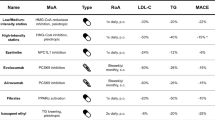
Abstract
Background
Various experimental studies demonstrated that atorvastatin exerted additive effects with anticancer drugs to impair tumor growth, delay relapse, and prolong survival time in lung cancer. However, it is indistinct whether there are survival benefits of atorvastatin in the treatment of small-cell lung cancer (SCLC) patients with dyslipidemia. Therefore, this study aimed to evaluate the efficacy and safety of atorvastatin plus first-line standard chemotherapy in SCLC combined dyslipidemia.
Methods
This was a retrospective analysis of 91 eligible SCLC patients with dyslipidemia registered at the First Teaching Hospital of Tianjin University of Traditional Chinese Medicine from October 2018 to October 2022. SCLC patients with confirmed dyslipidemia were assigned to the treatment group to receive atorvastatin plus first-line standard chemotherapy (n = 45) or to the control group to accept chemotherapy (n = 46) until disease progression or unmanageable toxicity occurred. The clinicopathological parameters and survival data were collected and analyzed. Univariate and multivariate analyses were performed to investigate the prognostic significance of SCLC. The median progression-free survival (mPFS) was considered to be the pivotal symbol as the primary endpoint. The second endpoints were recognized as the median overall survival (mOS) and toxicity.
Results
In the total of 91 enrolled patients, the curative effect can be evaluated in all patients. Research results showed that atorvastatin added to first-line standard chemotherapy was associated with a significant improvement in survival (mPFS: 7.4 vs 6.8 months, P = 0.031; mOS: 14.7 vs 13.2 months, P = 0.002).
Conclusion
Atorvastatin added to first-line standard chemotherapy achieved prospective efficacy and manageable safety in SCLC combined dyslipidemia.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary materials, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
References
Bjarnadottir O, Kimbung S, Johansson I et al (2015) Global transcriptional changes following statin treatment in breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res 21:3402–3411. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-14-1403
Bull CJ, Bonilla C, Holly JMP et al (2016) Blood lipids and prostate cancer: a Mendelian randomization analysis. Cancer Med 5:1125–1136. https://doi.org/10.1002/cam4.695
Chou R, Dana T, Blazina I et al (2016) Statins for prevention of cardiovascular disease in adults: evidence report and systematic review for the US Preventive Services Task Force. JAMA 316:2008–2024. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2015.15629
Cristea S, Coles GL, Hornburg D et al (2020) The MEK5-ERK5 kinase axis controls lipid metabolism in small-cell lung cancer. Cancer Res 80:1293–1303. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-19-1027
Dorsch M, Kowalczyk M, Planque M et al (2021) Statins affect cancer cell plasticity with distinct consequences for tumor progression and metastasis. Cell Rep 37:110056. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2021.110056
Hao B, Yu M, Sang C et al (2018) Dyslipidemia and non-small cell lung cancer risk in Chinese population: a case-control study. Lipids Health Dis 17:278. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12944-018-0925-z
Jiang W, Hu J-W, He X-R et al (2021) Statins: a repurposed drug to fight cancer. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 40:241. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-021-02041-2
Li F-F, Zhang H, Li J-J et al (2018) Interaction with adipocytes induces lung adenocarcinoma A549 cell migration and tumor growth. Mol Med Rep 18:1973–1980. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2018.9226
Luo D, Xiao H, Dong J et al (2017) B7–H3 regulates lipid metabolism of lung cancer through SREBP1-mediated expression of FASN. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 482:1246–1251. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2016.12.021
Mitchell JD, Fergestrom N, Gage BF et al (2018) Impact of statins on cardiovascular outcomes following coronary artery calcium scoring. J Am Coll Cardiol 72:3233–3242. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacc.2018.09.051
Murray M, Hraiki A, Bebawy M et al (2015) Anti-tumor activities of lipids and lipid analogues and their development as potential anticancer drugs. Pharmacol Ther 150:109–128. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pharmthera.2015.01.008
Murtola TJ, Syvälä H, Tolonen T et al (2018) Atorvastatin versus placebo for prostate cancer before radical prostatectomy—a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial. Eur Urol 74:697–701. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eururo.2018.06.037
Prendeville H, Lynch L (2022) Diet, lipids, and antitumor immunity. Cell Mol Immunol 19:432–444. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41423-021-00781-x
Thai AA, Solomon BJ, Sequist LV et al (2021) Lung cancer. Lancet 398:535–554. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(21)00312-3
Touvier M, Fassier P, His M et al (2015) Cholesterol and breast cancer risk: a systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective studies. Br J Nutr 114:347–357. https://doi.org/10.1017/S000711451500183X
Tuerdi G, Ichinomiya S, Sato H et al (2013) Synergistic effect of combined treatment with gamma-tocotrienol and statin on human malignant mesothelioma cells. Cancer Lett 339:116–127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2013.07.015
Xu D, Tong X, Sun L et al (2019) Inhibition of mutant Kras and p53-driven pancreatic carcinogenesis by atorvastatin: mainly via targeting of the farnesylated DNAJA1 in chaperoning mutant p53. Mol Carcinog 58:2052–2064. https://doi.org/10.1002/mc.23097
Funding
This work was supported by grants from the Seventh Batch of National Traditional Chinese Medicine Experts Academic Experience Inheritance Project and the National Key Research and Development (R&D) Plan (no. 2018YFC1707400).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Data collection and formal analysis were performed by FK and NW. The first draft of the manuscript was written by NW and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There are no conflicts of interest.
Ethics statements
Ethical review and approval were not required for the study of human participants in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kong, F., Wang, N., Gao, F. et al. The clinical application of atorvastatin in patients with small-cell lung cancer with dyslipidemia. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 149, 13697–13704 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-023-05102-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-023-05102-5