Abstract
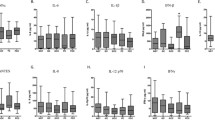
Inflammatory mediators like pro-inflammatory cytokines have been linked with the pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). Neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) has also recently emerged as a possible reliable and cost-effective marker of diabetes. This study was designed to evaluate pro-inflammatory cytokine levels (IL-6 and IL-1β) and NLR in T2DM subjects in Nigerian population. This was a case-control study involving 75 physician diagnosed T2DM subjects attending the Endocrine Clinic of a Tertiary Health Institution in Nigeria and 75 age- and sex-matched healthy individuals (used as control) who were recruited from the Blood Donor Center of the same institution. Based on physician assessment, the diabetic subjects were grouped differently into those with complications (48) and those without complications (27). Serum levels of IL-6 and IL-1β were measured using ELISA technique, while neutrophil and lymphocyte counts were evaluated using a hematology autoanalyzer from which NLR was calculated. NLR and serum levels of IL-6 were significantly (P < 0.05) higher in the diabetic group compared to control. However, there was no significant difference in NLR and IL-6 between diabetic subjects with or without complications. Furthermore, there was no significant difference in serum levels of IL-1β among the different groups. The results suggest that serum level of IL-1β is unaltered in T2DM subjects, but the disease is associated with elevations of IL-6 and NLR in Nigerian population. In addition, NLR and IL-6 may be useful diagnostic biomarkers of T2DM in Nigerian population but not for complications of the disease.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akbas EM, Demirtas L, Ozcicek A, Timuroglu A, Bakirci EM, Hamur H, Ozcicek F, Turkmen K (2014) Association of epicardial adipose tissue, neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio and platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio with diabetic nephropathy. Int J Clin Exp Med 7:1794–1801 https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4132146/
Akyel A, Yayla C, Erat M, Çimen T, Doğan M, Acikel S, Aydoğdu S, Yeter E (2015) Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio predicts hemodynamic significance of coronary artery stenosis. Anatol J Cardiol 15:1002–1007. https://doi.org/10.5152/akd.2015.5909
Al-Shukaili A, Al-Ghafri S, Al-Marhoobi S, Al-Abri S, Al-Lawati J, Al-Maskari M (2013) Analysis of inflammatory mediators in type 2 diabetes patients. Int J Endocrinol 2013:976810 https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3671680/
Badawi A, Klip A, Haddad P, Cole DEC, Bailo BG, El-Sohemy A, Karmali M (2006) Type 2 diabetes mellitus and inflammation: prospects for biomarkers of risk and nutritional intervention. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes 3:173–186 https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3047967/
Chang FY, Shaio MF (1995) Decreased cell mediated immunity in patients with noninsulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 28:137–146 https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/0168822795001688
Cho NH, Shaw JE, Karuranga S, Huang Y, da Rocha Fernandes JD, Ohlrogge AW, Malanda B (2018) IDF diabetes atlas: global estimates of diabetes prevalence for 2017 and projections for 2045. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 138:271–281. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diabres.2018.02.023
Dinarello CA, Donath MY, Mandrup-Poulsend T (2010) Role of IL-1b in type 2 diabetes. Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes 17:314–321. https://doi.org/10.1097/MED.0b013e32833bf6dc
Donath MY, Boni-Schnetzler M, Ellingsgaard H, Ehses JA (2009) Islet inflammation impairs the pancreatic β-cell in type 2 diabetes. Physiology 24:325–331. https://doi.org/10.1152/physiol.00032.2009
Donath MY, Boni-Schnetzler M, Ellingsgaard H, Halban PA, Ehses JA (2010) Cytokine production by islets in health and diabetes: cellular origin, regulation and function. Trends Endocrinol Metab 21:261–267. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tem.2009.12.010
Donath MY, Dalmas D, Sauter NS, Boni-Schnetzler M (2013) Inflammation in obesity and diabetes: islet dysfunction and therapeutic opportunity. Cell Metab 17:860–872. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2013.05.001
Donath MY, Shoelson SE (2011) Type 2 diabetes as an inflammatory disease. Nat Rev Immunol 11:98–107. https://doi.org/10.1038/nri2925
Donate-Correa J, Martín-Núñez E, Muros-de-Fuentes M, Mora-Fernández C, Navarro-González JF (2015) Inflammatory cytokines in diabetic nephropathy. J Diab Res 2015:948417. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/948417
Esser N, Legrand-Poels S, Piette J, Scheen AJ, Paquot N (2014) Inflammation as a link between obesity, metabolic syndrome and type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 105(2):141–150. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diabres.2014.04.006
Festa A, D’Agostino R, Howard G, Mykkanen L, Tracy RP, Haffner SM (2000) Chronic subclinical inflammation as part of the insulin resistance syndrome: the insulin resistance atherosclerosis study (IRAS). Circulation 102:42–47. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.CIR.102.1.42
Geerlings SE, Hoepelman AI (1999) Immune dysfunction in patients with diabetes mellitus (DM). FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol 26:259–265. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1574-695X.1999.tb01397.x
Goldberg RB (2009) Cytokine and cytokine-like inflammation markers, endothelial dysfunction, and imbalanced coagulation in development of diabetes and its complications. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 94:3171–3182. https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2008-2534
Guo X, Zhang S, Zhang Q, Liu L, Wu H, Du H, Shi H, Wang C, Xia Y, Liu X, Li C, Sun S, Wang X, Zhou M, Huang G, Jia Q, Zhao H, Song K, Niu K (2015) Neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio is positively related to type 2 diabetes in a large-scale adult population: a Tianjin chronic low-grade systemic inflammation and health cohort study. Eur J Endocrinol 173:217–225
Gupta S, Maratha A, Siednienko J, Natarajan A, Gajanayake T, Hoashi S, Miggin S (2017) Analysis of inflammatory cytokine and TLR expression levels in type 2 diabetes with complications. Sci Rep 7:7633. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-07230-8
Herder C, Dalmas E, Boni-Schnetzler M, Donath MY (2015) The IL-1 pathway in type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular complications. Trends Endocrinol Metab 26:551–563. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tem.2015.08.001
Herder C, Illig T, Rathmann W, Martin S, Haastert B, Muller-Scholze SM, Holle R, Thorand B, Koenig W, Wichmann HE, Kolb H (2005) Inflammation and type 2 diabetes: results from KORA Augsburg. Gesundheitswesen 67:S115–S121. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-2005-858252
Larsen CM, Faulenbach M, Vaag A, Ehses JA, Donath MY, Mandrup-Poulsen T (2009) Sustained effects of interleukin-1 receptor antagonist treatment in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 32:1663–1668. https://doi.org/10.2337/dc09-0533
Li C, Chen R, Wang H, Liang F (2015) Mechanisms linking inflammation to insulin resistance. Int J Endocrinol 2015:508409. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/508409
Li X, Shen J, Lu Z, Chen M, Fang X, Wang G (2016) High neutrophil-to lymphocyte ratio is associated with increased carotid artery intima-media thickness in type 2 diabetes. J Diabetes Investig 8:101–107. https://doi.org/10.1111/jdi.12541
Liu J, Du J, Fan J, Liu K, Zhang B, Wang S, Wang W, Wang Z, Cai Y, Li C, Yu T, Zhu G, Chen J, Li C (2015) The neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio correlates with age in patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma. ORL J Otorhinolaryngol Relat Spec 77:109–116. https://doi.org/10.1159/000375534
Luger A, Schernthaner G, Urbanski A, Luger TA (1988) Cytokine production in patients with newly diagnosed insulin-dependent (type 1) diabetes mellitus. Eur J Clin Investig 18:233–236. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2362.1988.tb01251.x
Mirza S, Hossain M, Mathews C, Martinez P, Pino P, Gay JL, Rentfro A, McCormick JB, Fisher-Hoch SP (2012) Type 2-diabetes is associated with elevated levels of TNF-alpha, IL-6 and adiponectin and low levels of leptin in a population of Mexican Americans: a cross-sectional study. Cytokine 57:136–142. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cyto.2011.09.029
Mooney RA (2007) Counterpoint: interleukin-6 does not have a beneficial role in insulin sensitivity and glucose homeostasis. J Appl Physiol 102:816–818 https://www.physiology.org/doi/pdf/10.1152/japplphysiol.01208a.2006
Navarro JF, Mora C (2006) Diabetes, inflammation, proinflammatory cytokines, and diabetic nephropathy. Sci World J 6:908–917 https://doi.org/10.1100/tsw.2006.179
Nazari A, Sardoo AM, Fard ET, Hassanshahi G, Goujani R, Bagheri E, Ahmadirad H, Mazarian F, Khorramdelazad H (2017) Is IL-6 increased in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients independent of nephropathic complication? J Endocrinol Diabetes Obes 5(2):1102
Öztürk ZA, Kuyumcu ME, Yesil Y, Savas E, Yıldız H, Kepekçi Y, Arıoğul S (2013) Is there a link between neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio and microvascular complications in geriatric diabetic patients? J Endocrinol Investig 36:593–599. https://doi.org/10.3275/8894
Shiny A, Bibin YS, Shanthirani CS, Regin BS, Anjana RM, Balasubramanyam M, Jebarani S, Mohan V (2014) Association of neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio with glucose intolerance: an indicator of systemic inflammation in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Technol Ther 16(8):524–530. https://doi.org/10.1089/dia.2013.0264
Spranger J, Kroke A, Mohlig M, Hoffmann K, Bergmann MM, Ristow M, Boeing H, Pfeiffer AF (2003) Inflammatory cytokines and the risk to develop type 2 diabetes results of the prospective population-based European prospective investigation into cancer and nutrition (EPIC)-Potsdam study. Diabetes 52:812–817. https://doi.org/10.2337/diabetes.52.3.812
Stumvoll M, Goldstein B, van Haeften T (2005) Type 2 diabetes: principles of pathogenesis and therapy. Lancet 365:1333–1346. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(05)61032-X
Talukdar S, Oh DY, Bandyopadhyay G, Li D, Xu J, McNelis J, Lu M, Li P, Yan Q, Zhu Y, Ofrecio J, Lin M, Brenner MB, Olefsky JM (2012) Neutrophils mediate insulin resistance in mice fed a high-fat diet through secreted elastase. Nat Med 18:1407–1412. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.2885
Tanaka S, Isoda F, Ishihara Y, Kimura M, Yamakawa T (2001) T lymphopaenia in relation to body mass index and TNF-a in human obesity: adequate weight reduction can be corrective. Clin Endocrinol 54:347–354. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2265.2001.1139cn2155.x
Tang SC, Yiu WH, Lin M, Lai KN (2015) Diabetic nephropathy and proximal tubular damage. J Ren Nutr 25:230–233. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.jrn.2014.10.020
Ulu SM, Dogan M, Ahsen A, Altug A, Demir K, Acarturk G, Inan S (2013) Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio as a quick and reliable predictive marker to diagnose the severity of diabetic retinopathy. Diabetes Technol Ther 15:942–947. https://doi.org/10.1089/dia.2013.0097
Acknowledgments
The authors are thankful to Mr. Gbenga Olugbenga of the Department of Chemical Pathology, University of Port Harcourt Teaching Hospital, for his assistance in sample analysis and Mr. Linus Ochai for his help in analyzing the data. We would also like to thank the Diabetes Association of Nigeria, Port Harcourt Chapter, and all participants who were involved in the study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection, and analysis were performed by Eugene E. Akujuru and Jonah S. Aprioku. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Eugene E. Akujuru, and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in the study were approved by the Research Ethics Committee of the University of Port Harcourt, Nigeria (UPH/R&DD/REC/04). The research was also conducted in accordance with the Helsinki Declaration.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants before they were enrolled in the study.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Akujuru, E.E., Aprioku, J.S. & Okerengwo, A.A. Circulatory levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines (IL-6 and IL-1β) and neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) in diabetic patients in Nigerian population. Comp Clin Pathol 29, 539–545 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00580-019-03086-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00580-019-03086-8