Abstract
Purpose
To assess segmental angulation and mobility following implantation of the Charité artificial disc in combination with the posterior dynamic fixation device dynamic stabilization system (DSS) and the interspinous spacer Coflex at the L4–L5 segment, respectively.
Methods
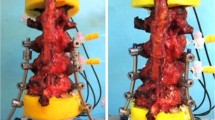
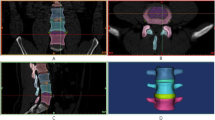
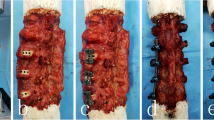
Six human L4–L5 specimens were loaded with pure moments of ±7.5 Nm in flexion/extension, lateral bending, and axial rotation in a custom-made spine tester. The testing protocol was as follows: (a) intact condition, (b) destabilization by resection of the anterior longitudinal ligament (ALL), (c) implantation of the Charité with retained posterior longitudinal ligament (PLL), (d) supplemental DSS implantation, (e) removal of DSS rods and PLL resection, (f) DSS rod re-implantation, (g) enlargement of rod length, and (h) removal of DSS and implantation of Coflex. Range of motion (ROM), neutral zone, and segmental angulation were determined.
Results
ALL resection did not influence significantly ROM. TDR increased lateral bending and axial rotation only after resection of the PLL, whereas flexion/extension remained unchanged. DSS limited all degrees of freedom prior to and after PLL resection. Rod length enlargement had no significant effect. Coflex limited significantly flexion/extension compared to the intact state and TDR, whereas lateral bending and axial rotation remained unchanged. TDR increased lordosis, whereas Coflex had a substantial kyphosing effect.
Conclusions
This study demonstrates that posterior dynamic stabilization in combination with TDR reduces flexion/extension ROM and segmental lordosis in a monosegmental biomechanical model.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cakir B, Richter M, Kafer W, Puhl W, Schmidt R (2005) The impact of total lumbar disc replacement on segmental and total lumbar lordosis. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon) 20(4):357–364
Rohlmann A, Zander T, Bergmann G (2005) Effect of total disc replacement with ProDisc on intersegmental rotation of the lumbar spine. Spine 30(7):738–743
Kafer W, Clessienne CB, Daxle M, Kocak T, Reichel H, Cakir B (2008) Posterior component impingement after lumbar total disc replacement: a radiographic analysis of 66 ProDisc-L prostheses in 56 patients. Spine 33(22):2444–2449
Hallab N, Link HD, McAfee PC (2003) Biomaterial optimization in total disc arthroplasty. Spine 28(20):139–152
Kurtz SM, Peloza J, Siskey R, Villarraga ML (2005) Analysis of a retrieved polyethylene total disc replacement component. Spine J 5(3):344–350
Kurtz SM, van Ooij A, Ross R, de Waal Malefijt J, Peloza J, Ciccarelli L, Villarraga ML (2007) Polyethylene wear and rim fracture in total disc arthroplasty. Spine J 7(1):12–21
van Ooij A, Kurtz SM, Stessels F, Noten H, van Rhijn L (2007) Polyethylene wear debris and long-term clinical failure of the Charite disc prosthesis: a study of 4 patients. Spine 32(2):223–229
van Ooij A, Oner FC, Verbout AJ (2003) Complications of artificial disc replacement: a report of 27 patients with the SB Charite disc. J Spinal Disord Tech 16(4):369–383
Punt IM, Visser VM, van Rhijn LW, Kurtz SM, Antonis J, Schurink GW, van Ooij A (2008) Complications and reoperations of the SB Charite lumbar disc prosthesis: experience in 75 patients. Eur Spine J 17(1):36–43
Siepe CJ, Mayer HM, Heinz-Leisenheimer M, Korge A (2007) Total lumbar disc replacement: different results for different levels. Spine 32(7):782–790
Siepe CJ, Korge A, Grochulla F, Mehren C, Mayer HM (2008) Analysis of post-operative pain patterns following total lumbar disc replacement: results from fluoroscopically guided spine infiltrations. Eur Spine J 17(1):44–56
Shim CS, Lee SH, Shin HD, Kang HS, Choi WC, Jung B, Choi G, Ahn Y, Lee S, Lee HY (2007) CHARITE versus ProDisc: a comparative study of a minimum 3-year follow-up. Spine 32(9):1012–1018
Goel VK, Grauer JN, Patel T, Biyani A, Sairyo K, Vishnubhotla S, Matyas A, Cowgill I, Shaw M, Long R, Dick D, Panjabi MM, Serhan H (2005) Effects of charite artificial disc on the implanted and adjacent spinal segments mechanics using a hybrid testing protocol. Spine 30(24):2755–2764
Wiseman CM, Lindsey DP, Fredrick AD, Yerby SA (2005) The effect of an interspinous process implant on facet loading during extension. Spine 30(8):903–907
Wilke HJ, Drumm J, Haussler K, Mack C, Steudel WI, Kettler A (2008) Biomechanical effect of different lumbar interspinous implants on flexibility and intradiscal pressure. Eur Spine J 17(8):1049–1056
Kettler A, Drumm J, Heuer F, Haeussler K, Mack C, Claes L, Wilke HJ (2008) Can a modified interspinous spacer prevent instability in axial rotation and lateral bending? A biomechanical in vitro study resulting in a new idea. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon) 23(2):242–247
Nockels RP (2005) Dynamic stabilization in the surgical management of painful lumbar spinal disorders. Spine 30(16 Suppl):S68–S72
Schmoelz W, Erhart S, Unger S, Disch AC (2012) Biomechanical evaluation of a posterior non-fusion instrumentation of the lumbar spine. Eur Spine J 21(5):939–945
Niosi CA, Zhu QA, Wilson DC, Keynan O, Wilson DR, Oxland TR (2006) Biomechanical characterization of the three-dimensional kinematic behaviour of the Dynesys dynamic stabilization system: an in vitro study. Eur Spine J 15(6):913–922
Schmoelz W, Huber JF, Nydegger T, Dipl I, Claes L, Wilke HJ (2003) Dynamic stabilization of the lumbar spine and its effects on adjacent segments: an in vitro experiment. J Spinal Disord Tech 16(4):418–423
Schmoelz W, Huber JF, Nydegger T, Claes L, Wilke HJ (2006) Influence of a dynamic stabilisation system on load bearing of a bridged disc: an in vitro study of intradiscal pressure. Eur Spine J 15(8):1276–1285
Beastall J, Karadimas E, Siddiqui M, Nicol M, Hughes J, Smith F, Wardlaw D (2007) The Dynesys lumbar spinal stabilization system: a preliminary report on positional magnetic resonance imaging findings. Spine 32(6):685–690
Link HD (2002) History, design and biomechanics of the LINK SB Charite artificial disc. Eur Spine J 11(Suppl 2):S98–S105
Wilke HJ, Heuer F, Schmidt H (2009) Prospective design delineation and subsequent in vitro evaluation of a new posterior dynamic stabilization system. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 34(3):255–261
Wilke HJ, Rohlmann F, Neidlinger-Wilke C, Werner K, Claes L, Kettler A (2006) Validity and interobserver agreement of a new radiographic grading system for intervertebral disc degeneration: part I. Lumbar spine. Eur Spine J 15(6):720–730
Wilke HJ, Claes L, Schmitt H, Wolf S (1994) A universal spine tester for in vitro experiments with muscle force simulation. Eur Spine J 3(2):91–97
Bland JM, Altman DG (1986) Statistical methods for assessing agreement between two methods of clinical measurement. Lancet 1(8476):307–310
Wilke HJ, Wenger K, Claes L (1998) Testing criteria for spinal implants: recommendations for the standardization of in vitro stability testing of spinal implants. Eur Spine J 7(2):148–154
Wilke HJ, Rohlmann A, Neller S, Schultheiss M, Bergmann G, Graichen F, Claes LE (2001) Is it possible to simulate physiologic loading conditions by applying pure moments? A comparison of in vivo and in vitro load components in an internal fixator. Spine 26(6):636–642
Cakir B, Richter M, Puhl W, Schmidt R (2006) Reliability of motion measurements after total disc replacement: the spike and the fin method. Eur Spine J 15(2):165–173
Mayer HM (2005) Total lumbar disc replacement. J Bone Joint Surg Br 87(8):1029–1037
Cunningham BW, Gordon JD, Dmitriev AE, Hu N, McAfee PC (2003) Biomechanical evaluation of total disc replacement arthroplasty: an in vitro human cadaveric model. Spine 28(20):S110–S117
Panjabi M, Henderson G, Abjornson C, Yue J (2007) Multidirectional testing of one- and two-level ProDisc-L versus simulated fusions. Spine 32(12):1311–1319
Panjabi M, Malcolmson G, Teng E, Tominaga Y, Henderson G, Serhan H (2007) Hybrid testing of lumbar CHARITE discs versus fusions. Spine 32(9):959–966 (discussion 967)
Wilke HJ, Schmidt H, Werner K, Schmolz W, Drumm J (2006) Biomechanical evaluation of a new total posterior-element replacement system. Spine 31(24):2790–2796 (discussion 2797)
Leivseth G, Braaten S, Frobin W, Brinckmann P (2006) Mobility of lumbar segments instrumented with a ProDisc II prosthesis: a two-year follow-up study. Spine 31(15):1726–1733
Jackson RP, McManus AC (1994) Radiographic analysis of sagittal plane alignment and balance in standing volunteers and patients with low back pain matched for age, sex, and size. A prospective controlled clinical study. Spine 19(14):1611–1618
Vialle R, Levassor N, Rillardon L, Templier A, Skalli W, Guigui P (2005) Radiographic analysis of the sagittal alignment and balance of the spine in asymptomatic subjects. J Bone Joint Surg Am 87(2):260–267
Dooris AP, Goel VK, Grosland NM, Gilbertson LG, Wilder DG (2001) Load-sharing between anterior and posterior elements in a lumbar motion segment implanted with an artificial disc. Spine 26(6):122–129
Zander T, Rohlmann A, Bergmann G (2004) Analysis of simulated single ligament transection on the mechanical behaviour of a lumbar functional spinal unit. Biomed Tech (Berl) 49(1–2):27–32
Hopf C, Heeckt H, Beske C (2004) Indikation, Biomechanik und Frühergebnisse des künstlichen Bandscheibenersatzes. Z Orthop Ihre Grenzgeb 142(2):153–158
McAfee PC, Cunningham BW, Hayes V, Sidiqi F, Dabbah M, Sefter JC, Hu N, Beatson H (2006) Biomechanical analysis of rotational motions after disc arthroplasty: implications for patients with adult deformities. Spine 31(19 Suppl):152–160
Cakir B, Richter M, Schmoelz W, Schmidt R, Reichel H, Wilke HJ (2012) Resect or not to resect: the role of posterior longitudinal ligament in lumbar total disc replacement. Eur Spine J 21(Suppl 5):S592–S598
Geisler FH (2006) The CHARITE artificial disc: design history, FDA IDE study results, and surgical technique. Clin Neurosurg 53:223–228
Gedet P, Haschtmann D, Thistlethwaite PA, Ferguson SJ (2009) Comparative biomechanical investigation of a modular dynamic lumbar stabilization system and the Dynesys system. Eur Spine J 18(10):1504–1511
Schulte TL, Hurschler C, Haversath M, Liljenqvist U, Bullmann V, Filler TJ, Osada N, Fallenberg EM, Hackenberg L (2008) The effect of dynamic, semi-rigid implants on the range of motion of lumbar motion segments after decompression. Eur Spine J 17(8):1057–1065
Legaye J (2005) Consequences defavorables sur l’equilibre sagittal du rachis du systeme de neutralisation dynamique. Rev Chir Orthop Reparatrice Appar Mot 91(6):542–550
Siddiqui M, Karadimas E, Nicol M, Smith FW, Wardlaw D (2006) Effects of X-STOP device on sagittal lumbar spine kinematics in spinal stenosis. J Spinal Disord Tech 19(5):328–333
Siddiqui M, Nicol M, Karadimas E, Smith F, Wardlaw D (2005) The positional magnetic resonance imaging changes in the lumbar spine following insertion of a novel interspinous process distraction device. Spine 30(23):2677–2682
Cakir B, Schmidt R, Huch K, Puhl W, Richter M (2004) Sagittales Alignement und segmentale Beweglichkeit nach endoprothetischer Versorgung lumbaler Bewegungssegmente. Z Orthop Ihre Grenzgeb 142(2):159–165
Wilke HJ, Schmidt R, Richter M, Schmoelz W, Reichel H, Cakir B (2012) The role of prosthesis design on segmental biomechanics: semi-constrained versus unconstrained prostheses and anterior versus posterior centre of rotation. Eur Spine J 21(Suppl 5):577–584
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Käfer, W., Cakir, B., Midderhoff, S. et al. Circumferential dynamic stabilization of the lumbar spine: a biomechanical analysis. Eur Spine J 23, 2330–2339 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-014-3286-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-014-3286-y