Abstract
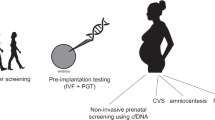
Next-generation sequencing and other genomic technologies are transforming prenatal and reproductive screening and testing for fetal genetic disorders at an unprecedented pace. Original approaches of screening and testing for fetal genetic and genomic disorders were focused on a few more prevalent conditions that were easily diagnosable with pre-genomic era diagnostic tools. First, chromosomal microarray analysis and then next-generation sequencing brought technology capable of more detailed genomic evaluation to prenatal genetic screening and diagnosis. This has facilitated parallel introduction of a variety of new tests on maternal blood samples, including expanded carrier screening and cell-free DNA-based non-invasive screening for fetal aneuploidy, selected copy number variants, and single-gene disorders. Genomic tests on fetal DNA samples, obtained primarily through amniocentesis or chorionic villus sampling, include chromosomal microarray analysis and gene panel and exome sequencing. All these form the diagnostic pillar of the emerging field of fetal precision medicine, but their implementation is associated with ethical, counseling and healthcare resource utilization challenges. We discuss where in the reproductive and prenatal care continuum these exciting new technologies are integrated, along with associated challenges. We propose areas of priority for research to gain the data in support of their responsible implementation into clinical reproductive and prenatal care.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abou Tayoun AN, Spinner NB, Rehm HL, Green RC, Bianchi DW (2018) Prenatal DNA sequencing: clinical, counseling, and diagnostic laboratory considerations. Prenat Diagn 38:26–32. https://doi.org/10.1002/pd.5038
Akolekar R, Beta J, Picciarelli G, Ogilvie C, D’Antonio F (2015) Procedure-related risk of miscarriage following amniocentesis and chorionic villus sampling: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 45:16–26. https://doi.org/10.1002/uog.14636
American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics (ACMG) Board of Directors (2015) ACMG policy statement: updated recommendations regarding analysis and reporting of secondary findings in clinical genome-scale sequencing. Genet Med 17:68–69. https://doi.org/10.1038/gim.2014.151
American College of Obstetrics and Gynecology (ACOG) (2019) Practice Advisory Cell-free DNA to Screen for Single-Gene Disorders. https://www.acog.org/Clinical-Guidance-and-Publications/Practice-Advisories/Cell-free-DNA-to-Screen-for-Single-Gene-Disorders. Accessed 21 Feb 2019
American College of Obstetrics and Gynecology (ACOG) Committee on Genetics (2016a) Practice Bulletin No. 162 Summary: prenatal diagnostic testing for genetic disorders. Obstet Gynecol 127:976–978. https://doi.org/10.1097/aog.0000000000001438
American College of Obstetrics and Gynecology (ACOG) Committee on Genetics (2016b) Practice Bulletin No. 163 Summary: screening for fetal aneuploidy. Obstet Gynecol 127:979–981. https://doi.org/10.1097/aog.0000000000001439
Antonarakis SE (2019) Carrier screening for recessive disorders. Nat Rev Genet 20:549–561. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41576-019-0134-2
Baird PA, Anderson TW, Newcombe HB, Lowry RB (1988) Genetic disorders in children and young adults: a population study. Am J Hum Genet 42:677–693
Beaudet AL (2016) Using fetal cells for prenatal diagnosis: History and recent progress. Am J Med Genet C 172:123–127. https://doi.org/10.1002/ajmg.c.31487
Bell CJ et al (2011) Carrier testing for severe childhood recessive diseases by next-generation sequencing. Sci Transl Med 3:65ra64. https://doi.org/10.1126/scitranslmed.3001756
Best S, Wou K, Vora N, Van den Veyver IB, Wapner R, Chitty LS (2018) Promises, pitfalls and practicalities of prenatal whole exome sequencing. Prenat Diagn 38:10–19. https://doi.org/10.1002/pd.5102
Bianchi DW, Chiu RWK (2018) Sequencing of circulating cell-free DNA during pregnancy. N Engl J Med 379:464–473. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMra1705345
Biesecker LG, Green RC (2014) Diagnostic clinical genome and exome sequencing. N Engl J Med 371:1170. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMc1408914
Chitty LS, David AL, Gottschalk I, Oepkes D, Westgren M, Götherström C, Consortium O (2016) EP21.04. BOOSTB4: clinical study to determine safety and efficacy of pre- and/or postnatal stem cell transplantation for treatment of osteogenesis imperfecta. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 48(S1):356. https://doi.org/10.1002/uog.17084
Chiu RW et al (2008) Noninvasive prenatal diagnosis of fetal chromosomal aneuploidy by massively parallel genomic sequencing of DNA in maternal plasma. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105:20458–20463. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0810641105
Chokoshvili D, Borry P, Vears DF (2017) A systematic analysis of online marketing materials used by providers of expanded carrier screening. Genet Med. https://doi.org/10.1038/gim.2017.222
Clark MM, Stark Z, Farnaes L, Tan TY, White SM, Dimmock D, Kingsmore SF (2018) Meta-analysis of the diagnostic and clinical utility of genome and exome sequencing and chromosomal microarray in children with suspected genetic diseases. NPJ Genom Med 3:16. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41525-018-0053-8
Dhillon RK, Hillman SC, Morris RK, McMullan D, Williams D, Coomarasamy A, Kilby MD (2014) Additional information from chromosomal microarray analysis (CMA) over conventional karyotyping when diagnosing chromosomal abnormalities in miscarriage: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BJOG 121:11–21. https://doi.org/10.1111/1471-0528.12382
Drury S et al (2015) Exome sequencing for prenatal diagnosis of fetuses with sonographic abnormalities. Prenat Diagn 35:1010–1017. https://doi.org/10.1002/pd.4675
Drury S, Mason S, McKay F, Lo K, Boustred C, Jenkins L, Chitty LS (2016) Implementing non-invasive prenatal diagnosis (NIPD) in a national health service laboratory; From Dominant to Recessive Disorders. Adv Exp Med Biol 924:71–75. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-42044-8_14
Eddleman K et al (2003) Pregnancy loss rates after midtrimester amniocentesis: the faster trial. Am J Obstet Gynecol 189:S111
Edwards JG et al (2015) Expanded carrier screening in reproductive medicine-points to consider: a joint statement of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics, American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, National Society of Genetic Counselors, Perinatal Quality Foundation, and Society for Maternal-Fetal Medicine. Obstet Gynecol 125:653–662. https://doi.org/10.1097/AOG.0000000000000666
Evans MI, Wapner RJ, Berkowitz RL (2016) Noninvasive prenatal screening or advanced diagnostic testing: caveat emptor. Am J Obstet Gynecol 215:298–305. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajog.2016.04.029
Fan HC, Blumenfeld YJ, Chitkara U, Hudgins L, Quake SR (2008) Noninvasive diagnosis of fetal aneuploidy by shotgun sequencing DNA from maternal blood. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105:16266–16271. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0808319105
Fan HC, Gu W, Wang J, Blumenfeld YJ, El-Sayed YY, Quake SR (2012) Non-invasive prenatal measurement of the fetal genome. Nature 487:320–324. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature11251
Filges I, Friedman JM (2015) Exome sequencing for gene discovery in lethal fetal disorders—harnessing the value of extreme phenotypes. Prenat Diagn 35:1005–1009. https://doi.org/10.1002/pd.4464
Friedman JM (1981) Genetic disease in the offspring of older fathers. Obstet Gynecol 57:745–749
Gil MM, Quezada MS, Revello R, Akolekar R, Nicolaides KH (2015) Analysis of cell-free DNA in maternal blood in screening for fetal aneuploidies: updated meta-analysis. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 45:249–266. https://doi.org/10.1002/uog.14791
Gray KJ, Wilkins-Haug LE, Herrig NJ, Vora NL (2019) Fetal phenotypes emerge as genetic technologies become robust. Prenat Diagn. https://doi.org/10.1002/pd.5532
Green RC et al (2013) ACMG recommendations for reporting of incidental findings in clinical exome and genome sequencing. Genet Med 15:565–574. https://doi.org/10.1038/gim.2013.73
Gregg AR, Edwards JG (2018) Prenatal genetic carrier screening in the genomic age. Semin Perinatol 42:303–306. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.semperi.2018.07.019
Hayward J, Chitty LS (2018) Beyond screening for chromosomal abnormalities: advances in non-invasive diagnosis of single gene disorders and fetal exome sequencing. Semin Fetal Neonatal Med 23:94–101. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.siny.2017.12.002
Henneman L et al (2016) Responsible implementation of expanded carrier screening. Eur J Hum Genet 24:e1–e12. https://doi.org/10.1038/ejhg.2015.271
Hillman SC et al (2013) Use of prenatal chromosomal microarray: prospective cohort study and systematic review and meta-analysis. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 41:610–620. https://doi.org/10.1002/uog.12464
ISPD, SMFM, PQF (2018) Joint Position Statement from the International Society for Prenatal Diagnosis (ISPD), the Society for Maternal Fetal Medicine (SMFM), and the Perinatal Quality Foundation (PQF) on the use of genome-wide sequencing for fetal diagnosis. Prenat Diagn 38:6–9. https://doi.org/10.1002/pd.5195
Kalia SS et al (2017) Recommendations for reporting of secondary findings in clinical exome and genome sequencing, 2016 update (ACMG SF v2.0): a policy statement of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics. Genet Med 19:249–255. https://doi.org/10.1038/gim.2016.190
Kitzman JO et al (2012) Noninvasive whole-genome sequencing of a human fetus. Sci Transl Med 4:137ra176. https://doi.org/10.1126/scitranslmed.3004323
Kong A et al (2012) Rate of de novo mutations and the importance of father’s age to disease risk. Nature 488:471–475. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature11396
Langlois S, Benn P, Wilkins-Haug L (2015) Current controversies in prenatal diagnosis 4: pre-conception expanded carrier screening should replace all current prenatal screening for specific single gene disorders. Prenat Diagn 35:23–28. https://doi.org/10.1002/pd.4532
Larson JE, Cohen JC (2000) In utero gene therapy. Ochsner J 2:107–110
Lefkowitz RB et al (2016) Clinical validation of a non-invasive prenatal test for genome-wide detection of fetal copy number variants. Am J Obstet Gynecol 215:227.e216–227.e221. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajog.2016.02.030
Lo YM, Corbetta N, Chamberlain PF, Rai V, Sargent IL, Redman CW, Wainscoat JS (1997) Presence of fetal DNA in maternal plasma and serum. Lancet 350:485–487
Lo YM et al (2010) Maternal plasma DNA sequencing reveals the genome-wide genetic and mutational profile of the fetus. Sci Transl Med 2:61ra91. https://doi.org/10.1126/scitranslmed.3001720
Lord J et al (2019) Prenatal exome sequencing analysis in fetal structural anomalies detected by ultrasonography (PAGE): a cohort study. Lancet 393:747–757. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(18)31940-8
Martin J et al (2015) Comprehensive carrier genetic test using next-generation deoxyribonucleic acid sequencing in infertile couples wishing to conceive through assisted reproductive technology. Fertil Steril 104:1286–1293. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fertnstert.2015.07.1166
McKie AB et al (2014) Germline mutations in RYR1 are associated with foetal akinesia deformation sequence/lethal multiple pterygium syndrome. Acta Neuropathol Commun 2:148. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40478-014-0148-0
Meier N et al (2019) Exome sequencing of fetal anomaly syndromes: novel phenotype-genotype discoveries. Eur J Hum Genet 27:730–737. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41431-018-0324-y
Meng L et al (2017) Use of exome sequencing for infants in intensive care units: ascertainment of severe single-gene disorders and effect on medical management. JAMA Pediatr. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamapediatrics.2017.3438
Normand EA, Alaimo JT, Van den Veyver IB (2018a) Exome and genome sequencing in reproductive medicine. Fertil Steril 109:213–220. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fertnstert.2017.12.010
Normand EA et al (2018b) Clinical exome sequencing for fetuses with ultrasound abnormalities and a suspected Mendelian disorder genome medicine 10:74. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13073-018-0582-x
Petrovski S et al (2019) Whole-exome sequencing in the evaluation of fetal structural anomalies: a prospective cohort study. Lancet 393:758–767. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(18)32042-7
Reddy UM et al (2012) Karyotype versus microarray testing for genetic abnormalities after stillbirth. N Engl J Med 367:2185–2193. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1201569
Rezaei M et al (2018) A reappraisal of circulating fetal cell noninvasive prenatal testing. Trends Biotechnol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tibtech.2018.11.001
Richards S et al (2015) Standards and guidelines for the interpretation of sequence variants: a joint consensus recommendation of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics and the Association for Molecular Pathology. Genet Med 17:405–424. https://doi.org/10.1038/gim.2015.30
Rifai N, Topol E, Chan E, Lo YM, Wittwer CT (2015) Disruptive innovation in laboratory medicine. Clin Chem 61:1129–1132. https://doi.org/10.1373/clinchem.2015.243667
Sagar R, Walther-Jallow L, David AL, Götherström C, Westgren M (2018) Fetal mesenchymal stromal cells: an opportunity for prenatal cellular therapy. Curr Stem Cell Rep 4:61–68. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40778-018-0118-8
Schneider H et al (2018) Prenatal correction of X-linked hypohidrotic ectodermal dysplasia. N Engl J Med 378:1604–1610. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1714322
Sun K et al (2018) Size-tagged preferred ends in maternal plasma DNA shed light on the production mechanism and show utility in noninvasive prenatal testing. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1804134115
Suzumori N et al (2018) Compound heterozygous RYR1 mutations by whole exome sequencing in a family with three repeated affected fetuses with fetal akinesia. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 230:200–202. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejogrb.2018.09.013
Toriello HV, Meck JM, Professional P, Guidelines C (2008) Statement on guidance for genetic counseling in advanced paternal age. Genet Med 10:457–460. https://doi.org/10.1097/GIM.0b013e318176fabb
Vestergaard EM et al (2017) On the road to replacing invasive testing with cell-based NIPT: five clinical cases with aneuploidies, microduplication, unbalanced structural rearrangement or mosaicism. Prenat Diagn 37:1120–1124. https://doi.org/10.1002/pd.5150
Vora NL, Hui L (2018) Next-generation sequencing and prenatal ‘omics: advanced diagnostics and new insights into human development. Genet Med 20:791–799. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41436-018-0087-4
Vora NL et al (2017) Prenatal exome sequencing in anomalous fetuses: new opportunities and challenges. Genet Med 19:1207–1216. https://doi.org/10.1038/gim.2017.33
Vossaert L et al (2018) Reliable detection of subchromosomal deletions and duplications using cell-based noninvasive prenatal testing. Prenat Diagn 38:1069–1078. https://doi.org/10.1002/pd.5377
Wapner RJ et al (2012) Chromosomal microarray versus karyotyping for prenatal diagnosis. N Engl J Med 367:2175–2184. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1203382
Williams J 3rd, Rad S, Beauchamp S, Ratousi D, Subramaniam V, Farivar S, Pisarska MD (2015) Utilization of noninvasive prenatal testing: impact on referrals for diagnostic testing. Am J Obstet Gynecol 213(102):e101–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajog.2015.04.005
Wulff CB, Gerds TA, Rode L, Ekelund CK, Petersen OB, Tabor A, Danish Fetal Medicine Study G (2016) Risk of fetal loss associated with invasive testing following combined first-trimester screening for Down syndrome: a national cohort of 147,987 singleton pregnancies. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 47:38–44. https://doi.org/10.1002/uog.15820
Yang Y et al (2014) Molecular findings among patients referred for clinical whole-exome sequencing. JAMA 312:1870–1879. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2014.14601
Zhang J et al (2019) Non-invasive prenatal sequencing for multiple Mendelian monogenic disorders using circulating cell-free fetal DNA. Nat Med 25:439–447. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41591-018-0334-x
Funding
This work is supported in part by the administrative core of the Baylor College of Medicine Intellectual and Developmental disabilities Research Center, National Institutes of Health (NIH) grant U54HD083092. IVdV also receives support for research on prenatal genome sequencing from NIH grant HD055651. The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not represent the official views of the Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development or the National Institutes of Health.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
RS has no conflicts to declare. IVdV conducts research on prenatal genome sequencing research that receives support from Illumina.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sabbagh, R., Van den Veyver, I.B. The current and future impact of genome-wide sequencing on fetal precision medicine. Hum Genet 139, 1121–1130 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00439-019-02088-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00439-019-02088-4