Abstract
Background
Traumatic distal anterior cerebral artery (dACA) aneurysm is rare and can be easily neglected and misdiagnosed in patients with trauma. The aim of this study was to explore the radiologic characteristics of and therapeutic strategies for traumatic dACA aneurysm and to improve our understanding of unusual complications after trauma.
Methods
The clinical data of nine cases of traumatic dACA aneurysm from our neurosurgical department from July 1, 2010, to July 1, 2018, were retrospectively analysed.
Results
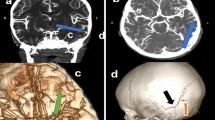
All 9 patients had a history of brain trauma. The initial computed tomography scan immediately after trauma showed subarachnoid haemorrhage in 8 cases. Among these cases, delayed intracranial haemorrhage occurred in 7 cases. The average interval between injury and diagnosis was 13.67 ± 9.43 days. All 9 cases were confirmed as traumatic dACA aneurysm by computed tomography angiography (CTA) and/or digital subtraction angiography. According to Lehecka’s classification system, traumatic dACA aneurysm located in the A3 and A4 segment was found in 3 and 6 cases, respectively. Surgical treatment was performed in 8 cases, including neck clipping, with or without wrapping in 3 cases, trapping in 4 cases, aneurysm excision and suturing in 1 case and conservative treatment in 1 case. Three patients required a ventriculoperitoneal shunt due to severe hydrocephalus. According to the Glasgow Outcome Scale scoring system, good recovery was achieved in 4 cases, moderate disability in 2 cases, severe disability in 1 case, and death in 2 cases.
Conclusion
Traumatic dACA aneurysm is a rare complication of brain trauma. Delayed intracranial haemorrhage and the sudden deterioration of neurologic function were the typical characteristics in patients with traumatic dACA aneurysm. CTA is the first-line screening modality for patients who present with intracerebral haemorrhage in the corpus callosum after trauma, particularly for patients who are older, in a poorer or critical condition. When the aneurysm is located in the A4 segment or involves a small branch, surgical trapping is the preferred definitive therapy to prevent further growth and disastrous bleeding. Early diagnosis and prompt treatment could help to improve clinical outcomes.


Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
13 December 2019
Incorrect family name of Dongsheng Guo.
References
Amirjamshidi A, Rahmat H (1996) Traumatic aneurysms and arteriovenous fistulas of intracranial vessels associated with penetrating head injuries occurring during war: principles and pitfalls in diagnosis and management. A survey of 31 cases and review of the literature. J Neurosurg 84:769–780
Barua NU, Ross AH, Sanderman DR (2007) Traumatic callosomarginal aneurysm following orbital gunshot wound in a 16-year-old girl. Br J Neurosurg 21:237–238
Burton C, Velasco F, Dorman J (1968) Traumatic aneurysm of a peripheral cerebral artery. Review and case report. J Neurosurg 28:468–474
Cohen JE, Gomori JM, Segal R, Spivak A, Margolin E, Sviri G, Rajz G, Fraifeld S, Spektor S (2008) Results of endovascular treatment of traumatic intracranial aneurysms. Neurosurgery 63:476–485
Cohen JE, Rajz G, Itshayek E, Shoshan Y, Umansky F, Gomori JM (2005) Endovascular management of traumatic and iatrogenic aneurysms of the pericallosal artery. Report of two case. J Neurosurg 102:555–557
Cummings TJ, Johnson RR, Diaz FG, Michael DB (2000) The relationship of blunt head trauma, subarachnoid hemorrhage, and rupture of pre-existing intracranial saccular aneurysms. Neurol Res 22:165–170
Dunn GP, Gerrard JL, Jho DH, Ogilvy CS (2011) Surgical treatment of a large fusiform distal anterior cerebral artery aneurysm with in situ end-to-side A3—A3 bypass graft and aneurysm trapping. Neurosurgery 68:E587–E591
Dunn IF, Woodworth GF, Siddiqui AH, Smith ER, Vates GE, Day AL, Goumnerova LC (2007) Traumatic pericallosal artery aneurysm: a rare complication of transcallosal surgery. Case report. J Neurosurg 106:153–157
Gillis CC, Gooderham PA, Haw CS (2013) Traumatic entrapment of the anterior cerebral artery: a case report. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 115:498–500
Holmes B, Harbaugh RE (1993) Traumatic intracranial aneurysms: a contemporary review. J Trauma 35:855–860
Hsieh CT, Lin EY, Tsai TH, Chiang YH, Ju DT (2007) Delayed rupture of pre-existing cerebral aneurysm in a young patient with minor head trauma. J Clin Neurosci 14:1120–1122
Jung SH, Kim SH, Kim TS, Joo SP (2017) Surgical treatment of traumatic intracranial aneurysms: experiences at a single center over 30 years. World Neurosurg 98:243–250
Kim MS, Sim SY (2014) Traumatic aneurysm of the callosomarginal artery-cortical artery junction from penetrating injury by scissors. J Korean Neurosurg 55:222–225
Kumar A, Jakubovic R, Yang V, Dacosta L (2016) Traumatic anterior cerebral artery aneurysms and management options in the endovascular era. J Clin Neurosci 25:90–95
Lam CH, Montes J, Farmer JP, O’Gorman AM, Meagher-Villemure K (1996) Traumatic aneurysm from shaken baby syndrome: case report. Neurosurgery. 39:1252–1255
Lath R, Vaniprasad A, Kat E, Brophy BP (2002) Traumatic aneurysm of the callosomarginal artery. J Clin Neurosci 9:466–468
Lehecka M, Porras M, Dashti R, Niemela M, Hernesniemi JA (2008) Anatomic features of distal anterior cerebral artery aneurysms: a detailed angiographic analysis of 101 patients. Neurosurgery 63:219–228
Levine NB, Tanaka T, Jones BV, Crone KR (2004) Minimally invasive management of a traumatic artery aneurysm resulting from shaken baby syndrome. Pediatr Neurosurg 40:128–131
Mao Z, Wang N, Hussain M, Li M, Zhang H, Zhang Q, Zhang P, Zhi X, Ling F (2012) Traumatic intracranial aneurysms due to blunt brain injury-a single center experience. Acta Neurochir 154:2187–2193
Nakstad PH, Gjertsen O, Pedersen HK (2008) Correlation of head trauma and traumatic aneurysms. Interv Neuroradiol 14:33–38
O’Brien D Jr, O’Dell MW, Eversol A (1997) Delayed traumatic cerebral aneurysm after brain injury. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 78:883–885
Pradilla G, Wicks RT, Hadelsberg U, Gailloud P, Coon AL, Huang J, Tamargo RJ (2013) Accuracy of computed tomography angiography in the diagnosis of intracranial aneurysms. World Neurosurg 80:845–852
Scholtes F, Henroteaux A, Otto B, Martin D (2015) Head trauma and distal anterior cerebral artery aneurysm: potential role of an adhesion to the falx. J Neurol Surg A Cent Eur Neurosurg 76:72–75
Senegor (1991) Traumatic pericallosal aneurysm in a patient with no major trauma. Case report. J Neurosurg 75:475–477
Shih TY, Kuo YL (2002) Development of intracranial complications following transoral stab wounds in children. Report of two cases. Pediatr Neurosurg 37:35–37
Sim SY, Shin YS, Yoon SH (2008) Endovascular internal trapping of traumatic pericallosal pseudoaneurysm with hydrogel-coated self-expandable coil in a child: a case report. Surg Neurol 69:418–422
Sui M, Mei Q, Sun K (2015) Surgical treatment achieves better outcome in severe traumatic pericallosal aneurysm: case report and literature review. Int J Clin Exp 8:1598–1603
Tubbs RS, Acakpo-Satchivi L, Blount JP, Oakes WJ, Wellons JC (2006) Pericallosal artery pseudoaneurysm secondary to endoscopic-assisted ventriculoperitoneal shunt placement. Case report. J Neurosurg 105:140–142
Türe U, Yaşargil MG, Krisht AF (1996) The arteries of the corpus callosum: a microsurgical anatomic study. Neurosurgery. 39:1075–1084
Van Rooij WJ, Van Rooij SB (2013) Endovascular treatment of traumatic pericallosal artery aneurysms. A case report. Interv Neuroradiol 19:56–59
Yamanaka K, Ishihara M, Nakajima S, Yamasaki M, Yoshimine T (2011) Coil embolization of a traumatic intracranial aneurysm of the distal part of the azygos anterior cerebral artery followed up for 4 years. Neurol Med Chir 51:572–575
Yang TC, Lo YL, Huang YC, Yang ST (2007) Traumatic anterior cerebral artery aneurysm following blunt craniofacial trauma. Eur Neurol 58:239–245
Yuen CM, Kuo YL, Ho JT, Liao JJ (2007) Rapid regrowth of a successfully coiled traumatic pericallosal aneurysm. J Clin Neurosci 14:1215–1219
Acknowledgements
We would like to acknowledge the help of all the staff involved in this study taking part in the medical record collection and review.
Funding
This study was supported by a grant from the National Natural Science Foundation of China No.81671154 to Dr. He.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This study was approved by the institutional review board and ethics committee of Tongji Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, HuBei province, China. And written informed consent was accepted by all the patients or their guardians.
Consent for publication
Written informed consent was obtained from the patient for publication of this report.
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Vascular Neurosurgery - Aneurysm
The original version of this article was revised. The name of Dongsheng Guo was incorrectly captured and is now corrected.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
He, Y., Wang, L., Ou, Y. et al. Surgical treatment of traumatic distal anterior cerebral artery aneurysm: a report of nine cases from a single centre. Acta Neurochir 162, 523–529 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-019-04121-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-019-04121-x