Abstract
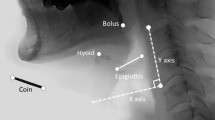
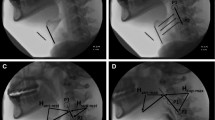
Hyoid bone excursion (HBE) is one of the most critical events in the pharyngeal phase of swallowing. Most previous studies focused on the total displacement and average velocity of HBE. However, HBE during swallowing is not one-dimensional, and the change of velocity and acceleration is not linear. This study aims to elucidate the relationship between the instantaneous kinematics parameters of HBE and the severity of penetration/aspiration and pharyngeal residue in patients with stroke. A total of 132 sets of video-fluoroscopic swallowing study images collected from 72 dysphagic stroke patients were analyzed. The maximal instantaneous velocity, acceleration, displacement, and the time required to reach these values in the horizontal and vertical axes were measured. Patients were grouped according to the severity of the Penetration-Aspiration Scale and the Modified Barium Swallow Impairment Profile- Pharyngeal Residue. The outcome was then stratified according to the consistencies of swallowing materials. Stroke patients with aspiration were associated with a lower maximal horizontal instantaneous velocity and acceleration of HBE, a shorter horizontal displacement, and prolonged time to maximal vertical instantaneous velocity compared to the non-aspirators. In patients with pharyngeal residue, the maximal horizontal displacement of HBE was decreased. After stratification according to bolus consistencies, the temporal parameters of HBE were more significantly associated with aspiration severity when swallowing thin bolus. Meanwhile spatial parameters such as displacement had a bigger influence on aspiration severity when swallowing viscous bolus. These novel kinematic parameters of HBE could provide important reference for estimating swallowing function and outcomes in dysphagic stroke patients.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cohen DL, et al. Post-stroke dysphagia: a review and design considerations for future trials. Int J Stroke. 2016;11(4):399–411. https://doi.org/10.1177/1747493016639057.
Matsuo K, Palmer JB. Anatomy and physiology of feeding and swallowing: normal and abnormal. Phys Med Rehabil Clin N Am. 2008;19(4):691–vii. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pmr.2008.06.001.
Ishida R, Palmer JB, Hiiemae KM. Hyoid motion during swallowing: factors affecting forward and upward displacement. Dysphagia. 2002;17(4):262–72. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00455-002-0064-5.
Inamoto Y, et al. Evaluation of swallowing using 320-detector-row multislice CT Part II: kinematic analysis of laryngeal closure during normal swallowing. Dysphagia. 2011;26(3):209–17. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00455-010-9276-2.
Lee WH, et al. Hyoid kinematic features for poor swallowing prognosis in patients with post-stroke dysphagia. Sci Rep. 2021;11(1):1471–1471. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-80871-4.
Feng MC, et al. The mortality and the risk of aspiration pneumonia related with dysphagia in stroke patients. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2019;28(5):1381–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2019.02.011.
Bingjie L, et al. Quantitative videofluoroscopic analysis of penetration-aspiration in post-stroke patients. Neurol India. 2010;58(1):42–7. https://doi.org/10.4103/0028-3886.60395.
Hsiao MY, et al. Application of ultrasonography in assessing oropharyngeal dysphagia in stroke patients. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2012;38(9):1522–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultrasmedbio.2012.04.017.
Kim Y, McCullough GH. Maximal hyoid excursion in poststroke patients. Dysphagia. 2010;25(1):20–5. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00455-009-9224-1.
Seo HG, Oh BM, Han TR. Swallowing kinematics and factors associated with laryngeal penetration and aspiration in stroke survivors with dysphagia. Dysphagia. 2016;31(2):160–8. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00455-015-9670-x.
Wei KC, et al. Swallowing kinematic analysis might be helpful in predicting aspiration and pyriform sinus stasis. Sci Rep. 2022;12(1):1354. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-05441-2.
Stokely SL, et al. The relationship between pharyngeal constriction and post-swallow residue. Dysphagia. 2015;30(3):349–56. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00455-015-9606-5.
Smaoui S, Peladeau-Pigeon M, Steele CM. Determining the relationship between hyoid bone kinematics and airway protection in swallowing. J Speech Lang Hear Res. 2022;65(2):419–30. https://doi.org/10.1044/2021_jslhr-21-00238.
Nagy A, et al. The effect of bolus volume on hyoid kinematics in healthy swallowing. Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:738971–738971. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/738971.
Lee T, et al. Failed deglutitive upper esophageal sphincter relaxation is a risk factor for aspiration in stroke patients with oropharyngeal dysphagia. J Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2017;23(1):34–40. https://doi.org/10.5056/jnm16028.
Eisenhuber E, et al. Videofluoroscopic assessment of patients with dysphagia: pharyngeal retention is a predictive factor for aspiration. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2002;178(2):393–8. https://doi.org/10.2214/ajr.178.2.1780393.
Perlman AL, Booth BM, Grayhack JP. Videofluoroscopic predictors of aspiration in patients with oropharyngeal dysphagia. Dysphagia. 1994;9(2):90–5. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf00714593.
Jacob P, et al. Upper esophageal sphincter opening and modulation during swallowing. Gastroenterology. 1989;97(6):1469–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/0016-5085(89)90391-0.
Rosenbek JC, et al. A penetration-aspiration scale. Dysphagia. 1996;11(2):93–8. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf00417897.
Martin-Harris B, et al. MBS measurement tool for swallow impairment–MBSImp: establishing a standard. Dysphagia. 2008;23(4):392–405. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00455-008-9185-9.
Nagy A, et al. The effect of bolus consistency on hyoid velocity in healthy swallowing. Dysphagia. 2015;30(4):445–51. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00455-015-9621-6.
Hsiao M-Y, et al. Effects of bolus consistency and volume on hyoid bone displacement during swallowing. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2017;43:S200. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultrasmedbio.2017.08.1681.
Saconato M, et al. Temporal and sequential analysis of the pharyngeal phase of swallowing in poststroke patients. Dysphagia. 2020;35(4):598–615. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00455-019-10069-y.
Ekberg O, Sigurjónsson SV. Movement of the epiglottis during deglutition. A cineradiographic study Gastrointest Radiol. 1982;7(2):101–7. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf01887619.
Kendall KA, Leonard RJ. Hyoid movement during swallowing in older patients with dysphagia. Arch Otolaryngol-Head Neck Surg. 2001;127(10):1224–9. https://doi.org/10.1001/archotol.127.10.1224.
Konecny P, Elfmark M. Electrical stimulation of hyoid muscles in post-stroke dysphagia. Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub. 2018;162(1):40–2. https://doi.org/10.5507/bp.2017.043.
Okada T, et al. Dynamic change in hyoid muscle length associated with trajectory of hyoid bone during swallowing: analysis using 320-row area detector computed tomography. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2013;115(8):1138–45. https://doi.org/10.1152/japplphysiol.00467.2013.
Feng X, et al. Aging-related geniohyoid muscle atrophy is related to aspiration status in healthy older adults. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2013;68(7):853–60. https://doi.org/10.1093/gerona/gls225.
Jui Su, Daniel C, et al. Hyoid bone displacement during swallowing have no association with penetration/aspiration severity in dysphagic stroke patients. Arch Phys Med and Rehab. 2014;95(10):e16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apmr.2014.07.028.
Vandaele DJ, Perlman AL, Cassell MD. Intrinsic fibre architecture and attachments of the human epiglottis and their contributions to the mechanism of deglutition. J Anat. 1995;186(1):1–15.
Kocdor P, Siegel ER, Tulunay-Ugur OE. Cricopharyngeal dysfunction: a systematic review comparing outcomes of dilatation, botulinum toxin injection, and myotomy. Laryngoscope. 2016;126(1):135–41. https://doi.org/10.1002/lary.25447.
McCullough GH, Kim Y. Effects of the Mendelsohn maneuver on extent of hyoid movement and UES opening post-stroke. Dysphagia. 2013;28(4):511–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00455-013-9461-1.
Lee WH, et al. Differential kinematic features of the hyoid bone during swallowing in patients with Parkinson’s disease. J Electromyogr Kinesiol. 2019;47:57–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelekin.2019.05.011.
Smaoui S, Peladeau-Pigeon M, Steele CM. Variations in hyoid kinematics across liquid consistencies in healthy swallowing. J Speech Lang Hear Res. 2021;64(1):51–8. https://doi.org/10.1044/2020_jslhr-20-00508.
Acknowledgements
The material was also provided to Yu-Chen Wang, MS, Jiun-Jen Yang, MD, and AetherAI Co., Ltd. for data collection and analysis while they are working for or collaborating with the Department of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, National Taiwan University Hospital from May 1st, 2015, to May 1st, 2020.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
TGW, MD, MYH, MD, PhD, and SYC, MD: conceptualized the study. TGW, MD, MYH, MD, PhD: designed the methodology of the study. KCW, MD, SHC, MD, SYC, MD: analyzed the data. SYC, MD: drafted the manuscript. All authors reviewed and edited the manuscript and approved the final version.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
No funds, grants, or other support was received for this study. The authors have no competing interests to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, SY., Wei, KC., Cheng, SH. et al. The Hyoid Bone Kinematics in Dysphagic Stroke Patients: Instantaneous Velocity, Acceleration and Temporal Sequence Matters. Dysphagia 38, 1598–1608 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00455-023-10587-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00455-023-10587-w