Abstract
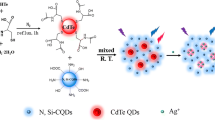
A ratiometric fluorescent nanoprobe is described for the detection of H2O2. It is based on the use of a mixture of green-emitting CdTe quantum dots (GQDs) and red-emitting CdTe QDs (RQDs). The two kinds of QDs have different size and different fluorescence response towards H2O2. The ratio of the emission intensities at 606 and 510 nm (under 365 nm photoexcitation) can be used as the analytical information. Even without any chemical modification of the surface of the QDs, the probe display high sensitivity and selectivity for H2O2. The fluorescence of small QDs is more effectively quenched by H2O2. Stern-Volmer analysis showed both static and dynamic quenching to occur. The probe works well in the 10~125 μM H2O2 concentration range and has a 0.3 μM detection limit (3σ/slope).

Schematic presentation of the ratiometric fluorescent nanoprobe composed of green-emitting and red-emitting CdTe QDs. λ, I, and k are the emission wavelength, emission intensity, and quenching/enhancement coefficient, respectively. The subscript 0 and 1 present the green-emitting and red-emitting CdTe QDs, respectively.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Huang X, Song J, Yung BC, Huang X, Xiong Y, Chen X (2018) Ratiometric optical nanoprobes enable accurate molecular detection and imaging. Chem Soc Rev 47:2873–2920
Zu F, Yan F, Bai Z, Xu J, Wang Y, Huang Y, Zhou X (2017) The quenching of the fluorescence of carbon dots: a review on mechanisms and applications. Microchim Acta 184:1899–1914
Ma N, Sargent EH, Kelley SO (2009) One-step DNA programmed growth of luminescent and biofunctionalized nanocrystals. Nat Nanotechnol 4:121–125
He H, Feng M, Hu J, Chen CX, Wang JQ, Wang XJ, Xu H, Lu JR (2012) Designed short RGD peptides for one-pot aqueous synthesis of integrin-binding CdTe and CdZnTe quantum dots. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 4:6362–6370
Wang Y, Yan XP (2013) Fabrication of vascular endothelial growth factor antibody bioconjugated utrasmall near-infrared fluorescent Ag2S quantum dots for targeted cancer imaging in vivo. Chem Commun 49:3324–3326
Dan L, Wang HF (2013) Mn-doped ZnS quantum dot imbedded two-fragment imprinting silica for enhanced room temperature phosphorescence probing of domoic acid. Anal Chem 85:4844–4848
Zrazhevskiy P, Sena M, Gao XH (2010) Designing multifunctional quantum dots for bioimaging, detection, and drug delivery. Chem Soc Rev 39:4326–4354
Karakoti AS, Shukla R, Shanker R, Singh S (2015) Surface functionalization of quantum dots for biological applications. Adv Colloid Interf Sci 215:28–45
Jiao H, Zhang L, Liang Z, Peng G, Lin H (2014) Size-controlled sensitivity and selectivity for the fluorometric detection of Ag+ by homocysteine capped CdTe quantum dots. Microchim Acta 181:1393–1399
Xia YS, Cao C, Zhu CQ (2008) Two distinct photoluminescence responses of CdTe quantum dots to Ag (I). J Lumin 128:166–172
Laferrière M, Galian RE, Maurel V, Scaiano JC (2006) Non-linear effects in the quenching of fluorescent quantum dots by nitroxyl free radicals. Chem Commun 3:257–259
Clarke SJ, Hollmann CA, Zhang Z, Suffern D, Bradforth SE, Dimitrijevic NM, Minarik WG, Nadeau JL (2006) Photophysics of dopamine-modified quantum dots and effects on biological systems. Nat Mater 5:409–417
Marco G, Mirella T, Enrica M, Pier GP (2007) Hydrogen peroxide: a metabolic by-product or a common mediator of ageing signals. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 8:722–728
Reth M (2002) Hydrogen peroxide as second messenger in lymphocyte activation. Nat Immunol 3:1129–1134
Shan C, Yang H, Song J, Han D, Ivaska A, Niu L (2009) Direct electrochemistry of glucose oxidase and biosensing for glucose based on graphene. Anal Chem 81:2378–2382
Finkel T, Holbrook NJ (2000) Oxidants, oxidative stress and the biology of ageing. Nature 408:239–247
Miller EW, Dickinson BC, Chang CJ (2010) Aquaporin-3 mediates hydrogen peroxide uptake to regulate downstream intracellular signaling. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 107:15681–15686
Long LH, Evans PJ, Halliwell B (1999) Hydrogen peroxide in human urine: implications for antioxidant defense and redox regulation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 262:605–609
Zhang K, Zhou H, Mei Q, Wang S, Guan G, Liu R, Zhang J, Zhang Z (2011) Instant visual detection of trinitrotoluene particulates on various surfaces by ratiometric fluorescence of dual-emission quantum dots hybrid. J Am Chem Soc 133:8424–8427
Yao J, Zhang K, Zhu H, Ma F, Sun M, Yu H, Sun J, Wang S (2013) Efficient ratiometric fluorescence probe based on dual-emission quantum dots hybrid for on-site determination of copper ions. Anal Chem 85:6461–6468
Jing L, Kershaw SV, Li Y, Huang X, Li Y, Rogach AL, Gao M (2016) Aqueous based semiconductor nanocrystals. Chem Rev 116:10623–10730
Wang Y, Si B, Lu S, Ma X, Liu E, Fan J, Li X, Hu X (2016) Effective improvement in optical properties of colloidal CdTe@ZnS quantum dots synthesized from aqueous solution. Nanotechnology 27:365707
Yu WW, Qu L, Guo W, Peng X (2003) Experimental determination of the extinction coefficient of CdTe, CdSe, and CdS nnanocrystals. Chem Mater 15:2854–2860
Zhang J, Zhang X, Zhang JY (2009) Size-dependent time-resolved photoluminescence of colloidal CdSe nanocrystals. J Phys Chem C 113:9512–9515
Masumoto Y, Sonobe K (1997) Size-dependent energy levels of CdTe quantum dots. Phys Rev B 56:9734–9737
Kloepfer JA, Bradforth S, Nadeau JL (2005) Photo-physical properties of biologically compatible CdSe quantum dot structures. J Phys Chem B 109:9996–10003
Yang D, Luo M, Di J, Tu Y, Yan J (2018) Gold nanocluster-based ratiometric fluorescent probes for hydrogen peroxide and enzymatic sensing of uric acid. Microchim Acta 185:305
Sharma AK, Pandey S, Sharma KH, Nerthigan Y, Khan MS, Hang DR, Wu HF (2018) Two dimensional a-MoO3-x nanoflakes as bare eye probe for hydrogen peroxide in biological fluids. Anal Chim Acta 1015:58–65
Xue B, Li K, Gu S, Zhang L, Lu J (2018) Ni foam-supported ZnO nanowires and Co3O4/NiCo2O4 double-shelled nanocages for efficient hydrogen peroxide detection. Sensors Actuat B 262:828–836
Ge J, Xing K, Geng X, Hu YL, Shen XP, Zhang L, Li ZH (2018) Human serum albumin templated MnO2 nanosheets are oxidase mimics for colorimetric determination of hydrogen peroxide and for enzymatic determination of glucose. Microchim Acta 185:559
Chang HC, Ho JA (2015) Gold nanocluster-assisted fluorescent detection for hydrogen peroxide and cholesterol based on the inner filter effect of gold nanoparticles. Anal Chem 87:10362–10367
Bas SZ, Cummins C, Borah D, Ozmen M, Morris MA (2018) Electrochemical sensing of hydrogen peroxide using block copolymer templated iron oxide nanopatterns. Anal Chem 90:1122–1128
Walekar LS, Hu P, Liao F, Guo X, Long M (2018) Turn-on fluorometric and colorimetric probe for hydrogen peroxide based on the in-situ formation of silver ions from a composite made from N-doped carbon quantum dots and silver nanoparticles. Microchim Acta 185:31
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 21476183).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The author(s) declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 1075 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Y., Yang, M., Ren, Y. et al. Ratiometric determination of hydrogen peroxide based on the size-dependent green and red fluorescence of CdTe quantum dots capped with 3-mercaptopropionic acid. Microchim Acta 186, 277 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3390-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3390-0