Abstract
Purpose
The aim of this study was to elucidate the clinical impact of skeletal muscle area (SMA) in patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) treated with anti-programmed cell death-1 (PD-1) inhibitors.
Methods
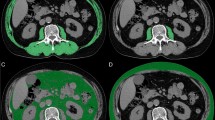
Univariate and multivariate analyses were performed on data of 103 patients with advanced or recurrent NSCLC treated with anti-PD-1 inhibitors. The SMA was measured at the level of the third lumbar vertebral (L3) on computed tomography images using OsiriX software (32-bit, version 5.8; OsiriX, Geneva, Switzerland). The L3 muscle index (cm2/m2) was defined as the SMA (cm2) at the L3 level divided by the height (m) squared.
Results
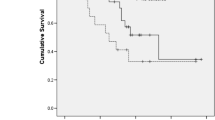
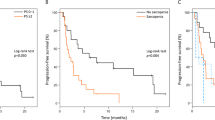
L3 muscle index Low was an independent predictor of both progression-free (P = 0.0399) and overall survival (P = 0.0155). Moreover, the disease control rate was significantly lower in the L3 muscle index Low group (49.0% [25/51]) than in the L3 muscle index High group (73.1% [38/52]; P = 0.0117). However, there was no significant difference between the response rates of the L3 muscle index Low group (21.6% [11/51]) and L3 muscle index High group (32.7% [17/52]; P = 0.2031).
Conclusions
L3 muscle index Low is an independent predictor of worse outcomes in NSCLC patients treated with anti-PD-1 inhibitors.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bahat G et al (2016) Cut-off points to identify sarcopenia according to European working group on sarcopenia in older people (EWGSOP) definition. Clin Nutr 35:1557–1563. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clnu.2016.02.002
Borghaei H et al (2015) Nivolumab versus docetaxel in advanced nonsquamous non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med 373:1627–1639. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1507643
Brahmer JR et al (2012) Safety and activity of anti-PD-L1 antibody in patients with advanced cancer. N Engl J Med 366:2455–2465. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1200694
Brahmer J et al (2015) Nivolumab versus docetaxel in advanced squamous-cell non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med 373:123–135. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1504627
Cortellini A et al (2019) A multicenter study of body mass index in cancer patients treated with anti-PD-1/PD-L1 immune checkpoint inhibitors: when overweight becomes favorable. J Immunother Cancer 7:57. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40425-019-0527-y
Cruz-Jentoft AJ et al (2010) Sarcopenia: European consensus on definition and diagnosis: report of the European working group on sarcopenia in older people. Age Ageing 39:412–423. https://doi.org/10.1093/ageing/afq034
Currow D, Temel JS, Abernethy A, Milanowski J, Friend J, Fearon KC (2017) ROMANA 3: a phase 3 safety extension study of anamorelin in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients with cachexia. Ann Oncol 28:1949–1956. https://doi.org/10.1093/annonc/mdx192
Daly LE et al (2017) The impact of body composition parameters on ipilimumab toxicity and survival in patients with metastatic melanoma. Br J Cancer 116:310–317. https://doi.org/10.1038/bjc.2016.431
Dobs AS et al (2013) Effects of enobosarm on muscle wasting and physical function in patients with cancer: a double-blind, randomised controlled phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol 14:335–345. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1470-2045(13)70055-x
Eisenhauer EA et al (2009) New response evaluation criteria in solid tumours: revised RECIST guideline (version 1.1). Eur J Cancer 45:228–247. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejca.2008.10.026
Rosemberg IH (1989) Epidemiologic and methodologic problems in determining nutritional status of older persons. Proceedings of a conference. Albuquerque, New Mexico, October 19–21, 1988. Am J Clin Nutr 50:1121–1235
Fehrenbacher L et al (2016) Atezolizumab versus docetaxel for patients with previously treated non-small-cell lung cancer (POPLAR): a multicentre, open-label, phase 2 randomised controlled trial. Lancet 387:1837–1846
Garon EB et al (2015) Pembrolizumab for the treatment of non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med 372:2018–2028. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1501824
Goldstraw P et al (2016) The IASLC lung cancer staging project: proposals for revision of the TNM stage groupings in the forthcoming (eighth) edition of the TNM classification for lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol 11:39–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtho.2015.09.009
Harimoto N et al (2016) Sarcopenia is a poor prognostic factor following hepatic resection in patients aged 70 years and older with hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatol Res 46:1247–1255. https://doi.org/10.1111/hepr.12674
Heidelberger V et al (2017) Sarcopenic overweight is associated with early acute limiting toxicity of anti-PD1 checkpoint inhibitors in melanoma patients. Investig New Drugs 35:436–441. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-017-0464-x
Herbst RS et al (2014) Predictive correlates of response to the anti-PD-L1 antibody MPDL3280A in cancer patients. Nature 515:563–567. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature14011
Herbst RS et al (2016) Pembrolizumab versus docetaxel for previously treated, PD-L1-positive, advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (KEYNOTE-010): a randomised controlled trial. Lancet 387:1540–1550
Ichihara E et al (2020) The impact of body mass index on the efficacy of anti-PD-1/PD-L1 antibodies in patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 139:140–145. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lungcan.2019.11.011
Kanai O, Fujita K, Okamura M, Nakatani K, Mio T (2016) Severe exacerbation or manifestation of primary disease related to nivolumab in non-small-cell lung cancer patients with poor performance status or brain metastases. Ann Oncol 27:1354–1356. https://doi.org/10.1093/annonc/mdw148
Kichenadasse G, Miners JO, Mangoni AA, Rowland A, Hopkins AM, Sorich MJ (2019) Association between body mass index and overall survival with immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy for advanced non-small cell lung cancer. JAMA Oncol. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamaoncol.2019.5241
Kim EY, Kim YS, Park I, Ahn HK, Cho EK, Jeong YM (2015) Prognostic significance of CT-determined sarcopenia in patients with small-cell lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol 10:1795–1799. https://doi.org/10.1097/jto.0000000000000690
Marchetti A et al (2016) ALK protein analysis by IHC staining after recent regulatory changes: a comparison of two widely used approaches, revision of the literature, and a new testing algorithm. J Thorac Oncol 11:487–495. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtho.2015.12.111
Martin L et al (2013) Cancer cachexia in the age of obesity: skeletal muscle depletion is a powerful prognostic factor, independent of body mass index. J Clin Oncol 31:1539–1547. https://doi.org/10.1200/jco.2012.45.2722
Mijnarends DM et al (2013) Validity and reliability of tools to measure muscle mass, strength, and physical performance in community-dwelling older people: a systematic review. J Am Med Dir Assoc 14:170–178. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jamda.2012.10.009
Mok TSK et al (2019) Pembrolizumab versus chemotherapy for previously untreated, PD-L1-expressing, locally advanced or metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer (KEYNOTE-042): a randomised, open-label, controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet 393:1819–1830. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(18)32409-7
Mourtzakis M, Prado CM, Lieffers JR, Reiman T, McCargar LJ, Baracos VE (2008) A practical and precise approach to quantification of body composition in cancer patients using computed tomography images acquired during routine care. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab 33:997–1006. https://doi.org/10.1139/h08-075
Nagai Y et al (2005) Genetic heterogeneity of the epidermal growth factor receptor in non-small cell lung cancer cell lines revealed by a rapid and sensitive detection system, the peptide nucleic acid-locked nucleic acid PCR clamp. Cancer Res 65:7276–7282. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.can-05-0331
Nishie K, Yamamoto S, Nagata C, Koizumi T, Hanaoka M (2017) Anamorelin for advanced non-small-cell lung cancer with cachexia: systematic review and meta-analysis. Lung Cancer 112:25–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lungcan.2017.07.023
Nishioka N et al (2019) Association of sarcopenia with and efficacy of Anti-PD-1/PD-L1 therapy in non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Med 8:450. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8040450
Pardoll DM (2012) The blockade of immune checkpoints in cancer immunotherapy. Nat Rev Cancer 12:252–264. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrc3239
Prado CM, Lieffers JR, McCargar LJ, Reiman T, Sawyer MB, Martin L, Baracos VE (2008) Prevalence and clinical implications of sarcopenic obesity in patients with solid tumours of the respiratory and gastrointestinal tracts: a population-based study. Lancet Oncol 9:629–635. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1470-2045(08)70153-0
Prado CM, Birdsell LA, Baracos VE (2009) The emerging role of computerized tomography in assessing cancer cachexia. Curr Opin Support Palliat Care 3:269–275. https://doi.org/10.1097/SPC.0b013e328331124a
Reck M et al (2016) Pembrolizumab versus chemotherapy for PD-L1-positive non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med 375:1823–1833. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1606774
Reck M et al (2019) Updated analysis of KEYNOTE-024: pembrolizumab versus platinum-based chemotherapy for advanced non-small-cell lung cancer with PD-L1 tumor proportion score of 50% or greater. J Clin Oncol 37:537–546. https://doi.org/10.1200/jco.18.00149
Rier HN, Jager A, Sleijfer S, Maier AB, Levin MD (2016) The prevalence and prognostic value of low muscle mass in cancer patients: a review of the literature. Oncologist 21:1396–1409. https://doi.org/10.1634/theoncologist.2016-0066
Rittmeyer A et al (2016) Atezolizumab versus docetaxel in patients with previously treated non-small-cell lung cancer (OAK): a phase 3, open-label, multicentre randomised controlled trial. Lancet. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(16)32517-x
Rosenberg IH (1997) Sarcopenia: origins and clinical relevance. J Nutr 127:990s–991s. https://doi.org/10.1093/jn/127.5.990S
Rutten IJ, van Dijk DP, Kruitwagen RF, Beets-Tan RG, Olde Damink SW, van Gorp T (2016) Loss of skeletal muscle during neoadjuvant chemotherapy is related to decreased survival in ovarian cancer patients. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 7:458–466. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcsm.12107
Sanada K et al (2010) A cross-sectional study of sarcopenia in Japanese men and women: reference values and association with cardiovascular risk factors. Eur J Appl Physiol 110:57–65. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-010-1473-z
Shachar SS, Williams GR, Muss HB, Nishijima TF (2016) Prognostic value of sarcopenia in adults with solid tumours: a meta-analysis and systematic review. Eur J Cancer 57:58–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejca.2015.12.030
Shiroyama T et al (2019) Impact of sarcopenia in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer treated with PD-1 inhibitors: a preliminary retrospective study. Sci Rep 9:2447. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-39120-6
Suzuki Y et al (2016) Clinical implications of sarcopenia in patients undergoing complete resection for early non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 101:92–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lungcan.2016.08.007
Takamori S et al (2018) Clinical impact and risk factors for skeletal muscle loss after complete resection of early non-small cell lung cancer. Ann Surg Oncol 25:1229–1236. https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-017-6328-y
Temel JS, Abernethy AP, Currow DC, Friend J, Duus EM, Yan Y, Fearon KC (2016) Anamorelin in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer and cachexia (ROMANA 1 and ROMANA 2): results from two randomised, double-blind, phase 3 trials. Lancet Oncol 17:519–531. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1470-2045(15)00558-6
Teraoka S et al (2017) Early immune-related adverse events and association with outcome in advanced non-small cell lung cancer patients treated with nivolumab: a prospective cohort study. J Thorac Oncol 12:1798–1805. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtho.2017.08.022
Tisdale MJ (2001) Cancer anorexia and cachexia. Nutrition 17:438–442
Topalian SL et al (2012) Safety, activity, and immune correlates of anti-PD-1 antibody in cancer. N Engl J Med 366:2443–2454. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1200690
Villasenor A, Ballard-Barbash R, Baumgartner K, Baumgartner R, Bernstein L, McTiernan A, Neuhouser ML (2012) Prevalence and prognostic effect of sarcopenia in breast cancer survivors: the HEAL study. J Cancer Surviv 6:398–406. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11764-012-0234-x
Wherry EJ (2011) T cell exhaustion. Nat Immunol 12:492–499
Zengin A et al (2017) Associations of muscle force, power, cross-sectional muscle area and bone geometry in older UK men. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 8:598–606. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcsm.12198
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr. Trish Reynolds, MBBS, FRACP, from Edanz Group (www.edanzediting.com/ac) for editing a draft of this manuscript.
Funding
This work was not supported by any funding sources.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. For this type of study formal consent is not required.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
432_2020_3146_MOESM1_ESM.tif
Supplementary file1 (TIF 10272 kb) Association between L3 muscle index and BMI in patients with non-small cell lung cancer treated with anti-PD-1 inhibitors. BMI, body mass index; L3, third lumbar vertebra; PD-1, programmed cell death-1
432_2020_3146_MOESM2_ESM.tif
Supplementary file2 (TIF 10272 kb) Kaplan–Meier curves showing survival of patients with non-small cell lung cancer treated with anti-PD-1 inhibitors according to BMI status. (a) Progression-free survival and (b) overall survival. BMI, body mass index; PD-1, programmed cell death-1
432_2020_3146_MOESM3_ESM.tif
Supplementary file3 (TIF 10272 kb) Association between BMI status and treatment response in patients with non-small cell lung cancer treated with anti-PD-1 inhibitors. (a) Response rate and (b) disease control rate. Responses were determined according to the Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors. BMI, body mass index; CR, complete response; PD, progressive disease; PD-1, programmed cell death-1; PR, partial response; SD, stable disease
432_2020_3146_MOESM5_ESM.tif
Supplementary file5 (TIF 10272 kb) Association between PD-L1 tumor expression status and treatment response in patients with non-small cell lung cancer treated with anti-PD-1 inhibitors. (a) Response rate and (b) disease control rate. Responses were determined according to the Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors. CR, complete response; PD, progressive disease; PD-1, programmed cell death-1; PD-L1, programmed cell death-ligand 1; PR, partial response; SD, stable disease; TPS, tumor proportion score
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Takada, K., Yoneshima, Y., Tanaka, K. et al. Clinical impact of skeletal muscle area in patients with non-small cell lung cancer treated with anti-PD-1 inhibitors. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 146, 1217–1225 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-020-03146-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-020-03146-5