Abstract
Background
Hypersplenism-related thrombocytopenia (HST) may delay or preclude chemotherapy. Partial splenic embolization (PSE) has been used at our center to overcome prolonged HST.
Patients and methods
Between November 2012 and April 2015, 11 PSE procedures were performed in 10 patients; 9 had metastatic colorectal cancer and 1 had widespread pancreatic cancer. PSE was performed by selective catheterization of the splenic artery followed by injection of embolic particles, ranging from 300–700 um, until a 50% reduction in the splenic parenchyma blush was achieved.
Results
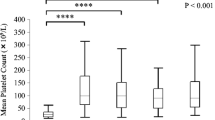
Splenomegaly was evaluated by splenic index, mean value 970 cm3 (range, 358–2277 cm3), normal mean 120–480 cm3. Mean platelet count immediately prior to PSE was 64.5 K/UL (range, 17–104 K/UL); within 10–14 days following the procedure, it increased to 224 K/UL (range, 83–669 K/UL). Only one patient’s count remained less than 100 K/UL 2 weeks after embolization. After the procedure, all patients complained of mild abdominal pain that lasted for a few days; one patient developed post-embolization syndrome. No other significant complications were observed. Mean hospital stay was 2.5 days (range, 2–5 days). Chemotherapy was resumed 7–53 days (mean, 18 days) after the procedure in nine patients. One patient did not receive chemotherapy; he underwent local treatment of liver metastasis. Prolonged thrombocytopenia recurred in four patients, one of whom was successfully retreated by PSE.
Conclusions
PSE can be considered as a treatment option for HST.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bhatia S, Venkat S, Rocha-Lima CM, Gonzalez E, Jun E, Narayanan G (2013) Treatment options for thrombocytopenia in cancer patients. Intervent Oncol 360(1):E34–E38
Elmakki E (2012) Hypersplenism: review article. J Biol Agric Healthc 2:89–99
Kauffman CR, Mahvash A, Kopetz S, Wolff RA, Ensor J, Wallace MJ (2008) Partial splenic embolization for cancer patients with thrombocytopenia requiring systemic chemotherapy. Cancer 112:2283–2288. https://doi.org/10.1002/cncr.23432
Guan YS, Hu Y (2014) Clinical application of partial splenic embolization. Sci World J 2014:961345. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/961345
Beji H, De La Fouchardière C, Desseigne F, Thiesse P, Richioud B, Pilleul F (2015) Thrombocytopenia due to hypersplenism in oncological disease: partial splenic embolization during palliative treatment. Diagn Interv Imaging 96:383–386. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diii.2014.08.005
Bhatia SS, Venkat S, Echenique A, Rocha-Lima C, Doshi MH, Salsamendi J, Barbery K, Narayanan G (2015) Proximal splenic artery embolization in chemotherapy-induced thrombocytopenia: a retrospective analysis of 13 patients. J Vasc Interv Radiol 26:1205–1211. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jvir.2015.04.003
Lokich J, Costello P (1983) Splenic embolization to prevent dose limitation of cancer chemotherapy. AJR Am J Roentgenol 140:159–161
Gonsalves CF, Mitchell EP, Brown DB (2010) Management of hypersplenism by partial splenic embolization with ethylene vinyl alcohol copolymer. AJR Am J Roentgenol 195:1241–1244. https://doi.org/10.2214/AJR.10.4401
Hiramoto K, Kuroki M, Nakano E, Kanno N, Matsumura Y, Miura A, Kikuchi Y, Hirakawa H (2011) Successful management with partial splenic embolization (PSE) of splenomegaly and thrombocytopenia caused by oxaliplatin-based chemotherapy for advanced colorectal cancer. Gan To Kagaku Ryoho 38:835–839
Gowda NK, D’Souza D, Golzarian J (2012) Partial splenic artery embolization. Endovascular Today 11:74–76
Luz JH, Luz PM, Marchiori E (2016) Partial splenic embolization to permit continuation of systemic chemotherapy. Cancer Med 5:2715–2720. https://doi.org/10.1002/cam4.856
Maddison FE (1973) Embolic therapy of hypersplenism. Investig Radiol 8:280–281
Gaba RC, Katz JR, Parvinian A, Reich S, Omene BO, Yap FY, Owens CA, Knuttinen MG, Bui JT (2013) Splenic artery embolization: a single center experience on the safety, efficacy, and clinical outcomes. Diagn Interv Radiol 19:49–55. https://doi.org/10.4261/1305-3825.DIR.5895-12.1.
Madoff DC, Denys A, Wallace MJ, Murthy R, Gupta S, Pillsbury EP, Ahrar K, Bessoud B, Hicks ME (2005) Splenic arterial interventions: anatomy, indications, technical considerations, and potential complications. Radiographics 25(Suppl 1):S191–S211
Ahuja C, Farsad K, Chadha M (2015) An overview of splenic embolization. AJR Am J Roentgenol 205:720–725. https://doi.org/10.2214/AJR.15.14637
Hadduck TA, McWilliams JP (2014) Partial splenic artery embolization in cirrhotic patients. World J Radiol 6:160–168. https://doi.org/10.4329/wjr.v6.i5.160
Zhu K, Meng X, Qian J, Huang M, Li Z, Guan S, Jiang Z, Shan H (2009) Partial splenic embolization for hypersplenism in cirrhosis: a long-term outcome in 62 patients. Dig Liver Dis 41:411–416. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dld.2008.10.005
Yoshida H, Mamada Y, Taniai N, Tajiri T (2008) Partial splenic embolization. Hepatol Res 38:225–233
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Passhak, M., Shachar, S.S., Ofer, A. et al. Partial splenic embolization in the treatment of prolonged thrombocytopenia due to hypersplenism in metastatic cancer patients. Support Care Cancer 26, 3527–3532 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00520-018-4192-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00520-018-4192-3