Abstract
Purpose
This study aimed at analyzing the association of gene mutations and other acute myeloid leukemia (AML) characteristics with engraftment outcomes in immunodeficient mice and to select the engraftment outcomes that best reflect patient survival.
Methods
Mutations in 19 genes as well as leukemia- and patient-related characteristics were analyzed for a group of 47 de novo AML samples with respect to three engraftment outcomes: engraftment ability, engraftment intensity (percentage of hCD45+ cells) and engraftment latency. Leukemia-related characteristics were additionally analyzed in an extended group of 68 samples that included the 47 de novo samples, and additional 21 samples from refractory and relapsed cases. Engraftment outcomes were compared with overall and event-free survival of the patients.
Results
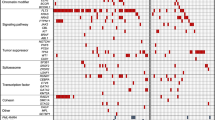
For the 47 de novo samples, no single mutation influenced engraftment, whereas the NPM1mut/DNMT3Amut co-mutation was associated with higher engraftment ability. NPM1mut/FLT3-ITDneg had lower engraftment intensity. Among leukemia-related characteristics, a complex karyotype was associated with higher engraftment intensity. Among patient-related characteristics, higher cytogenetic risk was associated with higher engraftment intensity, and failure to achieve clinical remission was associated with shorter engraftment latency. In the extended group of 68 samples, white blood count was associated with higher engraftment ability, and the presence of a complex karyotype was associated with higher engraftment intensity. Association with patient overall survival was seen only for engraftment intensity.
Conclusions
The engraftment of AML was influenced by mutation-interactions and other AML characteristics, rather than by single mutated genes, and engraftment intensity best reflected clinical penetrance of AML.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Antonelli A et al (2016) Establishing human leukemia xenograft mouse models by implanting human bone marrow-like scaffold-based niches. Blood 128:2949–2959. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2016-05-719021
Arber DA, Orazi A, Hasserjian R, Thiele J, Borowitz MJ, Le Beau MM, Bloomfield CD, Cazzola M, Vardiman JW (2016) The 2016 revision to the World Health Organization classification of myeloid neoplasms and acute leukemia. Blood 127:2391–2405. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2016-03-643544
Cancer Genome Atlas Research N (2013) Genomic and epigenomic landscapes of adult de novo acute myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med 368:2059–2074. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1301689
Corces-Zimmerman MR, Hong W-J, Weissman IL, Medeiros BC, Majeti R (2014) Preleukemic mutations in human acute myeloid leukemia affect epigenetic regulators and persist in remission. P Natl Acad Sci USA 111:2548–2553. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1324297111
Dohner H et al (2010) Diagnosis and management of acute myeloid leukemia in adults: recommendations from an international expert panel, on behalf of the European LeukemiaNet. Blood 115:453–474. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2009-07-235358
Dohner H et al (2017) Diagnosis and management of AML in adults: 2017 ELN recommendations from an international expert panel. Blood 129:424–447. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2016-08-733196
Ehninger A et al (2014) Distribution and levels of cell surface expression of CD33 and CD123 in acute myeloid leukemia. Blood Cancer J 4:e218. https://doi.org/10.1038/bcj.2014.39
Ellegast JM et al (2016) inv(16) and NPM1mut AMLs engraft human cytokine knock-in mice. Blood 128:2130–2134. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2015-12-689356
Gregory TK, Wald D, Chen Y, Vermaat JM, Xiong Y, Tse W (2009) Molecular prognostic markers for adult acute myeloid leukemia with normal cytogenetics. J Hematol Oncol 2:23–23. https://doi.org/10.1186/1756-8722-2-23
Grimwade D et al (1998) The importance of diagnostic cytogenetics on outcome in AML: analysis of 1612 patients entered into the MRC AML 10 trial. The Medical Research Council Adult and Children’s Leukaemia Working Parties. Blood 92:2322–2333
Kennedy JA, Mitchell A, Chen WC, McLeod J, Popescu AC, Arruda A, Minden MD, Dick JE, Wang JCY (2013) Leukemic engraftment In NOD.SCID mice is correlated with clinical parameters and predicts outcome in human AML. Blood 122:50
Khan N et al (2017) Expression of CD33 is a predictive factor for effect of Gemtuzumab Ozogamicin at different doses in adult acute myeloid leukemia. Leukemia 31:1059–1068. https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2016.309
Lumkul R et al (2002) Human AML cells in NOD/SCID mice: engraftment potential and gene expression. Leukemia 16:1818–1826. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2402632
Malaise M et al (2011) Stable and reproducible engraftment of primary adult and pediatric acute myeloid leukemia in NSG mice. Leukemia 25:1635–1639. https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2011.121
Metzeler KH et al (2016) Spectrum and prognostic relevance of driver gene mutations in acute myeloid leukemia. Blood 128:686–698. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2016-01-693879
Paczulla AM et al (2017) Long-term observation reveals high-frequency engraftment of human acute myeloid leukemia in immunodeficient mice. Haematologica 102:854–864. https://doi.org/10.3324/haematol.2016.153528
Papaemmanuil E et al (2016) Genomic classification and prognosis in acute myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med 374:2209–2221. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1516192
Pearce DJ et al (2006) AML engraftment in the NOD/SCID assay reflects the outcome of AML: implications for our understanding of the heterogeneity of AML. Blood 107:1166–1173. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2005-06-2325
Quek L et al (2016) Genetically distinct leukemic stem cells in human CD34-acute myeloid leukemia are arrested at a hemopoietic precursor-like stage. J Exp Med 213:1513–1535. https://doi.org/10.1084/jem.20151775
Risueno RM, Campbell CJV, Dingwall S, Levadoux-Martin M, Leber B, Xenocostas A, Bhatia M (2011) Identification of T-lymphocytic leukemia-initiating stem cells residing in a small subset of patients with acute myeloid leukemic disease. Blood 117:7112–7120. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2011-01-329078
Rombouts WJ, Blokland I, Lowenberg B, Ploemacher RE (2000) Biological characteristics and prognosis of adult acute myeloid leukemia with internal tandem duplications in the Flt3 gene. Leukemia 14:675–683. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2401731 doi
Sanchez PV et al (2009) A robust xenotransplantation model for acute myeloid leukemia. Leukemia 23:2109–2117. https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2009.143
Shlush LI et al (2014) Identification of pre-leukaemic haematopoietic stem cells in acute leukaemia. Nature 506:328–333. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature13038
Taussig DC, Pearce DJ, Simpson C, Rohatiner AZ, Lister TA, Kelly G, Luongo JL, Danet-Desnoyers GA, Bonnet D (2005) Hematopoietic stem cells express multiple myeloid markers: implications for the origin and targeted therapy of acute myeloid leukemia. Blood 106:4086–4092. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2005-03-1072
Taussig DC et al (2010) Leukemia-initiating cells from some acute myeloid leukemia patients with mutated nucleophosmin reside in the CD34(-) fraction. Blood 115:1976–1984. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2009-02-206565
Thol F et al (2017) Acute myeloid leukemia derived from lympho-myeloid clonal hematopoiesis. Leukemia 31:1286–1295. https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2016.345
Wunderlich M, Brooks RA, Panchal R, Rhyasen GW, Danet-Desnoyers G, Mulloy JC (2014) OKT3 prevents xenogeneic GVHD and allows reliable xenograft initiation from unfractionated human hematopoietic tissues. Blood 123:e134-144. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2014-02-556340
Zeijlemaker W, Kelder A, Wouters R, Valk PJ, Witte BI, Cloos J, Ossenkoppele GJ, Schuurhuis GJ (2015) Absence of leukaemic CD34(+) cells in acute myeloid leukaemia is of high prognostic value: a longstanding controversy deciphered. Br J Haematol. https://doi.org/10.1111/bjh.13572
Funding
This study was supported by funds from the Faculty of Medicine MU to junior researcher Martin Culen. Supported by Ministry of Health of the Czech Republic, Grant No. 15-25809A. All rights reserved. Supported by MUNI/A/0968/2017.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval
Samples were collected from AML patients treated at the University Hospital, Brno. Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study. The study was approved by the Institutional Review Board of the University Hospital, Brno. All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. All animal experiments were approved by institutional review board of the Masaryk University, Brno, and performed in accordance with all European guidelines for the protection of laboratory animals.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Culen, M., Kosarova, Z., Jeziskova, I. et al. The influence of mutational status and biological characteristics of acute myeloid leukemia on xenotransplantation outcomes in NOD SCID gamma mice. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 144, 1239–1251 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-018-2652-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-018-2652-2