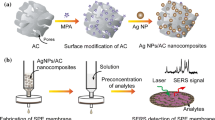
Abstract
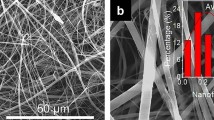
A sepiolite/chitosan/silver nanoparticles (Sep/CTs/AgNPs) membrane substrate has been developed for the fast separation, enrichment, and surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) determination of sulfamethoxazole all-in-one. The Sep/CTs/AgNPs membrane substrate possessed the ability of rapid separation and enrichment to simplify the process for pretreatment and improve the efficiency of analysis. The grown AgNPs can provide abundant hot spots and plasmonic areas to amplify the Raman signals of target molecules effectively. The membrane substrate exhibited good stability with relative standard deviations of 5.8% and 7.1% to same batch and different batches membrane substrate, respectively, by detecting sulfamethoxazole. The SERS method based on Sep/CTs/AgNPs membrane substrate was used for the determination of sulfamethoxazole with a linear range of 0.05–2.0 mg/L, and the limit of detection was 0.020 mg/L. The established SERS method was finally applied to the quantification of sulfamethoxazole in animal-derived food samples. Sulfamethoxazole was actually found in crucian sample with 12.4 μg/kg, and the result was confirmed by a high-performance liquid chromatography method with relative error of 5.3%. The whole process of analysis can be finished within 25 min with recoveries of 89.3–102.2%. The SERS method based on Sep/CTs/AgNPs membrane substrate provided an integrated strategy for rapid and accurate SERS analysis in food safety issues.
Graphical abstract








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wu J, Ma H, Bu X, Ma C, Zhu L, Hao B, Zhao B, Tian Y (2019) SERS determination of the antihypertensive drugs prazosin and losartan by using silver nanoparticles coated with β-cyclodextrin. Microchim Acta 186:801. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3946-z
Xia L, Yang J, Su R, Zhou W, Zhang Y, Zhong Y, Huang S, Chen Y, Li G (2020) Recent progress in fast sample preparation techniques. Anal Chem 92:34–48. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.9b04735
Ding Y, Cheng Y, Hao B, Zhu L, Zhang N, Zhao B, Tian Y (2021) Metal-organic framework modified by silver nanoparticles for SERS-based determination of sildenafil and pioglitazone hydrochloride. Microchim Acta 188:351. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-021-05008-4
Chen Z, Li G, Zhang Z (2017) Miniaturized thermal-assisted purge-and-trap technique coupling with surface-enhanced Raman scattering for trace analysis of complex samples. Anal Chem 89:9593–9600. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.7b02912
Zhang H, Lai H, Wu X, Li G, Hu Y (2020) CoFe2O4@HNTs/AuNPs substrate for rapid magnetic solid phase extraction and efficient SERS detection of complex samples all-in-one. Anal Chem 92:4607–4613. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.0c00144
Park SG, Mun CW, Lee MK, Jeon TY, Shim HS, Lee YJ, Kwon JD, Kim CS, Kim DH (2015) 3D hybrid plasmonic nanomaterials for highly efficient optical absorbers and sensors. Adv Mater 27:4290–4295. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201501587
Qu L-L, Liu Y-Y, Liu M-K, Yang G-H, Li D-W, Li H-T (2016) Highly reproducible AgNPs/CNT-intercalated GO membranes for enrichment and SERS detection of Antibiotics. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 8:28180–28186. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.6b08790
Lin S, Lin X, Han S, Liu Y, Hasi W, Wang L (2020) Flexible fabrication of a paper-fluidic SERS sensor coated with a monolayer of core-shell nanospheres for reliable quantitative SERS measurements. Anal Chim Acta 1108:167–176. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2020.02.034
Lei H, Hu Y, Li G (2017) A dual-functional membrane for bisphenol A enrichment and resonance amplification by surface-enhanced Raman scattering. Chinese Chem Let 29:509–512. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cclet.2017.08.012
Yu Z, Huang L, Zhang Z, Li G (2021) Simultaneous and accurate quantification of multiple antibiotics in aquatic samples by surface-enhanced Raman scattering using a Ti3C2Tx/DNA/Ag membrane substrate. Anal Chem 93:13072–13079. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.1c03019
Fu J, Lai H, Zhang Z, Li G (2021) UiO-66 metal-organic frameworks/gold nanoparticles based substrates for SERS analysis of food samples. Anal Chim Acta 1161:338464. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2021.338464
Falco G, Giulieri F, Volle N, Pagnotta S, Sbirrazzuoli N, Disdier EP, Mija A (2019) Self-organization of sepiolite fibbers in a biobased thermoset. Compos Sci Technol 171:226–233. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compscitech.2018.12.025
Yuan M, Gao G, Hu X, Luo X, Huang Y, Jin B, Liang Z (2018) Premodified sepiolite functionalized with triethylenetetramine as an effective and inexpensive adsorbent for CO2 Capture. Ind Eng Chem Res 57:6189–6200. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.iecr.8b00348
Ma Y, Wu X, Zhang G (2017) Core-shell Ag@Pt nanoparticles supported on sepiolite nanofibers for the catalytic reduction of nitrophenols in water: enhanced catalytic performance and DFT study. Appl Catal B-environ 205:262–270. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2016.12.025
Liang X, Xu Y, Sun G, Wang L, Sun Y, Sun Y. Qin X (2011) Preparation and characterization of mercapto functionalized sepiolite and their application for sorption of lead and cadmium. Chem Eng J 174:436-444. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2011.08.060
Moreira MA, Ciuffi KJ, Rives V, Vicente MA, Trujillano R, Gil A, Korili SA, Faria EH (2017) Effect of chemical modification of palygorskite and sepiolite by 3-aminopropyltriethoxisilane on adsorption of cationic and anionic dyes. Appl Clay Sci 135:394–404. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2016.10.022
Li D, Gao X, Huang X, Liu P, Xiong W, Wu S, Hao F, Luo H (2020) Preparation of organic-inorganic chitosan@silver/sepiolite composites with high synergistic antibacterial activity and stability. Carbohyd Polym 249:116858. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.116858
Liu L, Chen H, Shiko E, Fan X, Zhou Y, Zhang G, Luo X, Hu X (2018) Low-cost DETA impregnation of acid-activated sepiolite for CO2 capture. Chem Eng J 353:940–948. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2018.07.086
Yu J, He W, Liu B (2020) Adsorption of acid orange II with two step modified sepiolite: optimization, adsorption performance, kinetics, thermodynamics and regeneration. Int J Environ Res Public Health 17:1732. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17051732
Ruiz-Hitzky E, Madalena C, Sobral M, Gómez-Avilés A, Nunes C, Ruiz-García C, Ferreira P, Aranda P (2016) Clay-graphene nanoplatelets functional conducting composites. Adv Funct Mater 26:7394–7405. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.201603103
Gonzalez del Campo MM, Darder M, Aranda P, Akkari M, Huttel Y, Mayoral A, Bettini J, Ruiz-Hitzky E (2018) Functional hybrid nanopaper by assembling nanofibers of cellulose and sepiolite. Adv Funct Mater 28:1703048. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.201703048
Abbasian M, Jaymand M, Niroomand P, Farnoudian-Habibi A, Karaj-Abad SG (2017) Grafting of aniline derivatives onto chitosan and their applications for removal of reactive dyes from industrial effluents. Int J Biol Macromol 95:393–403. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2016.11.075
Liu K, Chen L, Huang L, Lai Y (2016) Evaluation of ethylenediamine-modified nanofibrillated cellulose/chitosan composites on adsorption of cationic and anionic dyes from aqueous solution. Carbohydr Polym 151:1115–1119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2016.06.071
Hu X, Feng X, Fei M, Tian M, Zhang R, Zhou Y, Liu Y, Zeng Z (2021) Preparation of acid Red73 adsorbed on chitosan-modified sepiolite with SiO2 coating as a highly stable hybrid pigment. Dyes Pigments 185:108938. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dyepig.2020.108938
Olshansky Y, Masaphy S, A. Root R, Rytwo G, (2018) Immobilization of Rhus vernicifera laccase on sepiolite; effect of chitosan and copper modification on laccase adsorption and activity. Appl Clay Sci 152:143–147. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2017.11.006
Cheng G, Li X, Li X, Chen J, Liu Y, Zhao G, Zhu G (2022) Surface imprinted polymer on a metal-organic framework for rapid and highly selective adsorption of sulfamethoxazole in environmental samples. J Hazard Mater 423:127087. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.127087
Shahriman MS, Mohamad S, Zain NNM, Alias Y, Chandrasekaram K, Raoov M (2021) Paper-based polymeric ionic liquid for thin film micro extraction of sulfonamides in environmental water samples prior to HPLC-DAD analysis. Microchem J 171:106798. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2021.106798
Jansomboon W, Boontanon SK, Boontanon N, Polprasert C (2016) Monitoring and determination of sulfonamide antibiotics (sulfamethoxydiazine, sulfamethazine, sulfamethoxazole and sulfadiazine) in imported pwangasius catfish products in thailand using liquid chromatography coupled with tandem mass spectrometry. Food Chem 212:635–640. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2016.06.026
Patze S, Huebner U, Liebold F, Weber K, Cialla-May D, Popp J (2017) SERS as an analytical tool in environmental science: the detection of sulfamethoxazole in the nanomolar range by applying a microfluidic cartridge setup. Anal Chim Acta 949:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2016.10.009
Markina NE, Markin AV, Weber K, Popp J, Cialla-May D (2020) Liquid-liquid extraction-assisted SERS-based determination of sulfamethoxazole in spiked human urine. Anal Chim Acta 1109:61–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2020.02.067
Rehan M, El-Naggar ME, Mashaly HM, Wilken R (2018) Nanocomposites based on chitosan/silver/clay for durable multi-functional properties of cotton fabrics. Carbohyd Polym 182:29–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2017.11.007
Yu Y, Ji J, Li K, Huang H, P. Shrestha R, Kim Oanh NT, Winijkul E, Deng J, (2020) Activated carbon supported MnO nanoparticles for efficient ozone decomposition at room temperature. Catal Today 355:573–579. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cattod.2019.05.063
Hallock AJ, Redmond PL, Brus LE (2005) Optical forces between metallic particles. Proc Natl Acad Sci 102:1280–1284. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0408604101
Vovusha H, Sanyal S, Sanyal B (2013) Interaction of nucleobases and aromatic amino acids with graphene oxide and graphene flakes. J Phys Chem Lett 4:3710–3718. https://doi.org/10.1021/jz401929h
Peng Y, Cai P, Yang L, Liu Y, Zhu L, Zhang Q, Liu J, Huang Z, Yang Y (2020) Theoretical and experimental studies of Ti3C2 MXene for surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy-based sensing. ACS Omega 5:26486–26496. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.0c03009
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (No. 2019YFC1606101), the Research and Development Plan for Key Areas of Food Safety in Guangdong Province of China (No. 2019B020211001), and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 21976213 and 22076223), and the State Key Program of National Natural Science of China (No.22134007), respectively.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, W., Chen, Y., Xia, L. et al. Flexible membrane composite based on sepiolite/chitosan/(silver nanoparticles) for enrichment and surface-enhanced Raman scattering determination of sulfamethoxazole in animal-derived food. Microchim Acta 189, 199 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-022-05265-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-022-05265-x