Abstract
Purpose
This study aimed to assess whether the perioperative use of gabapentin was associated with decreased opioid use.
Methods
A meta-analysis was performed using PubMed, Embase, Scopus, and Cochrane Library. The randomized clinical trials included were focused on patients with adolescent idiopathic scoliosis who underwent posterior fusion surgery and were treated with gabapentin versus placebo medicine. The primary outcomes were opioid consumption at 24, 48, 72, and 96 h; time to introduction of oral medication, length of hospital stay, and period of urinary catheterization were also recorded. Data were combined using the Review Manager 5.4 software.
Results
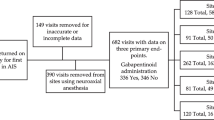
Four randomized clinical trials with a pool of 196 adolescent patients (mean age: 14.8 ± 2.0 years) were included. At 24 and 48 h after surgery, opioid consumption was significantly lower in the gabapentin group: (standardized mean difference [SMD]: -0.50; 95% confidence interval [CI] − 0.79 to − 0.22) and (SMD: − 0.59; 95% CI − 0.88 to − 0.30), respectively. At 72 and 96 h, there were no significant differences between studies: (SMD: − 0.19; 95% CI − 0.52 to 0.13) and (SMD: 0.12; 95% CI − 0.25 to 0.50), respectively. Regarding the administration type, there were significant differences in favor of the 15 mg/kg subgroup with 600 mg at 48 h (SMD: − 0.69; 95% CI − 1.08 to − 0.30). There were no significant differences concerning the time to introduction of oral medication (MD: − 0.08; 95% CI − 0.39 to 0.23), hospitalization time (MD: − 0.12; 95% CI − 0.40 to 0.16), or period of urinary catheterization (SMD: − 0.27; 95% CI − 0.58 to 0.05).
Conclusions
Gabapentin decreased opioid consumption during the first 48 h. Doses of 15 mg/kg showed superiority in reducing opioid consumption in the first 48 h.
Level of evidence I
Diagnostic: individual cross-sectional studies with consistently applied reference standard and blinding.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lee CS, Merchant S, Chidambaran V (2020) Postoperative pain management in pediatric spinal fusion surgery for idiopathic scoliosis. Paediatr Drugs 22(6):575–601. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40272-020-00423-1
Théroux J, Le May S, Fortin C et al (2015) Prevalence and management of back pain in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis patients: a retrospective study. Pain Res Manag 20(3):153–157. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/674354
Spinal Deformity Study Group, Landman Z, Oswald T, Sanders J et al (2011) Prevalence and predictors of pain in surgical treatment of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 36:825–829
Niraj G, Rowbotham DJ (2011) Persistent postoperative pain: where are we now? J Anaesth 107(1):25–29. https://doi.org/10.1093/bja/aer116
Danielsson AJ, Nachemson AL (2003) Back pain and function 23 years after fusion for adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: a case-control study-part II. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 28(18):E373–E383. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.BRS.0000084267.41183.75
Zhang Y, Shao G, Zhang W et al (2013) Gabapentin inhibits central sensitization during migraine. Neural Regen Res 8(32):3003–3012. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1673-5374.2013.32.003
Akeda K, Yamada J, Takegami N et al (2021) Evaluation of central sensitization inventory in patients undergoing elective spine surgery in a multicenter study. Glob Spine J. https://doi.org/10.1177/219256822110474
Akeda K, Takegami N, Yamada J et al (2022) Influence of central sensitization on surgical outcomes of patients with degenerative cervical myelopathy after posterior decompression surgery: a multicenter prospective study. Glob Spine J. https://doi.org/10.1177/21925682221139813
Mayer TG, Neblett R, Cohen H et al (2012) The development and psychometric validation of the central sensitization inventory. Pain Pract 12:276–285. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1533-2500.2011.00493.x
Routray SS, Pani N, Mishra D et al (2018) Comparison of pregabalin with gabapentin as preemptive analgesic in lumbar spine surgery. J Anaesthesiol Clin Pharmacol 34(2):232–236. https://doi.org/10.4103/joacp.JOACP_12_17
Liberati A, Altman DG, Tetzlaff J et al (2009) The PRISMA statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate health care interventions: explanation and elaboration. PLoS Med 6(7):e1000100. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmed.1000100
Guyatt GH, Thorlund K, Oxman AD et al (2013) GRADE guidelines: 13. Preparing summary of findings tables and evidence profiles-continuous outcomes. J Clin Epidemiol 66:173–183. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclinepi.2012.08.001
Anderson DE, Duletzke NT, Pedigo EB et al (2020) Multimodal pain control in adolescent posterior spinal fusion patients: a double-blind, randomized controlled trial to validate the effect of gabapentin on postoperative pain control, opioid use, and patient satisfaction. Spine Deform 8(2):177–185. https://doi.org/10.1007/s43390-020-00038-z
Li Y, Swallow J, Robbins C et al (2021) Gabapentin and intrathecal morphine combination therapy results in decreased oral narcotic use and more consistent pain scores after posterior spinal fusion for adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. J Orthop Surg Res 16(1):672. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13018-021-02525-z
Mayell A, Srinivasan I, Campbell F et al (2014) Analgesic effects of gabapentin after scoliosis surgery in children: a randomized controlled trial. Paediatr Anaesth 24(12):1239–1244. https://doi.org/10.1111/pan.12524
Rusy LM, Hainsworth KR, Nelson TJ et al (2010) Gabapentin use in pediatric spinal fusion patients: a randomized, double-blind, controlled trial. Anesth Analg 110(5):1393–1398. https://doi.org/10.1213/ANE.0b013e3181d41dc2
Shah SA, Guidry R, Kumar A et al (2020) Current trends in pediatric spine deformity surgery: multimodal pain management and rapid recovery. Glob Spine J 10(3):346–352. https://doi.org/10.1177/2192568219858308
Turan A, Karamanlioglu B, Memis D et al (2004) Analgesic effects of gabapentin after spinal surgery. Anesthesiology 100:935–938. https://doi.org/10.1097/00000542-200404000-00025
Choudhry DK, Brenn BR, Sacks K et al (2019) Evaluation of gabapentin and clonidine use in children following spinal fusion surgery for idiopathic scoliosis: a retrospective review. J Pediatr Orthop 39(9):e687–e693. https://doi.org/10.1097/BPO.0000000000000989
Ghai A, Gupta M, Hooda S et al (2011) A randomized controlled trial to compare pregabalin with gabapentin for postoperative pain in abdominal hysterectomy. Saudi J Anaesth 5:252–257. https://doi.org/10.4103/1658-354X.84097
Pandey CK, Priye S, Singh S et al (2004) Preemptive use of gabapentin significantly decreases postoperative pain and rescue analgesic requirements in laparoscopic cholecystectomy. Can J Anaesth 51:358–363. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03018240
Dirks J, Fredensborg BB, Christensen D et al (2002) A randomized study of the effects of single dose gabapentin versus placebo on postoperative pain and morphine consumption after mastectomy. Anesthesiology 97:560–564. https://doi.org/10.1097/00000542-200209000-00007
Javaherforooshzadeh F, Amirpour I, Janatmakan F et al (2018) Comparison of effects of melatonin and gabapentin on post operative anxiety and pain in lumbar spine surgery: a randomized clinical trial. Anesth Pain Med 8(3):e68763. https://doi.org/10.5812/aapm.68763
Savvides P, Gerdhem P, Grauers A et al (2020) Self-experienced trunk appearance in individuals with and without idiopathic scoliosis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 45(8):522–527. https://doi.org/10.1097/BRS.0000000000003308
Escrivá D, Moreno-Latorre E, Caplliure-Llopis J et al (2021) Relationship of overweight and obesity with body self-image dissatisfaction in urban mediterranean adolescents. Int J Environ Res Public Health 18(15):7770. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18157770
Lamontagne LL, Hepworth JT, Salisbury MH (2001) Anxiety and postoperative pain in children who undergo major orthopedic surgery. Appl Nurs Res 14(3):119–124. https://doi.org/10.1053/apnr.2001.24410
Giménez-Campos MS, Pimenta-Fermisson-Ramos P, Díaz-Cambronero JI et al (2022) A systematic review and meta-analysis of the effectiveness and adverse events of gabapentin and pregabalin for sciatica pain. Aten Primaria 54(1):102144. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aprim.2021.102144
Mao J, Chen L (2000) Gabapentin in pain management. Anesth Analg 91(3):680–687. https://doi.org/10.1213/00000539-200009000-00034
Glassman SD, Rose SM, Dimar JR et al (1998) The effect of postoperative nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug administration on spinal fusion. Spine 23:834–838. https://doi.org/10.1097/00007632-199804010-00020
Pedroso JL, Nakama GY, Carneiro Filho M et al (2012) Delirium, psychosis, and visual hallucinations induced by pregabalin. Arq Neuropsiquiatr 70(12):960–961. https://doi.org/10.1590/s0004-282x2012001200012
Mousailidis G, Papanna B, Salmon A et al (2020) Pregabalin induced visual hallucinations—a rare adverse reaction. BMC Pharmacol Toxicol 21(1):16. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40360-020-0395-6. (32111255)
Haas MF, Latchman J, Guastella AM et al (2022) Lucid dreams associated with pregabalin: implications for clinical practice. J Pain Palliat Care Pharmacother 36(3):194–199. https://doi.org/10.1080/15360288.2022.2081754
Bonnet U, Scherbaum N (2017) How addictive are gabapentin and pregabalin? A Syst Rev Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 27(12):1185–1215. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.euroneuro.2017.08.430
Funding
No funding was received.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no relevant financial or nonfinancial interests to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Bas, J.L., Bas, P., Bonilla, F. et al. Efficacy of perioperative gabapentin use in patients with idiopathic scoliosis undergoing fusion surgery: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur Spine J 32, 2521–2532 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-023-07764-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-023-07764-8