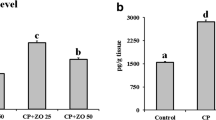
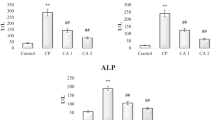
Abstract
Cisplatin (CP) as a potent chemotherapeutic agent is restricted due to its hepatotoxicity, nephrotoxicity, and multiple organ toxicity. The current study investigates the possible mechanisms responsible for the hepatorenal protective effects of ginger extract (GE) against cisplatin-induced hepatorenal toxicity in rats. Thirty-two male albino rats (240–250 g) were divided into four equal groups (n = 8) as follows: control group (single i.p. saline dose 7.5 ml/kg at the 15th day of the study), CP-treated group (7.5 mg/kg single i.p. injection of CP at the 15th day of the study), GE-treated group (500 mg/kg/ p.o daily for 20 days), and GE + CP-treated group (GE 500 mg/kg/day, p.o daily for 15 days prior to CP injection and 5 days after CP injection). At day 21st of the experiment, blood samples were collected, and serum was isolated for biochemical assessments. Then, rats were euthanized, and hepatic and renal tissues were collected for tissue biochemical parameters, histopathology, and immunohistochemistry evaluations. Cisplatin-injected rats showed marked alterations in the serum liver and kidney functions, oxidant/antioxidant biomarkers, pro-inflammatory cytokines; tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), interleukin-1β (IL-1β), and interleukin-6 (IL-6) and anti-inflammatory cytokine; interleukin-10 (IL-10). CP also induced overexpression of oxidative (INOS) and apoptotic (caspase-3) immunohistochemical markers in hepatic and renal tissues. Conversely, the combining administration of ginger extract before, with, and after CP treatment ameliorated the aforementioned biochemical, pathological, and immunohistochemical adverse effects induced by CP. In conclusion, ginger extract has protective effects against CP adverse effects, possibly via its antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anti-apoptotic properties.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdel-Daim MM, Aleya L, El-Bialy BE, Abushouk AI, Alkahtani S, Alarifi S, Alkahtane AA, AlBasher G, Ali D, Almeer RS, Al-Sultan NK, Alghamdi J, Alahmari A, Bungau SG (2019) The ameliorative effects of ceftriaxone and vitamin E against cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 26(15):15248–15254. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-04801-2
Abdel-Daim MM, Abdel-Rahman HG, Dessouki AA, El-Far AH, Khodeer DM, Bin-Jumah M, Alhader MS, Alkahtani S, Aleya L (2020) Impact of garlic (Allium sativum) oil on cisplatin-induced hepatorenal biochemical and histopathological alterations in rats. Sci Total Environ 710:136338. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.136338
Abuzinadah MF, Ahmad A (2020) Pharmacological studies on the efficacy of a thymoquinone-containing novel polyherbal formulation against cisplatin induced hepatorenal toxicity in rats. J Food Biochem 44(2):e13131. https://doi.org/10.1111/jfbc.13131
Ahmad B, Rehman MU, Amin I, Arif A, Rasool S, Bhat SA, Afzal I, Hussain I, Bilal S (2015) A review on pharmacological properties of zingerone (4-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)-2-butanone). Sci World J 2015:816364. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/816364
Aimbire F, Penna SC, Rodrigues M, Rodrigues KC, Lopes-Martins RA, Sertié JAA (2007) Effect of hydroalcoholic extract of Zingiber officinalis rhizomes on LPS-induced rat airway hyperreactivity and lung inflammation. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids 77(3–4):129–138. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plefa.2007.08.008
Al-Amin ZM, Thomson M, Al-Qattan KK, Peltonen-Shalaby R, Ali M (2006) Anti-diabetic and hypolipidaemic properties of ginger (Zingiber officinale) in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Brit J Nutr 96(4):660–666. https://doi.org/10.1079/bjn20061849
Ali DA, Abdeen AM, Ismail MF, Mostafa MA (2015) Histological, ultrastructural and immunohistochemical studies on the protective effect of ginger extract against cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity in male rats. Toxicol Ind Health 31(10):869–880. https://doi.org/10.1177/0748233713483198
Allen CT (1992) Hematoxylin and eosin. In: Prophet EB, Mills B, Arrington JB, Sobin LH (ed) Laboratory methods in histochemistry. Washington, DC: Armed Forced Institute of Pathology, American Registry of Pathology, p. 53
Al-Shathly MR, Ali SS, Ayuob NN (2020) Zingiber officinale preserves testicular structure and the expression of androgen receptors and proliferating cell nuclear antigen in diabetic rats. Andrologia 52:e13528. https://doi.org/10.1111/and.13528
Antunes GLM, Darin JD, Bianchi MD (2000) Protective effects of vitamin C against cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity and lipid peroxidation in adult rats: a dose-dependent study. Pharmacol Res 41(4):405–411. https://doi.org/10.1006/phrs.1999.0600
Ajith TA, Nivitha V, Usha S (2007) Zingiber officinale Roscoe alone and in combination with alpha-tocopherol protect the kidney against cisplatin-induced acute renal failure. Food Chem Toxicol 45(6):921–927. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2006.11.014
Babu D, Leclercq G, Goossens V, Remijsen Q, Vandenabeele P, Motterlini R, Lefebvre RA (2015) Antioxidant potential of CORM-A1 and resveratrol during TNF-alpha/cycloheximide-induced oxidative stress and apoptosis in murine intestinal epithelial MODE-K cells. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 288(2):161–178. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.taap.2015.07.007
Bancroft JD, Layton C (2013) The hematoxylins and eosin (chapter 10). In: Suvarna SK, Layton C, and Bancroft JD (2013) Bancroft’s Theory and Practice of Histological Techniques, 7th edn. UK: Churchill, Living Stone, Elsevier, Ebook (Online) ISBN: 978–0–7020–5032–9. Available from: https://books.google.com.eg/books. p 173–186
Beagloo IE, Valilu MR, Motiei M, Rahbar M, Hejazi A (2019) The antioxidant and hepatoprotective effect of alcoholic extract of ginger against the cisplatin induced oxidative stress in rats. Biomed J Sci Tech Res 19(2):14240–14245. https://doi.org/10.26717/BJSTR.2019.19.003283
Bevilacqua MP, Pober JS, Wheeler ME, Cotran RS, Gim-brone MA (1985) Interleukin 1 acts on cultured human vascular endothelium to increase the adhesion of poly morpho nuclear leukocytes, monocytes, and related leukocyte cell lines. J Clin Invest 76(5):2003–2011. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI112200
Caglayan C, Kandemir FM, Yıldırım S, Kucukler S, Kılınc MA, Saglam YS (2018) Zingerone ameliorates cisplatin-induced ovarian and uterine toxicity via suppression of sex hormone imbalances, oxidative stress, inflammation and apoptosis in female Wistar rats. Biomed Pharmacother 102:517–530. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2018.03.119
Dinarello CA (2009) Immunological and inflammatory functions of the interleukin 1 family. Annu Rev Immunol 27(519):550. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.immunol.021908.132612
Dkhil MA, Al-Quraishy S, Aref AM, Othman MS, El-Dieb KM, Moniem A (2013) The potential role of Azadirachta indica treatment on cisplatin-induced hepatotoxicity and oxidative stress in female rats. Oxid Med Cell Longev 741817. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/741817
Eldutar E, Kandemir FM, Kucukler S, Caglayan C (2017) Restorative effects of Chrysin pretreatment on oxidant–antioxidant status, inflammatory cytokine production, and apoptotic and autophagic markers in acute paracetamol-induced hepatotoxicity in rats: an experimental and biochemical study. J Biochem Mol Toxicol 31:e21960. https://doi.org/10.1002/jbt.21960
Elkomy A, Abdelhiee EY, Fadl SE, Emam MA, Gad F, Sallam A, Alarifi S, Abdel-Daim MM, Aboubakr M (2020) L-carnitine mitigates oxidative stress and disorganization of cytoskeleton intermediate filaments in cisplatin-induced hepato- renal toxicity in rats. Front Pharmacol 11:574441. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2020.574441
El-Kordy EA (2019) Effect of suramin on renal proximal tubular cells damage induced by cisplatin in rats (histological and immunohistochemical study). J Microsc Ultrastruct 79(4):153–164. https://doi.org/10.4103/JMAU.JMAU_21_19
El-Sheikh AAK (2020) P-glycoprotein/ABCB1 might contribute to morphine/cisplatin-induced hepatotoxicity in rats. Sci Pharm 88(1):14. https://doi.org/10.3390/scipharm88010014
Farber E (1994) Programmed cell death: necrosis versus apoptosis. Mod Pathol 7(5):605–609
Farid AS, El Shemy MA, Nafie E, Hegazy AM, Abdelhiee EY (2021) Anti-inflammatory, anti-oxidant and hepatoprotective effects of lactoferrin in rats. Drug Chem Toxicol 44(3):286–293. https://doi.org/10.1080/01480545.2019.1585868
Faubel S, Lewis EC, Reznikov L, Ljubanovic D, Hoke TS, Somerset H, Oh DG, Lu L, Klein CL, Dinarello CA, Edelstein CL (2007) Cisplatin-induced acute renal failure is associated with an increase in the cytokines interleukin (IL)-1beta, IL-18, IL-6, and neutrophil infiltration in the kidney. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 322(1):8–15. https://doi.org/10.1124/jpet.107.119792
Franciscoa M, Morenob DA, Carteaa ME, Ferreres F, García-Viguera C, Velasco P (2009) Simultaneous identification of glucosinolates and phenolic compounds in a representative collection of vegetable Brassica rapa. J Chromatogr A 1216(38):6611–6619. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2009.07.055
Grant KL, Lutz RB (2000) Ginger Am J Health System Pharm 57(10):945–947. https://doi.org/10.1093/ajhp/57.10.945
Gruol DL, Puro A, Hao C, Blakely P, Janneke E, Vo K (2011) Neuroadaptive changes in cerebellar neurons induced by chronic exposure to IL-6. J Neuroimmunol 239(1–2):28–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jneuroim.2011.08.009
Holmin S, Mathiesen T (2000) Intra cerebral administration of interleukin-1beta and induction of inflammation, apoptosis, and vasogenic edema. J Neurosurg 92(1):108–120. https://doi.org/10.3171/jns.2000.92.1.0108
Hong KO, Hwang JK, Park KK, Kim SH (2005) Phosphorylation of c-Jun N-terminal Kinases (JNKs) is involved in the preventive effect of xanthorrhizol on cisplatin-induced hepatotoxicity. Arch Toxicol 79(4):231–236. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-004-0623-7
Hsu BG, Lee RP, Yang FL, Harn HJ, Chen HI (2006) Post-treatment with N-acetylcysteine ameliorates the endotoxin shock-induced organ damage in conscious rats. Life Sci 79(21):2010–2016. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2006.06.040
Ingawale DK, Mandlik SK, Naik SR (2014) Models of hepatotoxicity and the underlying cellular, biochemical and immunological mechanism(s): a critical discussion. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 37(1):118–133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.etap.2013.08.015
Ishikawa T (2009) Future perspectives on the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma with cisplatin. World J Hepatol 1(1):8–16. https://doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v1.i1.8
Kandemir FM, Kucukler S, Caglayan C, Gur C, Batil AA, Gülçin İ (2017) Therapeutic effects of silymarin and naringin on methotrexate-induced nephrotoxicity in rats: biochemical evaluation of anti-inflammatory, antiapoptotic, and antiautophagic properties. J Food Biochem 41:e12398. https://doi.org/10.1111/jfbc.12398
Kandemir FM, Yildirim S, Caglayan C, Kucukler S, Eser G (2019) Protective effects of zingerone on cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity in female rats. Environ Sci and Pollut Res Int 26(22):22562–22574. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-05505-3
Karadeniz A, Simsek N, Karakus E, Yildirim S, Kara A, Can I, Kisa F, Emre H, Turkeli M (2011) Royal jelly modulates oxidative stress and apoptosis in liver and kidneys of rats treated with cisplatin. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2011:981793. https://doi.org/10.1155/2011/981793
Kishimoto S, Miyazawa K, Terakawa Y, Ashikari H, Ohtani A, Fukushima S, Takeuchi Y (2000) Cytotoxicity of cis-[((1R,2R)-1,2-cyclohexanediamine-N, N’)bis(myristato)]-platinum (II) suspended in Lipiodol in a newly established cisplatin-resistant rat hepatoma cell line. Jpn J Cancer Res 91(12):1326–1332. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1349-7006.2000.tb00921.x
Kishimoto T, Akira S, Narazaki M, Taga T (1995) Interleukin‑6 family of cytokines and gp130. Blood 86:1243–1254. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood.V86.4.1243.bloodjournal8641243
Knoblach SM, Faden AI (1998) Interleukin-10 improves outcome and alters pro-inflammatory cytokine expression after experimental traumatic brain injury. Exp Neurol 153(1):143–151. https://doi.org/10.1006/exnr.1998.6877
Knoblach SM, Fan L, Faden AI (1999) Early neuronal expression of tumor necrosis factor-alpha after experimental brain injury contributes to neurological impairment. J Neuroimmunol 95(1–2):115–125. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0165-5728(98)00273-2
Lantz RC, Chena GJ, Sarihana M, Solyomb M, Joladb SD, Timmermannb BN (2007) The effect of extracts from ginger rhizome on inflammatory mediator production. Phytomedicine 14(2–3):123–128. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phymed.2006.03.003
Lazarenko VA, Lyashev YD, Shevchenko NI (2014) Effect of a synthetic indolicidin analogue on lipid peroxidation in thermal burns. Bull Exp Biol Med 157(4):447–449. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-014-2587-9
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193(1):265–275
Luster MI, Simeonova PP, Gallucci R, Matheson J (1999) Tumor necrosis factor alpha and toxicology. Crit Rev Toxicol 29(5):491–511. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408449991349258
Ma P, Xiao H, Yu C, Liu J, Cheng Z, Song H, Zhang X, Li C, Wang J, Gu Z, Lin J (2017) Enhanced cisplatin chemotherapy by iron oxide nanocarrier-mediated generation of highly toxic reactive oxygen species. Nano Lett 17(2):928–937. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.nanolett.6b04269
Malik S, Suchal K, Gamad N, Dinda AK, Arya DS, Bhatia J (2015) Telmisartan ameliorates cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity by inhibiting MAPK mediated inflammation and apoptosis. Eur J Pharmacol 748:54–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2014.12.008
Mohamed HE, Badawy MM (2019) Modulatory effect of zingerone against cisplatin or y-irradiation induced hepatotoxicity by molecular targeting regulation. Appl Radiat Isot 154:108891. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apradiso.2019.108891
Nežić L, Amidžić L, Škrbić R, Gajanin R, Nepovimova E, Vališ M, Kuca K, Jacević V (2019) Simvastatin inhibits endotoxin- induced apoptosis in liver and spleen through up-regulation of survivin/NF-_B/p65 expression. Front Pharmacol 10:54. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2019.00054
Ozkok A, Edelstein CL (2014) Pathophysiology of cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury. Biomed Res Int 2014:967826. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/967826
Pan MH, Hsieh MC, Kuo JM, Lai CS, Wu H, Sang Sh, Ho CT (2008) 6-Shogaol induces apoptosis in human colorectal carcinoma cells via ROS production, caspase activation, and GADD 153 expression. Mol Nutr Food Res 52(5):527–537. https://doi.org/10.1002/mnfr.200700157
Perez RP (1998) Cellular and molecular determinants of cisplatin resistance. Eur J Cancer 34(10):1535–1542. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0959-8049(98)00227-5
Pober JS, Min W (2006) Endothelial cell dysfunction, injury and death. Handb Exp Pharmacol (176 Pt 2):135–156. https://doi.org/10.1007/3-540-36028-x_5
Ramesh G, Reeves WB (2002) TNF-alpha mediates chemokine and cytokine expression and renal injury in cisplatin nephrotoxicity. J Clin Invest 110(6):835–842. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI15606
Rana SVS (2008) Metals and apoptosis: recent developments. J Trace Elem Med Biol 22(4):262–284. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtemb.2008.08.002
Romano M, Sironi M, Toniatti C, Polentarutti N, Fruscella P, Ghezzi P, Luini W, Hinsbergh V, Sozzani S, Bussolino F, Poli V, Ciliberto G, Mantovani A (1997) Role of IL-6and its soluble receptor in induction of chemokines and leukocyte recruitment. Immunity 6(3):315–325. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1074-7613(00)80334-9
Sadeghi H, Mansourian M, PanahiKokhdan E, Salehpour Z, Sadati I, Abbaszadeh-Goudarzi K, Asfaram A, Doustimotlagh AH (2020) Antioxidant and protective effect of Stachys pilifera Benth against nephrotoxicity induced by cisplatin in rats. J Food Biochem 44(5):e13190. https://doi.org/10.1111/jfbc.13190
Sen S, De B, Devanna N, Chakraborty R (2013) Cisplatin induced nephrotoxicity in mice: protective role of Leea asiatica leaves. Renal Fail 35(10):1412–1417. https://doi.org/10.3109/0886022X.2013.829405
Sendecor GW, Cochran WG (1987) The comparison of two samples. Statistical methods, 4th ed. Iowa State University, p 91–110
Shaw J, Chen B, Huang WH, Lee AR, Media J, Valeriote FA (2011) The small-molecule TNF-alpha modulator, UTL-5g, reduces side effects induced by cisplatin and enhances the therapeutic effect of cisplatin in vivo. J Exp Ther Oncol 9(2):129–137
Singh RP, Agarwal R (2002) Flavonoid antioxidant silymarin and skin cancer. Antioxid Redox Signal 4(4):655–663. https://doi.org/10.1089/15230860260220166
Sun C, Nie J, Zheng Z, Zhao J, Wu L, Zhu Y, Su Z, Zheng G, Feng B (2019) Renoprotective effect of scutellarin on cisplatin-induced renal injury in mice: impact on inflammation, apoptosis, and autophagy. Biomed Pharmacother 112:108647. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2019.108647
Surh YJ (2002) Anti-tumor promoting potential of selected spice ingredients with antioxidative and anti-inflammatory activities: a short review. Food and Chem Toxicol 40(8):1091–1097. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0278-6915(02)00037-6
Tadagavadi RK, Reeves WB (2010) Endogenous IL-10 attenuates cisplatin nephrotoxicity: role of dendritic cells. J Immunol 185(8):4904–4911. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.1000383
Wojcik M, Burzynska Pedziwiatr I, Wozniak LA (2010) A review of natural and synthetic antioxidants important for health and longevity. Curr Med Chem 17(28):3262–3288. https://doi.org/10.2174/092986710792231950
Yao X, Panichpisal K, Kurtzman N, Nugent K (2007) Cisplatin nephrotoxicity: a review. Am J Med Sci 334(2):115–124. https://doi.org/10.1097/MAJ.0b013e31812dfe1e
Yiming L, Van HT, Colin CD, Basil DR (2012) Preventive and protective properties of Zingiber officinale (Ginger) in diabetes mellitus, diabetic complications, and associated lipid and other metabolic disorders: a brief review. Evid Based Complement and Alternat Med 516870:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/516870
Yang W, Yu XH, Wang C, He WS, Zhang SJ, Yan YG, Zhang J, Xiang YX, Wang WJ (2015) Interleukin-1β in intervertebral disk degeneration. Clin Chim Acta 450:262–272. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cca.2015.08.029
Yang R, Guo P, Ma Z, Chang C, Meng Q, Gao Y, Khan I, Wang X, Cui Z (2020) Effects of simvastatin on iNOS and caspase-3 levels and oxidative stress following smoke inhalation injury. Mol Med Rep 22(4):3405–3417. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2020.11413
Yiran Z, Chenyang J, Jiajing W, Yan Y, Jianhong G, Jianchun B, Zongping L (2013) Oxidative stress and mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways involved in cadmium-induced BRL 3A cell apoptosis. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2013:516051. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/516051
Yu ZQ, Jia Y, Chen G (2014) Possible involvement of cathepsin B/D and caspase-3 in deferoxamine-related neuro protection of early brain injury after subarachnoid haemorrhage in rats. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 40(3):270–283. https://doi.org/10.1111/nan.12091
Zhang QF (2017) Ulinastatin inhibits renal tubular epithelial apoptosis and interstitial fibrosis in rats with unilateral ureteral obstruction. Mol Med Rep 16(6):8916–8922. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2017.7692
Zhu S, Pabla N, Tang C, He L, Dong Z (2015) DNA damage response in cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity. Arch Toxicol 89(12):2197–2205. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-015-1633-3
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the laboratory technician at the Department of Veterinary Pathology, Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, for their great help during preparation of histopathological slides.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All the listed authors have made substantial contributions to the research design and acquisition, analysis, or interpretation of the data. ET and AE performed histopathology and IHC examination; GE performed chemical examination. All the authors have shared in writing the manuscript and approved the final submitted version.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
The Research Ethical Committee of Animal Experiments of faculty of veterinary medicine at University of Sadat city, Egypt has approved our experimental protocol (VUSC-017–5-20).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tahoun, E., Elgedawy, G. & El-Bahrawy, A. Cytoprotective effect of ginger extract on cisplatin-induced hepatorenal toxicity in rats via modulation of oxidative stress, inflammation and apoptosis: histopathological, biochemical and immunohistochemical study. Comp Clin Pathol 30, 647–663 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00580-021-03256-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00580-021-03256-7