Abstract.
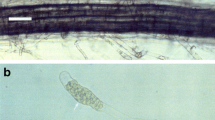
Monoxenic culture of Glomus intraradices Schenck and Smith with Ri T-DNA transformed roots in two-compartment Petri dishes is a very useful technique for physiological studies and the production of clean fungal tissues. Experiments were conducted to increase the efficiency of this method for the production of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus spores. Approximately 20,000 spores could be harvested every 2 months from the distal (fungus only) compartment of a 9-cm-diameter divided Petri dish. The method requires replacement of the gelled media in the distal compartment and resupply of 200 mg glucose to the proximal (root) compartment coincident with harvest of spores. These modifications resulted in an approximate threefold increase in spore production per unit time over the standard split-plate culture technique.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Douds, D.D. Increased spore production by Glomus intraradices in the split-plate monoxenic culture system by repeated harvest, gel replacement, and resupply of glucose to the mycorrhiza. Mycorrhiza 12, 163–167 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00572-002-0174-9
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00572-002-0174-9