Abstract
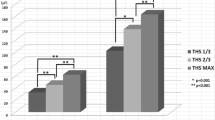
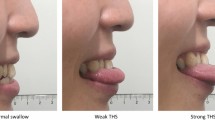
Our previous study regarding the tongue-hold swallow (THS) demonstrated that the tongue-to-palate contact during THS could be influenced by the maximum tongue protrusion length (MTPL) of individual subjects, resulting in two different patterns of pressure generation. The present study further analyzed the influence of MTPL on the tongue pressure production along with submental surface electromyography (sEMG) during THS, in order to establish an index to better control THS effects. Tongue pressure using a sensor sheet system and concurrent submental sEMG activities were measured during swallowing tasks in 18 healthy young adults. Task conditions comprised THS at two different degrees of tongue protrusion and dry swallow. Tongue pressures and sEMG activities were compared among three task conditions, and correlations of MTPL with tongue pressure were also investigated. Additionally, a ROC curve was used to find a cut-off value for MTPL to predict changes (increases and decreases) in tongue pressure during THS. The duration and the amount of submental muscle activity increased concurrently during THS. Two trends were shown on the change in tongue pressure at the posterior-circumferential part of the hard palate during THS compared to dry swallow; the maximal magnitude and the integrated value of tongue pressure increased in some subjects, while these values decreased in others. Thirty-two millimeters was found to be the cut-off value of MTPL, which distinguishes increase/decrease pattern of tongue pressure with sensitivities of 60.0–85.7%. The present finding suggests that more reliable THS effects should be attainable using MTPL to set the tongue-hold position.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fujiu M, Logemann JA. Effect of a tongue-holding maneuver on posterior pharyngeal wall movement during deglutition. Am J Speech Lang Pathol. 1996;5:23–30.
Kahrilas PJ, Logemann JA, Lin S, Ergun GA. Pharyngeal clearance during swallowing: a combined manometric and videofluoroscopic study. Gastroenterology. 1992;103:128–36.
Saigusa H, Yamashita K, Tanuma K, Saigusa M, Niimi S. Morphological studies for retrusive movement of the human adult tongue. Clin Anat. 2004;17:93–8.
Hammer Michael J, Jones Corrine A, Mielens Jason D, Kim Chloe H, McCulloch Timothy M. Evaluating the tongue-hold maneuver using high-resolution manometry and electromyography. Dysphagia. 2014;29:564–70.
Lazarus C, Logemann JA, Song CW, Rademaker AW, Kahrilas PJ. Effects of voluntary maneuvers on tongue base function for swallowing. Folia Phoniatr Logop. 2002;54:171–6.
Doeltgen SH, Witte U, Gumbley F, Huckabee ML. Evaluation of manometric measures during tongue-hold swallows. Am J Speech Lang Pathol. 2008;18:65–73.
Umeki H, Takasaki K, Enatsu K, Tanaka F, Kumagami H, Takahashi H. Effects of a tongue-holding maneuver during swallowing evaluated by high-resolution manometry. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2009;141:119–22.
Fujiu-Kurachi M, Fujiwara S, Tamine K, Kondo J, Minagi Y, Maeda Y, Hori K, Ono T. Tongue pressure generation during tongue-hold swallows in young healthy adults measured with different tongue positions. Dysphagia. 2014;29:17–24.
Hori K, Ono T, Tamine K, Kondo J, Hamanaka S, Maeda Y, Dong J, Hatuda M. Newly developed sensor sheet for measuring tongue pressure during swallowing. J Prosthodont Res. 2009;5:28–32.
Akobeng AK. Understanding diagnostic tests 3: receiver operating characteristic curves. Acta Paediatr. 2007;96:644–7.
Ono T, Hori K, Nokubi T. Pattern of tongue pressure on hard palate during swallowing. Dysphagia. 2004;19:259–64.
Tamine K, Ono T, Hori K, Kondoh J, Hamanaka S, Maeda Y. Age-related changes in tongue pressure during swallowing. J Dent Res. 2010;89:1097–101.
Dodds WJ, Taylor AJ, Stewart ET, Kern MK, Logemann JA, Cook IJ. Tipper and dipper types of oral swallow. Am J Roentgenol. 1989;153:1197–9.
Dodds WJ, Stewart ET, Logemann JA. Physiology and radiology of the normal oral and pharyngeal phase of swallowing. Am J Roentgenol. 1990;154:953–63.
Palmer JB, Hiiemae KM, Liu J. Tongue-jaw linkages in human feeding. Arch Oral Biol. 1997;6:429–41.
Steele CM, Van Lieshout PH. Use of electromagnetic midsagittal articulography in the study of swallowing. J Speech Lang Hear Res. 2004;47:342–52.
Steele CM, Van Lieshout P. Tongue movements during water swallowing in healthy young and older adults. J Speech Lang Hear Res. 2009;52:1255–67.
Stepp Cara E. Surface electromyography for speech and swallowing systems: measurement, analysis, and interpretation. J Speech Lang Hear Res. 2012;55:1232–46.
Palmer PM, Luschei ES, Jaffe D, McCulloch TM. Contributions of individual muscles to the submental surface electromyogram during swallowing. J Speech Lang Hear Res. 1999;42:1378–91.
Palmer PM, Jaffe DM, McCulloch TM, Finnegan EM, Van Daele DJ, Luschei ES. Quantitative contributions of the muscles of the tongue, floor-of-mouth, jaw, and velum to tongue-to-palate pressure generation. J Speech Lang Hear Res. 2008;51:828–35.
Yeates EM, Steele CM, Pelletier CA. Tongue pressure and submental surface electromyography measures during noneffortful and effortful saliva swallows in healthy women. Am J Speech Lang Pathol. 2010;19:274–81.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the Global COE Program “In Silico Medicine” at Osaka University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
None of the authors have financial or other relationships that would influence the assessment of the data or that would constitute a conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fujiwara, S., Fujiu-Kurachi, M., Hori, K. et al. Tongue Pressure Production and Submental Surface Electromyogram Activities During Tongue-Hold Swallow with Different Holding Positions and Tongue Length. Dysphagia 33, 403–413 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00455-017-9865-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00455-017-9865-4