Abstract
Purpose
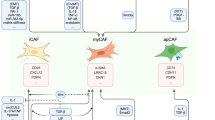
Lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD) accounts for approximately half of patients in lung cancer. Cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs) are the major component in the tumor microenvironment (TME). Targeting CAFs is a promising therapeutic strategy for cancer treatment. However, therapeutic targets of CAFs in LUAD remains largely unclear.
Methods
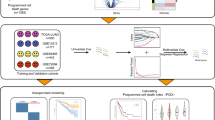
Seven CAFs and nine normal fibroblasts (NFs) were isolated from tumor and paratumor tissues of LUAD patients undergoing surgery, respectively. RNA-seq and bioinformatics analysis were performed to identify the differentially expressed genes (DEGs) and their functions in CAFs compared with NFs. DEGs of ten overlaying were obtained from RNA-seq, our previously reported lncRNA microarray and public datasets (E-MTAB-6149, E-MTAB-6653) and validated by RT-qPCR. Nik-related kinase (NRK) was further validated by RT-qPCR, immunofluorescence (IF), Western Blot (WB) in vitro, and in Cancer Cell Line Encyclopedia (CCLE) database. Survival analysis was performed on Kaplan–Meier plotter.
Results
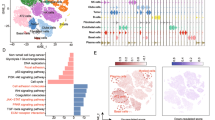
A total of 1799 DEGs were identified, including 650 upregulated DEGs and 1149 downregulated DEGs. The upregulated and downregulated DEGs were mostly enriched in extracellular matrix (ECM) functions and in glycolysis/gluconeogenesis pathways. Interestingly, NRK was the most significantly upregulated overlaying DEGs which was rarely associated with CAFs before. NRK was predominantly expressed in CAFs, but weakly expressed in NFs, normal lung bronchial epithelial cell line BEAS-2B, LUAD cell lines A549 and H1299, as well as in the majority of 191 lung cancer cell lines including LUAD. Moreover, elevated NRK predicted poor survival in LUAD patients.
Conclusion
Here, we first report that NRK is significantly elevated in LUAD-associated CAFs and may function as a promising therapeutic target for cancer combination treatment. Besides, modulation of ECM and glycolysis/gluconeogenesis pathways may be an efficient approach to alter CAFs functionality in LUAD.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article and its supplementary information files.
Abbreviations
- CAFs:
-
Cancer-associated fibroblasts
- CCLE:
-
Cancer Cell Line Encyclopedia
- CSCs:
-
Cancer stem cells
- DEGs:
-
Differentially expressed genes
- ECM:
-
Extracellular matrix
- FC:
-
Fold change
- GO:
-
Gene Ontology
- IF:
-
Immunofluorescence
- KEGG:
-
Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes
- LUAD:
-
Lung adenocarcinoma
- LUSC:
-
Lung squamous cell carcinoma
- NFs:
-
Normal fibroblasts
- NRK:
-
Nik-related kinase
- NSCLC:
-
Non-small cell lung cancer
- RT-qPCR:
-
Real-time Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction
- SCLC:
-
Small cell lung cancer
- TME:
-
Tumor microenvironment
- WB:
-
Western Blot
References
Alba-Castellón L et al (2016) Snail1-dependent activation of cancer-associated fibroblast controls epithelial tumor cell invasion and metastasis. Cancer Res 76:6205–6217. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.Can-16-0176
Au Yeung CL et al (2016) Exosomal transfer of stroma-derived miR21 confers paclitaxel resistance in ovarian cancer cells through targeting APAF1. Nat Commun 7:11150. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms11150
Belli C et al (2018) Targeting the microenvironment in solid tumors. Cancer Treat Rev 65:22–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ctrv.2018.02.004
Boesch M, Sopper S, Zeimet AG, Reimer D, Gastl G, Ludewig B, Wolf D (2016) Heterogeneity of cancer stem cells: rationale for targeting the stem cell niche. Biochem Biophys Acta 1866:276–289. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbcan.2016.10.003
Boesch M et al (2018) Interleukin 7-expressing fibroblasts promote breast cancer growth through sustenance of tumor cell stemness. Oncoimmunology 7:e1414129. https://doi.org/10.1080/2162402x.2017.1414129
Boesch M, Baty F, Rumpold H, Sopper S, Wolf D, Brutsche MH (2019) Fibroblasts in cancer: defining target structures for therapeutic intervention. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer 1872:111–121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbcan.2019.06.003
Brechbuhl HM et al (2017) Fibroblast subtypes regulate responsiveness of luminal breast cancer to estrogen. Clin Cancer Res 23:1710–1721. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.Ccr-15-2851
Bussard KM, Mutkus L, Stumpf K, Gomez-Manzano C, Marini FC (2016) Tumor-associated stromal cells as key contributors to the tumor microenvironment. Breast Cancer Res 18:84. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13058-016-0740-2
Calon A et al (2015) Stromal gene expression defines poor-prognosis subtypes in colorectal cancer. Nat Genet 47:320–329. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.3225
Chen X, Song E (2019) Turning foes to friends: targeting cancer-associated fibroblasts. Nat Rev Drug Discov 18:99–115. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41573-018-0004-1
Cheng HW et al (2018) CCL19-producing fibroblastic stromal cells restrain lung carcinoma growth by promoting local antitumor T-cell responses. J Allergy Clin Immunol 142:1257-1271.e1254. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaci.2017.12.998
Costa A et al (2018) Fibroblast heterogeneity and immunosuppressive environment in human breast cancer. Cancer Cell 33:463-479.e410. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccell.2018.01.011
De Wever O, Nguyen QD, Van Hoorde L, Bracke M, Bruyneel E, Gespach C, Mareel M (2004) Tenascin-C and SF/HGF produced by myofibroblasts in vitro provide convergent pro-invasive signals to human colon cancer cells through RhoA and Rac. Faseb J 18:1016–1018. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.03-1110fje
DeFilippis RA et al (2012) CD36 repression activates a multicellular stromal program shared by high mammographic density and tumor tissues. Cancer Discov 2:826–839. https://doi.org/10.1158/2159-8290.Cd-12-0107
Denda K et al (2011) Nrk, an X-linked protein kinase in the germinal center kinase family, is required for placental development and fetoplacental induction of labor. J Biol Chem 286:28802–28810. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M111.258160
Dong P, Yu B, Pan L, Tian X, Liu F (2018) Identification of key genes and pathways in triple-negative breast cancer by integrated bioinformatics analysis. Biomed Res Int 2018:2760918. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/2760918
Dumont N et al (2013) Breast fibroblasts modulate early dissemination, tumorigenesis, and metastasis through alteration of extracellular matrix characteristics. Neoplasia 15:249–262. https://doi.org/10.1593/neo.121950
Elyada E et al (2019) Cross-species single-cell analysis of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma reveals antigen-presenting cancer-associated fibroblasts. Cancer Discov 9:1102–1123. https://doi.org/10.1158/2159-8290.Cd-19-0094
Ernst C, Sequeira A, Klempan T, Ernst N, Ffrench-Mullen J, Turecki G (2007) Confirmation of region-specific patterns of gene expression in the human brain. Neurogenetics 8:219–224. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10048-007-0084-2
Feig C et al (2013) Targeting CXCL12 from FAP-expressing carcinoma-associated fibroblasts synergizes with anti-PD-L1 immunotherapy in pancreatic cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 110:20212–20217. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1320318110
Ferrer-Mayorga G et al (2017) Vitamin D receptor expression and associated gene signature in tumour stromal fibroblasts predict clinical outcome in colorectal cancer. Gut 66:1449–1462. https://doi.org/10.1136/gutjnl-2015-310977
Franco-Barraza J et al (2017) Matrix-regulated integrin α(v)β(5) maintains α(5)β(1)-dependent desmoplastic traits prognostic of neoplastic recurrence. Elife. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.20600
Froeling FE et al (2011) Retinoic acid-induced pancreatic stellate cell quiescence reduces paracrine Wnt-β-catenin signaling to slow tumor progression. Gastroenterology 141(1486–1497):1497.e1481–1414. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2011.06.047
Gaggioli C, Hooper S, Hidalgo-Carcedo C, Grosse R, Marshall JF, Harrington K, Sahai E (2007) Fibroblast-led collective invasion of carcinoma cells with differing roles for RhoGTPases in leading and following cells. Nat Cell Biol 9:1392–1400. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb1658
Gascard P, Tlsty TD (2016) Carcinoma-associated fibroblasts: orchestrating the composition of malignancy. Genes Dev 30:1002–1019. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.279737.116
Goetz JG et al (2011) Biomechanical remodeling of the microenvironment by stromal caveolin-1 favors tumor invasion and metastasis. Cell 146:148–163. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2011.05.040
Guinney J et al (2015) The consensus molecular subtypes of colorectal cancer. Nat Med 21:1350–1356. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.3967
Hah N, Sherman MH, Yu RT, Downes M, Evans RM (2015) Targeting transcriptional and epigenetic reprogramming in stromal cells in fibrosis and cancer. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol 80:249–255. https://doi.org/10.1101/sqb.2015.80.027185
Harryvan TJ, Verdegaal EME, Hardwick JCH, Hawinkels L, van der Burg SH (2019) Targeting of the cancer-associated fibroblast-T-cell axis in solid malignancies. J Clin Med. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8111989
Hegab AE et al (2019) Effect of FGF/FGFR pathway blocking on lung adenocarcinoma and its cancer-associated fibroblasts. J Pathol 249:193–205. https://doi.org/10.1002/path.5290
Herbst RS, Morgensztern D, Boshoff C (2018) The biology and management of non-small cell lung cancer. Nature 553:446–454. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature25183
Hirata E et al (2015) Intravital imaging reveals how BRAF inhibition generates drug-tolerant microenvironments with high integrin β1/FAK signaling. Cancer Cell 27:574–588. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccell.2015.03.008
Hofheinz RD et al (2003) Stromal antigen targeting by a humanised monoclonal antibody: an early phase II trial of sibrotuzumab in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. Onkologie 26:44–48. https://doi.org/10.1159/000069863
Hooper S, Gaggioli C, Sahai E (2010) A chemical biology screen reveals a role for Rab21-mediated control of actomyosin contractility in fibroblast-driven cancer invasion. Br J Cancer 102:392–402. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bjc.6605469
Kakarla S et al (2013) Antitumor effects of chimeric receptor engineered human T cells directed to tumor stroma. Mol Ther 21:1611–1620. https://doi.org/10.1038/mt.2013.110
Kalluri R (2016) The biology and function of fibroblasts in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 16:582–598. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrc.2016.73
Kanai-Azuma M, Kanai Y, Okamoto M, Hayashi Y, Yonekawa H, Yazaki K (1999) Nrk: a murine X-linked NIK (Nck-interacting kinase)-related kinase gene expressed in skeletal muscle. Mech Dev 89:155–159. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0925-4773(99)00193-8
Kaur A et al (2019) Remodeling of the collagen matrix in aging skin promotes melanoma metastasis and affects immune cell motility. Cancer Discov 9:64–81. https://doi.org/10.1158/2159-8290.Cd-18-0193
Kobayashi H, Enomoto A, Woods SL, Burt AD, Takahashi M, Worthley DL (2019) Cancer-associated fibroblasts in gastrointestinal cancer. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 16:282–295. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41575-019-0115-0
Kraman M et al (2010) Suppression of antitumor immunity by stromal cells expressing fibroblast activation protein-alpha. Science (New York, NY) 330:827–830. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1195300
Kumar D et al (2018) Cancer-associated fibroblasts drive glycolysis in a targetable signaling loop implicated in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma progression. Cancer Res 78:3769–3782. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.Can-17-1076
Li M et al (2016) Targeting of cancer-associated fibroblasts enhances the efficacy of cancer chemotherapy by regulating the tumor microenvironment. Mol Med Rep 13:2476–2484. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2016.4868
Liu T, Han C, Wang S, Fang P, Ma Z, Xu L, Yin R (2019) Cancer-associated fibroblasts: an emerging target of anti-cancer immunotherapy. J Hematol Oncol 12:86. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13045-019-0770-1
Lo A et al (2015) Tumor-promoting desmoplasia is disrupted by depleting FAP-expressing stromal cells. Cancer Res 75:2800–2810. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.Can-14-3041
Lu YJ et al (2020) Expression of Nik-related kinase in smooth muscle cells attenuates vascular inflammation and intimal hyperplasia. Aging (Albany NY) 12:7511–7533. https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.103104
Luo M et al (2018) Cancer-associated fibroblasts accelerate malignant progression of non-small cell lung cancer via connexin 43-formed unidirectional gap junctional intercellular communication. Cell Physiol Biochem 51:315–336. https://doi.org/10.1159/000495232
Madsen CD et al (2015) Hypoxia and loss of PHD2 inactivate stromal fibroblasts to decrease tumour stiffness and metastasis. EMBO Rep 16:1394–1408. https://doi.org/10.15252/embr.201540107
Morioka Y, Nam JM, Ohashi T (2017) Nik-related kinase regulates trophoblast proliferation and placental development by modulating AKT phosphorylation. PLoS ONE 12:e0171503. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0171503
Nakano K, Kanai-Azuma M, Kanai Y, Moriyama K, Yazaki K, Hayashi Y, Kitamura N (2003) Cofilin phosphorylation and actin polymerization by NRK/NESK, a member of the germinal center kinase family. Exp Cell Res 287:219–227. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0014-4827(03)00136-8
Niu X et al (2019) Dermal mesenchymal stem cells: a resource of migration-associated function in psoriasis? Stem Cell Res Ther 10:54. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13287-019-1159-3
Okami J et al (2019) Demographics, safety and quality, and prognostic information in both the seventh and eighth editions of the TNM classification in 18,973 surgical cases of the Japanese joint committee of lung cancer registry database in 2010. J Thorac Oncol 14:212–222. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtho.2018.10.002
Özdemir BC et al (2014) Depletion of carcinoma-associated fibroblasts and fibrosis induces immunosuppression and accelerates pancreas cancer with reduced survival. Cancer Cell 25:719–734. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccr.2014.04.005
Pavlides S et al (2009) The reverse Warburg effect: aerobic glycolysis in cancer associated fibroblasts and the tumor stroma. Cell Cycle 8:3984–4001. https://doi.org/10.4161/cc.8.23.10238
Pein M et al (2020) Metastasis-initiating cells induce and exploit a fibroblast niche to fuel malignant colonization of the lungs. Nat Commun 11:1494. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-15188-x
Puram SV et al (2017) Single-cell transcriptomic analysis of primary and metastatic tumor ecosystems in head and neck cancer. Cell 171:1611-1624.e1624. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2017.10.044
Roberts EW et al (2013) Depletion of stromal cells expressing fibroblast activation protein-α from skeletal muscle and bone marrow results in cachexia and anemia. J Exp Med 210:1137–1151. https://doi.org/10.1084/jem.20122344
Roma-Rodrigues C, Mendes R, Baptista PV, Fernandes AR (2019) Targeting tumor microenvironment for cancer therapy. Int J Mol Sci. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20040840
Sahai E et al (2020) A framework for advancing our understanding of cancer-associated fibroblasts. Nat Rev Cancer 20:174–186. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41568-019-0238-1
Sherman MH et al (2014) Vitamin D receptor-mediated stromal reprogramming suppresses pancreatitis and enhances pancreatic cancer therapy. Cell 159:80–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2014.08.007
Shi Y et al (2020) Clinicopathological characteristics and prediction of cancer-specific survival in large cell lung cancer: a population-based study. J Thorac Dis 12:2261–2269. https://doi.org/10.21037/jtd.2020.04.24
Su S et al (2018) CD10+GPR77+Cancer-associated fibroblasts promote cancer formation and chemoresistance by sustaining cancer stemness. Cell 172(841–856):e816. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2018.01.009
Sun S, Schiller JH, Gazdar AF (2007) Lung cancer in never smokers–a different disease. Nat Rev Cancer 7:778–790. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrc2190
Teng C et al (2019) Differential long noncoding RNAs expression in cancer-associated fibroblasts of non-small-cell lung cancer. Pharmacogenomics 20:143–153. https://doi.org/10.2217/pgs-2018-0102
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J, Lortet-Tieulent J, Jemal A (2015) Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin 65:87–108. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21262
US National Library of Medicine. ClinicalTrials.gov. (2017). https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01130142.
US National Library of Medicine. ClinicalTrials.gov. (2018). http://www.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01373164.
US National Library of Medicine. ClinicalTrials.gov. (2020). https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02688712.
Walters S et al (2013) Lung cancer survival and stage at diagnosis in Australia, Canada, Denmark, Norway, Sweden and the UK: a population-based study, 2004–2007. Thorax 68:551–564. https://doi.org/10.1136/thoraxjnl-2012-202297
Wang LC et al (2014) Targeting fibroblast activation protein in tumor stroma with chimeric antigen receptor T cells can inhibit tumor growth and augment host immunity without severe toxicity. Cancer Immunol Res 2:154–166. https://doi.org/10.1158/2326-6066.Cir-13-0027
Wu T, Dai Y (2017) Tumor microenvironment and therapeutic response. Cancer Lett 387:61–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2016.01.043
Xie J et al (2020) Antitumor immunity targeting fibroblast activation protein-α in a mouse Lewis lung carcinoma model. Oncol Lett 20:868–876. https://doi.org/10.3892/ol.2020.11637
Yanagawa T et al (2016) Deficiency of X-linked protein kinase Nrk during pregnancy triggers breast tumor in mice. Am J Pathol 186:2751–2760. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajpath.2016.06.005
Ye M et al (2017) Combined inhibitions of glycolysis and AKT/autophagy can overcome resistance to EGFR-targeted therapy of lung cancer. J Cancer 8:3774–3784. https://doi.org/10.7150/jca.21035
Ziani L, Chouaib S, Thiery J (2018) Alteration of the antitumor immune response by cancer-associated fibroblasts. Front Immunol 9:414. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2018.00414
Acknowledgements
We express our gratitude to research team of Prof. Huaxin Hou and Prof. Danrong Li, who provided countless assistance during experiment process.
Funding
This study is funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81860649), Natural Science Foundation of Guangxi (No. 2018GXNSFAA050053), and Innovation Project of Guangxi Graduate Education (No. YCBZ2020054). This research was also funded by the first batch of cultivating talents of young and middle-aged backbone teachers in Guangxi universities and Guangxi First-class Discipline Project for Pharmaceutical Sciences (No. GXFCDP-PS-2018) and the Project of Innovation, Entrepreneurship, and Joint Training Base for Pharmaceutical Postgraduates.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Experiments procedure and paper writing were conducted by TW. TW, JS and KL collected clinical specimens and pathological information, LL, XM, and NM helped to obtained signed informed consent from patients. Data were processed by TW, JS, and KL. ZH and GC offer excellent technical assistance. JY designed the study and revised the manuscript. All authors read and reached agreement on final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Patients signed the written informed consent and the study was approved by the Committee of Ethics, Guangxi Medical University, China.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wei, T., Song, J., Liang, K. et al. Identification of a novel therapeutic candidate, NRK, in primary cancer-associated fibroblasts of lung adenocarcinoma microenvironment. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 147, 1049–1064 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-020-03489-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-020-03489-z