Abstract
Purpose
Degenerative spondylolisthesis (DS) is common degenerative spinal disease. Recent studies highlighted relationship between DS and high pelvic incidence (PI). Moreover, impact of spinopelvic alignment on clinical outcomes has been emphasized. We aimed at describing epidemiologic and sagittal spinopelvic parameters in patients with DS, comparing them with asymptomatic volunteers, and determining a classification of DS patients.
Methods
In this retrospective multicenter study of prospectively collected data, any adult patients treated for lumbar DS were included. Demographic data as well as radiographic parameters such as PI, pelvic tilt (PT), maximal lumbar lordosis (LLmax), lumbosacral lordosis, thoracic kyphosis, and C7tilt were recorded. DS patients were compared to 709 asymptomatic, age-matched volunteers. Cluster analyses were used to classify patients in homogenous groups.
Results
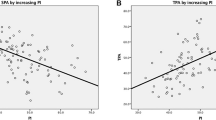
654 patients were included (72 % female, 67 years). DS patients had greater PI (58.8° vs. 53.2°, p < 0.001) and C7tilt (p < 0.001). LLmax and lumbosacral lordosis were significantly smaller in the DS group. Cluster analysis allowed for the identification of 2 groups of patients according to C7tilt—159 patients with anterior C7tilt and 495 with normal C7tilt. In each group, 3 subgroups were found with different PI and sagittal spinopelvic parameters.
Conclusion
Predominance of high PI and female gender was emphasized in DS population. Moreover, these findings highlighted the importance of sagittal alignment analysis in DS with 24 % of patients with anterior malalignment and in the remaining 76 % (normal C7Tilt), more than 50 % had pelvic retroversion. Consequently, DS sagittal malalignment should lead to specific surgical correction adapted to each subgroup of patients.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Benoist M (2003) Natural history of the aging spine. Eur Spine J 12(Suppl 2):S86–S89
Aono K, Kobayashi T, Jimbo S et al (2010) Radiographic analysis of newly developed degenerative spondylolisthesis in a mean twelve-year prospective study. Spine 35:887–891
Smorgick Y, Mirovsky Y, Fischgrund JS et al (2014) Radiographic predisposing factors for degenerative spondylolisthesis. Orthopedics 37:e260–e264
Liu H, Li S, Zheng Z et al (2014) Pelvic retroversion is the key protective mechanism of L4-5 degenerative spondylolisthesis. Eur Spine J. doi:10.1007/s00586-014-3395-7
Smorgick Y, Park DK, Baker KC et al (2013) Single- versus multilevel fusion for single-level degenerative spondylolisthesis and multilevel lumbar stenosis: four-year results of the spine patient outcomes research trial. Spine 38:797–805
Berlemann U, Jeszenszky DJ, Bühler DW, Harms J (1999) The role of lumbar lordosis, vertebral end-plate inclination, disc height, and facet orientation in degenerative spondylolisthesis. J Spinal Disord 12:68–73
Schuller S, Charles YP, Steib J-P (2011) Sagittal spinopelvic alignment and body mass index in patients with degenerative spondylolisthesis. Eur Spine J 20:713–719
Fujiwara A, Tamai K, An HS et al (2000) The relationship between disc degeneration, facet joint osteoarthritis, and stability of the degenerative lumbar spine. J Spinal Disord 13:444–450
Boden SD, Riew KD, Yamaguchi K et al (1996) Orientation of the lumbar facet joints: association with degenerative disc disease. J Bone Joint Surg Am 78:403–411
Matsunaga S, Sakou T, Morizono Y et al (1990) Natural history of degenerative spondylolisthesis. Pathogenesis and natural course of the slippage. Spine 15:1204–1210
Morel E, Ilharreborde B, Lenoir T et al (2005) Sagittal balance of the spine and degenerative spondylolisthesis. Rev Chir Orthop Reparatrice Appar Mot 91:615–626
Funao H, Tsuji T, Hosogane N et al (2012) Comparative study of spinopelvic sagittal alignment between patients with and without degenerative spondylolisthesis. Eur Spine J 21(11):2181–2187
Barrey C, Jund J, Perrin G, Roussouly P (2007) Spinopelvic alignment of patients with degenerative spondylolisthesis. Neurosurgery 61:981–986
Schwab FJ, Blondel B, Bess S et al (2013) Radiographical spinopelvic parameters and disability in the setting of adult spinal deformity: a prospective multicenter analysis. Spine 38:E803–E812
Roussouly P, Pinheiro-Franco JL (2011) Biomechanical analysis of the spino-pelvic organization and adaptation in pathology. Eur Spine J 20(Suppl 5):609–618
Barrey CC, Jund JJ, Noseda O, Roussouly P (2007) Sagittal balance of the pelvis-spine complex and lumbar degenerative diseases. A comparative study about 85 cases. Eur Spine J 16:1459–1467
Kim MK, Lee S-H, Kim E-S et al (2011) The impact of sagittal balance on clinical results after posterior interbody fusion for patients with degenerative spondylolisthesis: a Pilot study. BMC Musculoskelet Disord 12:69
Kumar MN, Jacquot F, Hall H (2001) Long-term follow-up of functional outcomes and radiographic changes at adjacent levels following lumbar spine fusion for degenerative disc disease. Eur Spine J 10:309–313
Schwab F, Farcy J, Bridwell K et al (2006) A clinical impact classification of scoliosis in the adult. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 31:2109–2114
Schwab FJ, Smith VA, Biserni M et al (2002) Adult scoliosis: a quantitative radiographic and clinical analysis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 27:387–392
Glassman SD, Hamill CL, Bridwell KH et al (2007) The impact of perioperative complications on clinical outcome in adult deformity surgery. Spine 32:2764–2770
Weiss HR (1995) Measurement of vertebral rotation: perdriolle versus Raimondi. Eur Spine J 4:34–38
Faro FD, Marks MC, Pawelek J, Newton PO (2004) Evaluation of a functional position for lateral radiograph acquisition in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Spine 29:2284–2289
Morvan G, Mathieu P, Vuillemin V et al (2011) Standardized way for imaging of the sagittal spinal balance. Eur Spine J 20(Suppl 5):602–608
Rillardon L, Levassor N, Guigui P et al (2003) Validation of a tool to measure pelvic and spinal parameters of sagittal balance. Rev Chir Orthop Reparatrice Appar Mot 89:218–227
Roussouly P, Gollogly S, Berthonnaud E, Dimnet J (2005) Classification of the normal variation in the sagittal alignment of the human lumbar spine and pelvis in the standing position. Spine 30:346–353
Duval-Beaupère G, Schmidt C, Cosson P (1992) A Barycentremetric study of the sagittal shape of spine and pelvis: the conditions required for an economic standing position. Ann Biomed Eng 20:451–462
Meyerding HW (1956) Spondylolisthesis; surgical fusion of lumbosacral portion of spinal column and interarticular facets; use of autogenous bone grafts for relief of disabling backache. J Int Coll Surg 26:566–591
Mac-Thiong J-M, Roussouly P, Berthonnaud E, Guigui P (2011) Age- and sex-related variations in sagittal sacropelvic morphology and balance in asymptomatic adults. Eur Spine J 20(Suppl 5):572–577
Mac-Thiong J-M, Roussouly P, Berthonnaud E, Guigui P (2010) Sagittal parameters of global spinal balance: normative values from a prospective cohort of seven hundred nine Caucasian asymptomatic adults. Spine 35:E1193–E1198
Legaye J, Duval-Beaupère G, Hecquet J, Marty C (1998) Pelvic incidence: a fundamental pelvic parameter for three-dimensional regulation of spinal sagittal curves. Eur Spine J 7:99–103
Schwab F, Ungar B, Blondel B et al (2012) Scoliosis Research Society-Schwab adult spinal deformity classification: a validation study. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 37:1077–1082
Kumar MN, Baklanov A, Chopin D (2001) Correlation between sagittal plane changes and adjacent segment degeneration following lumbar spine fusion. Eur Spine J 10:314–319
Hsu H-T, Yang SS, Chen TY (2013) The Correlation between Restoration of Lumbar Lordosis and Surgical Outcome in the Treatment of Low-grade Lumbar Degenerative Spondylolisthesis with Spinal Fusion. J Spinal Disord Tech 1–21 [Epub ahead of print]
Schwab F, Blondel B, Chay E et al (2013) The comprehensive anatomical spinal osteotomy classification. Neurosurgery 74:112–120
Barrey C, Roussouly P, Le Huec J-C et al (2013) Compensatory mechanisms contributing to keep the sagittal balance of the spine. Eur Spine J 22(Suppl 6):S834–S841
Smith JS, Klineberg E, Schwab F et al (2013) Change in Classification Grade by the SRS-Schwab Adult Spinal Deformity Classification Predicts Impact on Health-Related Quality of Life Measures: Prospective Analysis of Operative and Non-operative Treatment. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 38:1663–1671
Beckers LBJ (1991) The role of lordosis. Acta Orthop Belg 57:198–202
Acknowledgments
No grant support was received. IRB Approval was granted for this study at all participating sites.
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Consortia
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ferrero, E., Ould-Slimane, M., Gille, O. et al. Sagittal spinopelvic alignment in 654 degenerative spondylolisthesis. Eur Spine J 24, 1219–1227 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-015-3778-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-015-3778-4