Abstract
A colorimetric method is described for the sensitive detection of heparin (Hep). It is based on the finding that Hep can effectively inhibit the oxidase mimicking activity of cerium oxide nanoparticles (nanoceria). In the presence of Hep, the catalytic activity of nanoceria toward the oxidation of the chromogenic substrate 3,3′,5,5′-tetramethylbenzidine by oxygen is strongly decreased. The inhibition mechanism is attributed to the fact that Hep is adsorbed on the surface of the nanoceria. Under optimal condition, the absorbance (measured at 652 nm) decreases with increasing Hep concentrations in the range from 30 to 700 nM. The detection limit is 20 nM. The method was applied to the determination of Hep in medical injection sample and serum sample with satisfactory results.

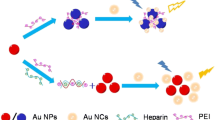
Schematic presentation of the inhibition of oxidase-like activity of nanoceria by heparin. This allows the sensitive detection of heparin in medical injection sample and serum sample with satisfactory results.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bromfield SM, Wilde E, Smith DK (2013) Hep sensing and binding - taking supramolecular chemistry towards clinical applications. Chem Soc Rev 42:9184–9195
Bergamaschini L, Rossi E, Vergani C, De Simoni MG (2009) Alzheimer's disease: another target for Hep therapy. Sci World J 9:891–908
Crowther MA, Warkentin TE (2008) Bleeding risk and the management of bleeding complications in patients undergoing anticoagulant therapy: focus on new anticoagulant agents. Blood 111:4871–4879
Murray DJ, Brosnahan WJ, Pennell B, Kapalanski D, Weiler JM, Olson J (1997) Hep detection by the activated coagulation time: a comparison of the sensitivity of coagulation tests and Hep assays. J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth 11:24–28
Thiangthum S, Heyden YV, Buchberger W, Viaene J, Prutthiwanasan B, Suntornsuk L (2014) Development and validation of an ion-exchange chromatography method for Hep and its impurities in Hep products. J Sep Sci 37:3195–3204
Sanderson P, Stickney M, Leach FE, Xia QW, Yu YL, Zhang FM, Linhardt R, Amster IJ (2018) Hep/heparan sulfate analysis by covalently modified reverse polarity capillary zone electrophoresis-mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A 1545:75–83
Crespo GA, Afshar MG, Bakker E (2012) Reversible sensing of the anticoagulant Hep with protamine permselective membranes. Angew Chem Int Ed 51:12575–12578
Cheng Q, He Y, Ge Y, Zhou J, Song G (2018) Ultrasensitive detection of Hep by exploiting the silver nanoparticle-enhanced fluorescence of graphitic carbon nitride (g-C3N4) quantum dots. Microchim Acta 185:332
Wang R, Wang X, Sun Y (2017) Aminophenol-based carbon dots with dual wavelength fluorescence emission for determination of Hep. Microchim Acta 184:187–193
Huang J, Li F, Guo R, Chen Y, Wang Z, Zhao C, Zheng Y, Weng S, Lin X (2018) A signal-on ratiometric fluorometric Hep assay based on the direct interaction between amino-modified carbon dots and DNA. Microchim Acta 185:260
Ding YB, Shi LL, Wei H (2015) A "turn on" fluorescent probe for Hep and its oversulfated chondroitin sulfate contaminant. Chem Sci 6:6361–6366
Wang X, Hu Y, Wei H (2016) Nanozymes in bionanotechnology: from sensing to therapeutics and beyond. Inorg Chem Front 3:41–60
Wei H, Wang E (2013) Nanomaterials with enzyme-like characteristics (nanozymes): next-generation artificial enzymes. Chem Soc Rev 42:6060–6093
Nasir M, Nawaz M, Latif U, Yaqub M, Hayat A, Rahim A (2017) An overview on enzyme-mimicking nanomaterials for use in electrochemical and optical assays. Microchim Acta 184:323–342
Liu B, Liu J (2017) Surface modification of nanozymes. Nano Res 10:1125–1148
Gao L, Zhuang J, Nie L, Zhang J, Zhang Y, Gu N, Wang T, Feng J, Yang D, Perrett S, Yan X (2007) Intrinsic peroxidase-like activity of ferromagnetic nanoparticles. Nat Nanotechnol 2:577–583
Lin Y, Ren J, Qu X (2014) Catalytically active nanomaterials: a promising candidate for artificial enzymes. Acc Chem Res 47:1097–1105
Zhang Z, Zhang X, Liu B, Liu J (2017) Molecular imprinting on inorganic nanozymes for hundred-fold enzyme specificity. J Am Chem Soc 139:5412–5419
Hu L, Liao H, Feng L, Wang M, Fu W (2018) Accelerating the peroxidase-like activity of gold nanoclusters at neutral pH for colorimetric detection of Hep and Hepase activity. Anal Chem 90:6247–6252
Liao H, Liu G, Liu Y, Li R, Fu W, Hu L (2017) Aggregation-induced accelerating peroxidase-like activity of gold nanoclusters and their applications for colorimetric Pb2+ detection. Chem Commun 53:10160–10163
Liao H, Hu L, Zhang Y, Yu X, Liu Y, Li R (2018) A highly selective colorimetric sulfide assay based on the inhibition of the peroxidase-like activity of copper nanoclusters. Microchim Acta 185:143
Wang S, Cazelles R, Liao W, Vazquez-Gonzalez M, Zoabi A, Abu-Reziq R, Willner I (2017) Mimicking horseradish peroxidase and NADH peroxidase by heterogeneous Cu2+-modified graphene oxide nanoparticles. Nano Lett 17:2043–2048
Wang X, Qin L, Zhou M, Lou Z, Wei H (2018) Nanozyme sensor arrays for detecting versatile Analytes from small molecules to proteins and cells. Anal Chem 90:11696–11702
Wu J, Li S, Wei H (2018) Integrated nanozymes: facile preparation and biomedical applications. Chem Commun 54:6520–6530
Wang N, Duan J, Shi W, Zhai X, Guan F, Yang L, Hou B (2018) A 3-dimensional C/CeO2 hollow nanostructure framework as a peroxidase mimetic, and its application to the colorimetric determination of hydrogen peroxide. Microchim Acta 185:417
Wang C, Tang G, Tan H (2018) Colorimetric determination of mercury(II) via the inhibition by ssDNA of the oxidase-like activity of a mixed valence state cerium-based metal-organic framework. Microchim Acta 185:475
Cheng H, Lin S, Muhammad F, Lin Y, Wei H (2016) Rationally modulate the oxidase-like activity of nanoceria for self-regulated bioassays. ACS Sens 1:1336–1343
Liu B, Huang Z, Liu J (2016) Boosting the oxidase mimicking activity of nanoceria by fluoride capping: rivaling protein enzymes and ultrasensitive F− detection. Nanoscale 8:13562–13567
Asati A, Santra S, Kaittanis C, Nath S, Perez J (2009) Oxidase-like activity of polymer-coated cerium oxide nanoparticles. Angew Chem Int Ed 48:2308–2312
Kim M, Park K, Park H (2014) Ultrafast colorimetric detection of nucleic acids based on the inhibition of the oxidase activity of cerium oxide nanoparticles. Chem Commun 50:9577–9580
Cao G, Jiang X, Zhang H, Croley T, Yin J (2017) Mimicking horseradish peroxidase and oxidase using ruthenium nanomaterials. RSC Adv 7:52210–52217
Shen X, Liu W, Gao X, Lu Z, Wu X, Gao X (2015) Mechanisms of oxidase and superoxide dismutation-like activities of gold, silver, platinum, and palladium, and their alloys: a general way to the activation of molecular oxygen. J Am Chem Soc 137:15882–15891
Pautler R, Kelly E, Huang P, Cao J, Liu B, Liu J (2013) Attaching DNA to nanoceria: regulating oxidase activity and fluorescence quenching. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 5:6820–6825
Montini T, Melchionna M, Monai M, Fornasiero P (2016) Fundamentals and catalytic applications of CeO2-based materials. Chem Rev 116:5987–6041
Li J, Cheng M, Li M (2017) A luminescent and colorimetric probe based on the functionalization of gold nanoparticles by ruthenium(ii) complexes for Hep detection. Analyst 142:3733–3739
You J, Liu Y, Lu C, Tseng W, Yu C (2016) Colorimetric assay of Hep in plasma based on the inhibition of oxidase-like activity of citrate-capped platinum nanoparticles. Biosens Bioelectron 92:442–448
Qu F, Liu Y, Lao H, Wang Y, You J (2017) Colorimetric detection of Hep with high sensitivity based on the aggregation of gold nanoparticles induced by polymer nanoparticles. New J Chem 41:10592–10597
Chen Z, Wang Z, Chen X, Xu H, Liu J (2013) Chitosan-capped gold nanoparticles for selective and colorimetric sensing of Hep. J Nanopart Res 15:1930–1939
Cho Y, Ahn K (2013) Molecular interactions between charged macromolecules: colorimetric detection and quantification of Hep with a polydiacetylene liposome. J Mater Chem B 1:1182–1189
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC, 21605012 and 21802012), Chongqing Research Program of Basic Research and Frontier Technology (No. cstc2016jcyjA0432), Scientific and Technological Research Program of Chongqing Municipal Education Commission (No. KJ1600328), and Chongqing Undergraduate Training Program for Innovation and Entrepreneurship (No. 201810637022).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 1197 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liao, H., Liu, Y., Chen, M. et al. A colorimetric heparin assay based on the inhibition of the oxidase mimicking activity of cerium oxide nanoparticles. Microchim Acta 186, 274 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3382-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3382-0