Abstract
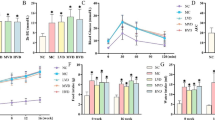
The purpose of this study was to assess the hypoglycemic and protective activities of the ethanolic extract of Allium saralicum (AS) in streptozotocin (STZ) induced diabetic mice. Diabetes was experimentally induced by intraperitoneal injection of STZ (60 mg/kg bw) in 35 mice. Fasting blood glucose (FBG) levels were measured everyday using glucometer strips. Mice with plasma glucose level > 250 mg/dL were considered diabetic. After 3 days, they were divided randomly into five groups. Groups 1 and 2 served as non-diabetic and untreated diabetic controls, respectively. Group 3 received 0.5 mg/kg glibenclamide orally. Groups 4 and 5 were given 200 and 400 μg/kg, respectively, of AS for 15 days orally. At 16th day, the animals were dissected and their kidney removed. The total volume of cortex, medulla, renal tubules, and glomeruli as well as the length of vessels and renal tubules was estimated using stereological method. Daily treatment of diabetic mice with high dose of AS significantly (p ≤ 0.05) declined FBG levels at days 10–13 of the experiment faster than glibenclamide. High dose of AS could significantly (p ≤ 0.05) improve the volume of cortex, glomeruli, proximal tubules, distal tubules, vessels, and total length of proximal tubules and vessels. Moreover, glomerular loss was significantly (p ≤ 0.05) inhibited with high dose of AS. It concluded that Allium saralicum could improve hyperglycemia and ameliorated renal changes following diabetes in STZ-induced diabetic mice. So, according to these features, it could be used as an antidiabetic supplement.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdel-Barry JA, Abdel-Hassan IA, Al-Hakiem MHH (1997) Hypoglycaemicand antihyperglycaemic effects of Trigonellafoenum-graecum leaf in normal and alloxan-induced diabetic rats. J Ethnopharmacol 58:149–155
Ahmed D, Kumar V, Verma A, Gupta PS, Kumar H, Dhingra V, Mishra V, Sharma M (2014) Antidiabetic, renal/hepatic/pancreas/cardiac protective and antioxidant potential of methanol/dichloromethane extract of Albizzia Lebbeck Benth. stem bark (ALEx) on streptozotocin induced diabetic rats. Complement Altern Med 14:243–260
Augusti KT, Sheela CG (1996) Antiperoxide effect of S-allyl cysteine sulfoxide, a insulin secretagogue, in diabetic rats. Experientia 52:115–120
Block E. Garlic and Other Alliums: The Lore and the Science (2010) Royal Society of Chemistry ISBN978-0-85404-190-9
Braendgaard H, Gundersen HJ (1986) The impact of recent stereological advances on quantitative studies of the nervous system. J Neurosci Methods 18(1–2):39–78
Chaiyasut C, Kusirisin W, Lailerd N et al (2011) Effects of phenolic compounds of fermented Thai indigenous plants on oxidative stress in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. J Evid Based Complement Altern Med:1–10
Christiansen JS, Gammelgaard J, Tronier B, Svendsen PA, Parving HH (1982) Kidney function and size in diabetes before and during initial insulin treatment. Kidney Int 21:683–688
Davies D (1992) Alliums: the ornamental onions. Timber Press. ISBN0-88192-241-2
DeRubertis FR, Craven PA (1994) Activation of protein kinase C in glomerular cells in diabetes: mechanisms and potential links to the pathogenesis of diabetic glomerulopathy. Diabetes 43:1–8
Eidi A, Eidi M, Esmaeili E (2006) Antidiabetic effect of garlic (Allium sativum L.) in normal and streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Phytomedicine 13:624–629
Foroughi A, Zangeneh MM, Kazemi N, Zangeneh A (2016) An in vitro study on antimicrobial properties of Allium noeanumreut ex regel: an ethnomedicinal plant. Iranian J Publ Health 45(2):32
Gondwe M, Kamadyaapa DR, Tufts M et al (2008) Sclerocaryabirrea[(A. Rich.) Hochst.] [Anacardiaceae] stem-barkethanolic extract (SBE) modulates blood glucose, glomerular filtrationrate (GFR) and mean arterial blood pressure (MAP) of STZ-induceddiabetic rats. Phytomedicine 15:699–709
Gundersen HJ, Bendtsen TF, Korbo L et al (1992) Some new, simple and efficient stereological methods and their use in pathological research and diagnosis. APMIS 96:379–394
Heidland A, Ling H, Vamvakas S, Paczek L (1996) Impaired proteolytic activity asa potential cause of progressive renal disease. Miner Electrolyte Metab 22:157–161
Hostetter T (2003) Hyperfiltration and glomerulosclerosis. SeminNephrol 23:194–199
Hostetter TH, Troy JL, Brenner BM (1981) Glomerular hemodynamic in experimental diabetes. Kidney Int 19:410–415
Jain RC, Vyas CR (1975) Hypoglycemic action of onion and garlic. Am J Clin Nutr 28:684–685
Liu C-T, Hse H, Lii C-K, Chen P-S, Sheen L-Y (2005) Effects of garlic oil and diallyltrisulfide onglycemic control in diabetic rats. Eur J Pharmacol 516:165–173
Mandarim-de-Lacerda CA (2003) Stereological tools in biomedical research. An Acad Bras Cienc 75(4):469–486
Mathew PT, Augusti KT (1973) Studies on the effect of allicin (diallyldisulphide-oxide) on alloxan diabetes I. Hypoglycaemic action and enhancement of serum insulin effect andglycogensynthesis. Indian J Biochem Biophys 10:209–212
McCrary RF, Pitts TO, Puschett JB (1981) Diabetic nephropathy. Natural course, survivorship, and therapy. Am J Nephrol 1:206–201
Mogensen CE, Anderson MJF (1975) Increased kidney size and glomerular filtration rate in untreated juvenile diabetes: normalization by insulin-treatment. Diabetologia 11:221–224
Musabayane CT (2012) The effects of medicinal plants on renal function and blood pressure in diabetes mellitus. Cardiovasc J Afr 23:462–468
Nyengaard JR (1999) Stereologic methods and their application in kidney research. J Am Soc Nephrol 10(5):1100–1123
Pushparaj P, Tan CH, Tan BKH (2000) Effects of Averrhoa Bilimbileaf extract on blood glucose and lipids in streptozotocin-diabetic rats. J Ethnopharmacol 72:69–76
Qattan KA, Thomson M, Muslim A (2008) Garlic (Allium sativum) and ginger (Zingiberofficinale) attenuate structural nephropathy progression in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Eur J Clin Nutr Metab 3:62–71
Rabkin R, Schechter P, Shi JD, Boner G (1996) Protein turnover in thehypertrophy in kidney. Miner Electrolyte Metab 22:153–156
Rahimi R, Nikfar S, Larijani B, Abdollahi M (2005) A review on the antioxidantsin the management of diabetes and its complications. Biomed Pharmacother 59:365–373
Salvatore T, Giugliano D (1996) Pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic relationshipof acarbose. Clin Pharmacokinet 30:94–106
Sharma K, Ziyadeh FN (1995) Hyperglycemia and diabetic kidney disease: the case for transforming growth factor-β as a key mediator. Diabetes 44:1139–1146
Sherkatolabbasieh H, Hagh-Nazari L, Shafiezadeh S, et al (2016) Ameliorative effects of the ethanolic extract of Allium saralicum R.M. Fritsch on CCl4-induced nephrotoxicity in mice: a stereological examination. Archives of Biological Science DOI: https://doi.org/10.2298/ABS160914129S
Stackhouse S, Miller PL, Park SK, Meyer TW (1990) Reversal of glomerular hyperfiltration and renal hypertrophy by blood glucose normalization in diabetic rats. Diabetes 39:989–995
Sterio DC (1984) The unbiased estimation of number and sizes of arbitrary particles using the dissector. J Microsc 134:127–36
Thomson M, Al-Amin ZM, Al-Qattan K et al (2007) Anti-diabetic and hypolipidaemic propertiesof garlic (Allium sativum) in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Int J Diabetes Metab 15:108–115
Weir GC, Clore ET, Zmachiroski CJ, Bonner-Weir S (1981) Islet secretion in a newexperiment model for non-insulin dependent diabetes. Diabetes 30:590–595
Welt K, Weis J, Martin R, et al (2007) Ginkgo biloba extract protects rat kidney from diabetic and hypoxic damage. Phytomedicine 14:(2–3): 196–203
WHO Expert Committee on Diabetes mellitus (1981) Technical Report Series 646, Second Report. World Health Organization Geneva
Wiseman MJ, Saunders AJ, Keen H, Viberti GC (1985) Effect of blood glucose control on increased glomerular filtration rate and kidney size in insulin dependent diabetes. N Engl J Med 312:617–621
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All institutional and national standards for the care and use of laboratory animals were followed. This article does not contain any studies with human participants performed by any of the authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zangeneh, M.M., Goodarzi, N., Zangeneh, A. et al. Amelioration of renal structural changes in STZ-induced diabetic mice with ethanolic extract of Allium saralicum R.M. Fritsch. Comp Clin Pathol 27, 861–867 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00580-018-2674-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00580-018-2674-9