Abstract
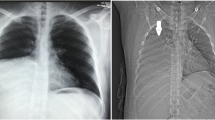
The endobronchial lipomas are extremely rare and consist of 0.1 to 0.5% of all lung tumors and 1.4–13% of benign lung neoplasms. We present a 42-year-old woman with endobronchial lipoma and the initial evaluation and appropriate management. A 42-year-old woman presented with history of dry cough and wheeze for eight months was candidate for bronchoscopy study. Histopathology examination of excised lesion confirmed endobronchial lipoma of the left lower lobe bronchus. The post-bronchoscopy period was uneventful. The patient was disease free in the following three years. The physicians, especially at major referral lung centers, are much more likely to be familiar with endobronchial lipoma and its clinical awareness, because misdiagnosis can delay the start of an appropriate treatment.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Basoglu A, Celik B, Akdag AO, Sengul AT (2004) Endobronchial lipoma: a rare cause of bronchial occlusion. Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg 3(2):263–264
Bhatia K, Ellis S (2006) Unusual lung tumours: an illustrated review of CT features suggestive of this diagnosis. Cancer Imaging 6(1):72–82
Huisman C, van Kralingen KW, Postmus PE, Sutedja TG (2000) Endobronchial lipoma: a series of three cases and the role of electrocautery. Respiration 67(6):689–692
Irani F, Kumar B, Reddy P, Narwal-Chadha R, Kasmani R, Tita J (2010) An endobronchial lipoma mimicking asthma and malignancy. Prim Care Respir J 19:281–283
Krüger S, Stanzel F, Morresi-Hauf A, Häussinger K (2004) Endobronchial lipoma: successful therapy by bronchoscopical laser resection vs. surgery. Pneumologie (Stuttgart, Germany) 58(11):769–772
Matsuba K, Saito T, Ando K, Shirakusa T (1991) Atypical lipoma of the lung. Thorax 46(9):685
Mauro A, Rapoport A, Paier LCI et al (2005) Endobronchial lipoma. J Bras Pneumol 31:555–558
Muraoka M, Oka T, Akamine S, Nagayasu T, Iseki M, Suyama N, Ayabe H (2003) Endobronchial lipoma: review of 64 cases reported in Japan. CHEST J 123(1):293–296
Piñero A, Giménez A, Lax FG, Parrilla P (1996) Hemoptysis caused by an endobronchial lipoma. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 111(5):1104–1105
Rodriguez E, Pombo F, Gallego C, Otero I (1994) Endobronchial lipoma. Computed tomography and magnetic resonance. Chest 105:1628
Surani S, Allen K, Surani S, Varon J (2014) Endobronchial lipomatous polyp: a rare benign tumor of the lung. Case Rep Pulmonol 25:2014
Terán SJ, Campo LJ, Rodríguez PL, García MJ, Gallo MF, Viejo BJ (1990) Pleural lipomas: their diagnosis by computed axial tomography. Rev Clin Esp 187(4):203
Triviño A, Mora-Cabezas M, Vallejo-Benitez A, García-Escudero A, González-Cámpora R (2013) Endobronchial lipoma: a rare cause of bronchial occlusion. Arch Bronconeumol 49(11):494–496
Yokozaki M, Kodama T, Yokose T, Nishimura M, Yoshida J, Mizokami H, Nagai K (1996) Endobronchial lipoma: a report of three cases. Jpn J Clin Oncol 26(1):53
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Samiee-rad, F., Zangivand, A.A. & Soleimanitadi, K. Endobronchial lipoma, the initial evaluation and appropriate management. Comp Clin Pathol 26, 1403–1406 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00580-017-2549-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00580-017-2549-5