediated by 5-HT2C receptors. Behav Brain Res 142(1–2):175–179. doi:10.1016/S0166-4328(02)00404-7
Guindon J, Hohmann AG (2009) The endocannabinoid system and pain. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets 8(6):403–421
Guindon J, Desroches J, Beaulieu P (2007) The antinociceptive effects of intraplantar injections of 2-arachidonoyl glycerol are mediated by cannabinoid CB2 receptors. Br J Pharmacol 150(6):693–701. doi:10.1038/Sj.Bjp.0706990
Gunduz O, Karadag HC, Ulugol A (2011) Synergistic anti-allodynic effects of nociceptin/orphanin FQ and cannabinoid systems in neuropathic mice. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 99(4):540–544. doi:10.1016/J.Pbb.05.029
Ikoma A, Cevikbas F, Kempkes C, Steinhoff M (2011) Anatomy and neurophysiology of pruritus. Semin Cutan Med Surg 30(2):64–70. doi:10.1016/J.Sder.04.001
Jayamanne A, Greenwood R, Mitchell VA, Aslan S, Piomelli D, Vaughan CW (2006) Actions of the FAAH inhibitor URB597 in neuropathic and inflammatory chronic pain models. Br J Pharmacol 147(3):281–288. doi:10.1038/Sj.Bjp.0706510
Jhaveri MD, Richardson D, Chapman V (2007) Endocannabinoid metabolism and uptake: novel targets for neuropathic and inflammatory pain. Br J Pharmacol 152(5):624–632. doi:10.1038/Sj.Bjp.0707433
Kinsey SG, Long JZ, O’Neal ST, Abdullah RA, Poklis JL, Boger DL, Cravatt BF, Lichtman AH (2009) Blockade of endocannabinoid-degrading enzymes attenuates neuropathic pain. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 330(3):902–910. doi:10.1124/Jpet.109.155465
Kinsey SG, Nomura DK, O’Neal ST, Long JZ, Mahadevan A, Cravatt BF, Grider JR, Lichtman AH (2011) Inhibition of monoacylglycerol lipase attenuates nonsteroidal anti-ınflammatory drug-ınduced gastric hemorrhages in mice. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 338(3):795–802. doi:10.1124/Jpet.110.175778
Koga K, Chen T, Li X-Y, Descalzi G, Ling J, Gu J, Zhuo M (2011) Glutamate acts as a neurotransmitter for gastrin releasing peptide-sensitive and insensitive itch-related synaptic transmission in mammalian spinal cord. Mol Pain 7:47-47
Kuraishi Y (2013) Potential new therapeutic targets for pathological pruritus. Biol Pharm Bull 36(8):1228–1234
Lazary J, Juhasz G, Hunyady L, Bagdy G (2011) Personalized medicine can pave the way for the safe use of CB1 receptor antagonists. Trends Pharmacol Sci 32(5):270–280. doi:10.1016/J.Tips.02.013
Lichtman AH, Shelton CC, Advani T, Cravatt BF (2004) Mice lacking fatty acid amide hydrolase exhibit a cannabinoid receptor-mediated phenotypic hypoalgesia. Pain 109(3):319–327. doi:10.1016/J.Pain.01.022
Long JZ, Nomura DK, Vann RE, Walentiny DM, Booker L, Jin X, Burston JJ, Sim-Selley LJ, Lichtman AH, Wiley JL, Cravatt BF (2009) Dual blockade of FAAH and MAGL identifies behavioral processes regulated by endocannabinoid crosstalk in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106(48):20270–20275. doi:10.1073/Pnas.0909411106
Maione S, Costa B, Piscitelli F, Morera E, De Chiaro M, Comelli F, Boccella S, Guida F, Verde R, Ortar G (2013) Di Marzo V (2013) Piperazinyl carbamate fatty acid amide hydrolase inhibitors and transient receptor potential channel modulators as “dual-target” analgesics. Pharmacol Res 76:98–105. doi:10.1016/J.Phrs.07.003
Mitchell VA, Greenwood R, Jayamanne A, Vaughan CW (2007) Actions of the endocannabinoid transport inhibitor AM404 in neuropathic and inflammatory pain models. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 34(11):1186–1190. doi:10.1111/J.1440-1681.2007.04692.X
Niphakis MJ, Johnson DS, Ballard TE, Stiff C, Cravatt BF (2012) O-Hydroxyacetamide carbamates as a highly potent and selective class of endocannabinoid hydrolase inhibitors. ACS Chem Neurosci 3(5):418–426. doi:10.1021/cn200089j
Nomura DK, Morrison BE, Blankman JL, Long JZ, Kinsey SG, Marcondes MCG, Ward AM, Hahn YK, Lichtman AH, Conti B, Cravatt BF (2011) Endocannabinoid hydrolysis generates brain prostaglandins that promote neuroinflammation. Science 334(6057):809–813. doi:10.1126/Science.1209200
Pertwee RG (2012) Targeting the endocannabinoid system with cannabinoid receptor agonists: pharmacological strategies and therapeutic possibilities. Philos Trans R Soc B 367(1607):3353–3363. doi:10.1098/Rstb.2011.0381
Rawls SM, Ding Z, Cowan A (2006) Role of TRPV1 and cannabinoid CB1 receptors in AM 404-evoked hypothermia in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 83(4):508–516. doi:10.1016/J.Pbb.03.011
Ross SE (2011) Pain and itch: insights into the neural circuits of aversive somatosensation in health and disease. Current Opinion in Neurobiology 21 (6):880-887. doi:Doi 10.1016/J.Conb.2011.10.012
Ross SE, Mardinly AR, McCord AE, Zurawski J, Cohen S, Jung C, Hu L, Mok SI, Shah A, Savner EM, Tolias C, Corfas R, Chen S, Inquimbert P, Xu Y, McInnes RR, Rice FL, Corfas G, Ma Q, Woolf CJ, Greenberg ME (2010) Loss of inhibitory interneurons in the dorsal spinal cord and elevated itch in Bhlhb5 mutant mice. Neuron 65(6):886–898
Russo R, LoVerme J, La Rana G, Compton TR, Parrott J, Duranti A, Tontini A, Mor M, Tarzia G, Calignano A, Piomelli D (2007) The fatty acid amide hydrolase inhibitor URB597 (cyclohexylcarbamic acid 3 ‘-carbamoylbiphenyl-3-yl ester) reduces neuropathic pain after oral administration in mice. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 322(1):236–242. doi:10.1124/Jpet.107.119941
Schlosburg JE, Boger DL, Cravatt BF, Lichtman AH (2009a) Endocannabinoid modulation of scratching response in an acute allergenic model: a new prospective neural therapeutic target for pruritus. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 329(1):314–323. doi:10.1124/Jpet.108.150136
Schlosburg JE, Kinsey SG, Lichtman AH (2009b) Targeting fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH) to treat pain and inflammation. AAPS J 11(1):39–44. doi:10.1208/S12248-008-9075-Y
Schlosburg JE, O’Neal ST, Conrad DH, Lichtman AH (2011) CB1 receptors mediate rimonabant-induced pruritic responses in mice: investigation of locus of action. Psychopharmacology 216(3):323–331. doi:10.1007/S00213-011-2224-5
Starowicz K, Di Marzo V (2013) Non-psychotropic analgesic drugs from the endocannabinoid system: “Magic bullet” or “multiple-target” strategies? Eur J Pharmacol 716(1–3):41–53. doi:10.1016/J.Ejphar.01.075
Ulugol A, Karadag HC, Ipci Y, Tamer M, Dokmeci I (2004) The effect of WIN 55,212-2, a cannabinoid agonist, on tactile allodynia in diabetic rats. Neurosci Lett 371(2–3):167–170
Ulugol A, Ozyigit F, Yesilyurt O, Dogrul A (2006) The additive antinociceptive interaction between WIN 55,212-2, a cannabinoid agonist, and ketorolac. Anesth Analg 102(2):443–447. doi:10.1213/01.Ane.0000194587.94260.1d
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by a grant from Trakya University Research Council (TUBAP-2012/187). The authors have no conflicts of interests to report.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Submitted to “15th World Congress on Pain”, Buenos Aires, Argentina, 6–11October 2014.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tosun, N.C., Gunduz, O. & Ulugol, A. Attenuation of serotonin-induced itch responses by inhibition of endocannabinoid degradative enzymes, fatty acid amide hydrolase and monoacylglycerol lipase. J Neural Transm 122, 363–367 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-014-1251-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-014-1251-x