Abstract
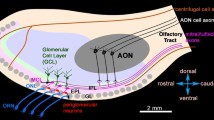
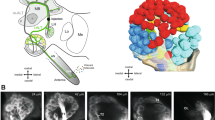
Apis dorsata is an open-nesting, undomesticated, giant honey bee found in southern Asia. We characterized a number of aspects of olfactory system of Apis dorsata and compared it with the well-characterized, western honeybee, Apis mellifera, a domesticated, cavity-nesting species. A. dorsata differs from A. mellifera in nesting behavior, foraging activity, and defense mechanisms. Hence, there can be different demands on its olfactory system. We elucidated the glomerular organization of A. dorsata by creating a digital atlas for the antennal lobe and visualized the antennal lobe tracts and localized their innervations. We showed that the neurites of Kenyon cells with cell bodies located in a neighborhood in calyx retain their relative neighborhoods in the pedunculus and the vertical lobe forming a columnar organization in the mushroom body. The vertical lobe and the calyx of the mushroom body were found to be innervated by extrinsic neurons with cell bodies in the lateral protocerebrum. We found that the species was amenable to olfactory conditioning and showed good learning and memory retention at 24 h after training. It was also amenable to massed and spaced conditioning and could distinguish trained odor from an untrained novel odor. We found that all the above mentioned features in A. dorsata are very similar to those in A. mellifera. We thereby establish A. dorsata as a good model system, strikingly similar to A. mellifera despite the differences in their nesting and foraging behavior.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abel R, Rybak J, Menzel R (2001) Structure and response patterns of olfactory interneurons in the honeybee, Apis mellifera. J Comp Neurol 437(3):363–383
Anton S, Homberg U (1999) Antennal lobe structure. Insect olfaction. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, pp 97–124
Arias MC, Sheppard WS (2005) Phylogenetic relationships of honey bees (Hymenoptera: Apinae: Apini) inferred from nuclear and mitochondrial DNA sequence data. Mol Phylogenet Evol 37(1):25–35
Arnold G, Masson C, Budharugsa S (1985) Comparative study of the antennal lobes and their afferent pathway in the worker bee and the drone (Apis mellifera). Cell Tissue Res 242(3):593–605
Bastin F, Couto A, Larcher V, Phiancharoen M, Koeniger G, Koeniger N, Sandoz JC (2018) Marked interspecific differences in the neuroanatomy of the male olfactory system of honey bees (genus Apis). J Comp Neurol 526(18):3020–3034
Bicker G, Kreissl S, Hofbauer A (1993) Monoclonal antibody labels olfactory and visual pathways in Drosophila and Apis brains. J Comp Neurol 335(3):413–424
Bitterman M, Menzel R, Fietz A, Schäfer S (1983) Classical conditioning of proboscis extension in honeybees (Apis mellifera). J Comp Psychol 97(2):107
Brandt R, Rohlfing T, Rybak J, Krofczik S, Maye A, Westerhoff M, Menzel R (2005) Three-dimensional average shape atlas of the honeybee brain and its applications. J Comp Neurol 492(1):1–19
Brockmann A, Brückner D (1995) Projection pattern of poreplate sensory neurones in honey bee worker, Apis mellifera L. (Hymenoptera: Apidae). Int J Insect Morphol Embryol 24(4):405–411
Brockmann A, Brückner D (2001) Structural differences in the drone olfactory system of two phylogenetically distant Apis species, A florea and A mellifera. Naturwissenschaften 88(2):78–81
Brockmann A, Brückner D (2003) Drone antennae and evolution of sex-pheromone communication in honey bees. Indian Bee J 65(3 & 4):131–138
Carlsson MA, Galizia CG, Hansson BS (2002) Spatial representation of odours in the antennal lobe of the moth Spodoptera littoralis (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). Chem Senses 27(3):231–244
Engel MS (1998) Fossil honey bees and evolution in the genus Apis (Hymenoptera: Apidae). Apidologie 29(3):265–281
Esslen J, Kaissling KE (1976) Zahl und Verteilung antennaler Sensillen bei der Honigbiene (A. mellifera L.). Zoomorphologie 83(3):227–251
Flanagan D, Mercer AR (1989) An atlas and 3-D reconstruction of the antennal lobes in the worker honey bee, Apis mellifera L (Hymenoptera: Apidae). Int J Insect Morphol Embryol 18(2-3):145–159
Fonta C, Sun X, Masson C (1993) Morphology and spatial distribution of bee antennal lobe interneurones responsive to odours. Chem Senses 18(2):101–119
Galizia CG (2008) Insect olfaction. In The Senses: A Comprehensive Reference. Vol 4. Olfaction & taste, ed. S Firestein GK Beauchamp San Diego: Academic: 725–70
Galizia CG, Menzel R (2000) Odour perception in honeybees: coding information in glomerular patterns. Curr Opin Neurobiol 10(4):504–510
Galizia CG, Rössler W (2010) Parallel olfactory systems in insects: anatomy and function. Annu Rev Entomol 55:399–420
Galizia CG, Szyszka P (2008) Olfactory coding in the insect brain: molecular receptive ranges, spatial and temporal coding. Entomologia experimentalis et applicata 128(1):81–92
Galizia CG, McIlwrath SL, Menzel R (1999) A digital three-dimensional atlas of the honeybee antennal lobe based on optical sections acquired by confocal microscopy. Cell Tissue Res 295(3):383–394
Giurfa M (2007) Behavioral and neural analysis of associative learning in the honeybee: a taste from the magic well. J Comp Physiol A 193(8):801–824
Giurfa M, Sandoz JC (2012) Invertebrate learning and memory: fifty years of olfactory conditioning of the proboscis extension response in honeybees. Learn Mem 19(2):54–66
Gowda V (2016) Allometric scaling of brain, brain components and neurons with body size of social bees. https://repository.arizona.edu/handle/10150/621438
Hammer M (1997) The neural basis of associative reward learning in honeybees. Trends Neurosci 20(6):245–252
Hansson BS, Anton S (2000) Function and morphology of the antennal lobe: new developments. Annu Rev Entomol 45(1):203–231
Hildebrand JG, Shepherd GM (1997) Mechanisms of olfactory discrimination: converging evidence for common principles across phyla. Annu Rev Neurosci 20(1):595–631
Ito I, Ong RC, Raman B, Stopfer M (2008) Sparse odor representation and olfactory learning. Nat Neurosci 11(10):1177–1184
Ito K, Shinomiya K, Ito M, Armstrong JD, Boyan G, Hartenstein V, Keshishian H (2014) A systematic nomenclature for the insect brain. Neuron 81(4):755–765
Jung J, Kim DI, Ilyasov R, Kim K, Kwon HW (2017) Comparative study of olfactory learning and memory in Apis cerana and Apis mellifera foragers. Jf Apicult 32(4):275–280
Karpe SD, Jain R, Brockmann A, Sowdhamini R (2016) Identification of complete repertoire of Apis florea odorant receptors reveals complex orthologous relationships with Apis mellifera. Genome Biol Evol 8(9):2879–2895
Kaspi R, Shafir S (2012) Associative olfactory learning of the red dwarf honeybee Apis florea. Apidologie 44(1):100–109
Kirschner S, Kleineidam CJ, Zube C, Rybak J, Grünewald B, Rössler W (2006) Dual olfactory pathway in the honeybee, Apis mellifera. J Comp Neurol 499(6):933–952
Kropf J, Kelber C, Bieringer K, Rossler W (2014) Olfactory subsystems in the honeybee: sensory supply and sex specificity. Cell Tissue Res 357(3):583–595
Kumar NR, Nayyar K, Sharma R, Anudeep A (2014) Ultramorphology of antennal sensilla of open-nesting honey bees Apis florea F. and Apis dorsata F.(Hymenoptera: Apidae). J Appl Nat Sci 6(1):315–319
Laurent G (1997) Olfactory processing: maps, time and codes. Curr Opin Neurobiol 7(4):547–553
Lin T, Li C, Liu J, Smith B H, Lei H, Zeng X (2018) Glomerular organization in the antennal lobe of the oriental fruit fly Bactrocera dorsalis. Front Neuroanat 12
Margulies C, Tully T, Dubnau J (2005) Deconstructing memory in Drosophila. Curr Biol 15(17):R700–R713
Masante-Roca I, Gadenne C, Anton S (2005) Three-dimensional antennal lobe atlas of male and female moths, Lobesia botrana (Lepidoptera: Tortricidae) and glomerular representation of plant volatiles in females. J Exp Biol 208(6):1147–1159
Matsumoto Y, Menzel R, Sandoz JC, Giurfa M (2012) Revisiting olfactory classical conditioning of the proboscis extension response in honey bees: a step toward standardized procedures. J Neurosci Methods 211(1):159–167
Menzel R (1993) Associative learning in honey bees. Apidologie 24(3):157–168
Menzel R (1999) Memory dynamics in the honeybee. J Comp Physiol A 185(4):323–340
Menzel R (2012) The honeybee as a model for understanding the basis of cognition. Nat Rev Neurosci 13(11):758
Menzel R, Erber J (1978) Learning and memory in bees. Sci Am 239(1):102–111
Menzel R, Müller U (1996) Learning and memory in honeybees: from behavior to neural substrates. Annu Rev Neurosci 19(1):379–404
Menzel R, Hammer M, Müller U, Rosenboom H (1996) Behavioral, neural and cellular components underlying olfactory learning in the honeybee. J Physiol 90(5–6):395–398
Menzel R, Manz G, Menzel R, Greggers U (2001) Massed and spaced learning in honeybees: the role of CS, US, the inter trial interval, and the test interval. Learn Mem 8(4):198–208
Mobbs P (1982) The brain of the honeybee Apis mellifera. I The connections and spatial organization of the mushroom bodies. Phil Trans R Soc Lond B 298(1091):309–354
Mombaerts P, Wang DC, Chao SK, Nemes A, Mendelsohn M, Axel R (1996) Visualizing an olfactory sensory map. Cell 87(4):675–686
Muller D, Abel R, Brandt R, Zockler M, Menzel R (2002) Differential parallel processing of olfactory information in the honeybee, Apis mellifera L. J Comp Physiol A Neuroethol Sens Neural Behav Physiol 188(5):359–370
Müller D, Abel R, Brandt R, Zöckler M, Menzel R (2002) Differential parallel processing of olfactory information in the honeybee, Apis mellifera L. J Comp Physiol A 188(5):359–370
Nawrot MP (2012) Dynamics of sensory processing in the dual olfactory pathway of the honeybee. Apidologie 43:269
Nishino H, Nishikawa M, Mizunami M, Yokohari F (2009) Functional and topographic segregation of glomeruli revealed by local staining of antennal sensory neurons in the honeybee Apis mellifera. J Comp Neurol 515(2):161–180
Pareto A (1972) Die zentrale Verteilung der Fühlerafferenz bei Arbeiterinnen der Honigbiene, Apis mellifera L. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat 131(1):109–140
Robertson HM, Wanner KW (2006) The chemoreceptor superfamily in the honey bee Apis mellifera: expansion of the odorant, but not gustatory, receptor family. Genome Res 16(11):000–000
Rospars JP (1988) Structure and development of the insect antennodeutocerebral system. Int J Insect Morphol Embryol 17(3):243–294
Rössler W, Brill MF (2013) Parallel processing in the honeybee olfactory pathway: structure, function, and evolution. J Comp Physiol A 199(11):981–996
Sachse S, Galizia CG (2006) In microcircuits: the interface between neurons and global brain function. Topography and dynamics of the olfactory system. MIT press, Cambridge, MA, pp 251–273
Sandoz JC, Menzel R (2001) Side-specificity of olfactory learning in the honeybee: generalization between odors and sides. Learn Mem 8(5):286–294
Schäfer S, Bicker G (1986) Distribution of GABA-like immunoreactivity in the brain of the honeybee. J Comp Neurol 246(3):287–300
Schindelin J, Arganda-Carreras I, Frise E, Kaynig V, Longair M, Pietzsch T, Tinevez JY (2012) Fiji: an open-source platform for biological-image analysis. Nat Methods 9(7):676
Sinakevitch IT, Smith AN, Locatelli F, Huerta R, Bazhenov M, Smith BH (2013) Apis mellifera octopamine receptor 1 (AmOA1) expression in antennal lobe networks of the honey bee (Apis mellifera) and fruit fly (Drosophila melanogaster). Front Syst Neurosci 7:70
Smith BH, Menzel R (1989) The use of electromyogram recordings to quantify odourant discrimination in the honey bee, Apis mellifera. J Insect Physiol 35(5):369–375
Soucy ER, Albeanu DF, Fantana AL, Murthy VN, Meister M (2009) Precision and diversity in an odor map on the olfactory bulb. Nat Neurosci 12(2):210–220
Squire LR (1987) Memory and brain. Oxford Univ. Press, New York/Oxford
Stopfer M, Jayaraman V, Laurent G (2003) Intensity versus identity coding in an olfactory system. Neuron 39(6):991–1004
Suzuki H (1975) Antennal movements induced by odour and central projection of the antennal neurones in the honey-bee. J Insect Physiol 21(4):831–847
Tully T, Preat T, Boynton S, Del Vecchio M (1994) Genetic dissection of consolidated memory in Drosophila. Cell 79(1):35–47
Wang Z, Tan K (2013) Comparative analysis of olfactory learning of Apis cerana and Apis mellifera. Apidologie 45(1):45–52
Witthöft W (1967) Absolute anzahl und verteilung der zellen im him der honigbiene. Zeitschrift für Morphologie der Tiere 61(1):160–184
Zwaka H, Münch D, Manz G, Menzel R, Rybak J (2016) The circuitry of olfactory projection neurons in the brain of the honeybee, Apis mellifera. Front Neuroanat 10:90
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Uttam Krishna Sharma for his support in procuring Apis dorsata and Shilpi Singh for her support in carrying out electrophysiology and in editing the manuscript. We thank Ravindra Kumar Pydi (National Institute of Rural Development, Hyderabad) for providing Apis mellifera bees. We also thank Prasad Miriyala (Central Instruments Laboratory, University of Hyderabad) and Nalini Manthapuram (Centre for Nanotechnology, University of Hyderabad) for their support in confocal imaging. We are grateful to the UPE scheme of University Grants Commission, India, and DST Purse for providing funding to the University of Hyderabad.
Funding
The study was funded by UPE-UGC, CSIR, and DST Purse.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mogily, S., VijayKumar, M., Sethy, S.K. et al. Characterization of the olfactory system of the giant honey bee, Apis dorsata. Cell Tissue Res 379, 131–145 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-019-03078-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-019-03078-8