Abstract
Purpose
To compare concentric and eccentric cycling performed by older adults for metabolic demand and post-exercise oxidative stress, inflammation and muscle damage.
Methods
Eight male and two female healthy older adults (60.4 ± 6.8 years) performed 30 min of moderate-intensity concentric (CONC-M: 50% maximum power output; POmax) and eccentric cycling (ECC-M: 50% POmax) and high-intensity eccentric cycling (ECC-H: 100% POmax) in a randomized order. Average power output (PO), oxygen consumption (VO2), heart rate (HR) and rate of perceived exertion were recorded during cycling. Some indirect markers of muscle damage were assessed before, and immediately, 24 and 48 h after cycling. Markers of oxidative stress (malondialdehyde: MDA, protein carbonyl), antioxidant (total antioxidant capacity, glutathione peroxidase activity: GPx) and inflammation (IL-6, TNF-α) were measured before and 5 min after cycling.
Results
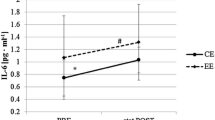
PO in ECC-H (202.6 ± 78.5 W) was > 50% greater (P < 0.05) than that of CONC-M (98.6 ± 33.1 W) and ECC-M (112.0 ± 42.1 W). VO2 and HR were also greater (P < 0.05) for ECC-H than CONC-M (50% and 17%, respectively) and ECC-M (40% and 23%, respectively). Muscle strength loss at 1 day post-exercise (8–22%), peak soreness (10–62 mm) and creatine kinase activity (30–250 IU/L) after ECC-H were greater (P < 0.05) than those after ECC-M and CONC-M. MDA decreased (P < 0.05) after CONC-M (− 28%) and ECC-M (− 22%), but not after ECC-H. GPx activity increased after all exercises similarly (20–27%). IL-6 increased (P < 0.05) only after ECC-H (18%).
Conclusion
Oxidative stress was minimal after eccentric cycling, but high-intensity eccentric cycling induced moderate muscle damage and inflammation, which is not desirable for older individuals.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bernecker C, Scherr J, Schinner S, Braun S, Scherbaum WA, Halle M (2013) Evidence for an exercise induced increase of TNF-alpha and IL-6 in marathon runners. Scand J Med Sci Sports 23:207–214
Berzosa C, Cebrian I, Fuentes-Broto L, Gomez-Trullen E, Piedrafita E, Martinez-Ballarin E, Lopez-Pingarron L, Reiter RJ, Garcia JJ (2011) Acute exercise increases plasma total antioxidant status and antioxidant enzyme activities in untrained men. J Biomed Biotech 2011:540458
Chasland LC, Green DJ, Maiorana AJ, Nosaka K, Haynes A, Dembo LG, Naylor LH (2017) Eccentric cycling: a promising modality for patients with chronic heart failure. Med Sci Sports Exer 49:646–651
Chen TC, Chen HL, Pearce AJ, Nosaka K (2012) Attenuation of eccentric exercise-induced muscle damage by preconditioning exercises. Med Sci Sports Exer 44:2090–2098
Chen TC, Hsieh CC, Tseng KW, Ho CC, Nosaka K (2017a) Effects of descending stair walking on health and fitness of elderly obese women. Med Sci Sports Exer 49:1614–1622
Chen TC, Tseng WC, Huang GL, Chen HL, Tseng KW, Nosaka K (2017b) Superior effects of eccentric to concentric knee extensor resistance training on physical fitness, insulin sensitivity and lipid profiles of elderly men. Front Physiol 8:209
Cobley JN, Close GL, Bailey DM, Davison GW (2017) Exercise redox biochemistry: conceptual, methodological and technical recommendations. Redox biol 12:540–548
Costamagna D, Costelli P, Sampaolesi M, Penna F (2015) Role of inflammation in muscle homeostasis and myogenesis. Mediators Inflamm 2015:805172
Crossley E, Seri S, Stern JS, Robertson MM, Cavanna AE (2014) Premonitory urges for tics in adult patients with Tourette syndrome. Brain Dev 36:45–50
Done AJ, Traustadottir T (2016) Aerobic exercise increases resistance to oxidative stress in sedentary older middle-aged adults. A pilot study. Age 38:505–512
Douglas J, Pearson S, Ross A, McGuigan M (2017) Eccentric exercise: physiological characteristics and acute responses. Sports Med 47:663–675
Elmer SJ, Madigan ML, Lastayo PC, Martin JC (2010) Joint-specific power absorption during eccentric cycling. Clin Biomech 25:154–158
Granic A, Davies K, Martin-Ruiz C, Jagger C, Kirkwood TBL, von Zglinicki T, Aihie Sayer A (2017) Grip strength and inflammatory biomarker profiles in very old adults. Age Ageing 46:976–982
James DA, Simjanovic M, Leadbetter R, Wearing S (2014) Design and test of a custom instrumented leg press for injury and recovery intervention. Procedia Eng 72:38–43
Lane-Cordova AD, Phillips SA, Baynard T, Woods JA, Motl RW, Fernhall B (2016) Effects of ageing and physical activity on blood pressure and endothelial function during acute inflammation. Exp Physiol 101:962–971
Lastayo P, Marcus RL, Dibble L, Frajacomo F, Lindstedt SL (2014) Eccentric exercise in rehabilitation: safety, feasibility and application. J Appl Physiol 116:1426–1434
Lastayo PC, Ewy GA, Pierotti DD, Johns RK, Lindstedt S (2003) The positive effects of negative work: increased muscle strength and decreased fall risk in a frail elderly population. J Gerontol 58:M419–424
Lastayo PC, Reich TE, Urquhart M, Hoppeler H, Lindstedt SL (1999) Chronic eccentric exercise: improvements in muscle strength can occur with little demand for oxygen. Am J Physiol 276:R611–R615
Lavender AP, Nosaka K (2006) Comparison between old and young men for changes in makers of muscle damage following voluntary eccentric exercise of the elbow flexors. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab 31:218–225
Lavender AP, Nosaka K (2008) A light load eccentric exercise confers protection against a subsequent bout of more demanding eccentric exercise. J Sci Med Sport 11:291–298
Liu M, Timmons BW (2016) The effect of acute exercise on neutrophil reactive oxygen species production and inflammatory markers in healthy prepubertal and adult males. Pediatric Exer Sci 28:55–63
Margaritelis NV, Theodorou AA, Paschalis V, Veskoukis AS, Dipla K, Zafeiridis A, Panayiotou G, Vrabas IS, Kyparos A, Nikolaidis MG (2018) Adaptations to endurance training depend on exercise-induced oxidative stress: exploiting redox interindividual variability. Acta Physiol 22(2):e12898
McKay BR, De Lisio M, Johnston AP, O'Reilly CE, Phillips SM, Tarnopolsky MA, Parise G (2009) Association of interleukin-6 signalling with the muscle stem cell response following muscle-lengthening contractions in humans. PloS one 4:e6027
Michailidis Y, Jamurtas AZ, Nikolaidis MG, Fatouros IG, Koutedakis Y, Papassotiriou I, Kouretas D (2007) Sampling time is crucial for measurement of aerobic exercise-induced oxidative stress. Med Sci Sports Exerc 39:1107–1113
Monteiro-Junior RS, de Maciel-Pinheiro Tarso P, da Matta Mello Portugal E, da Silva Figueiredo LF, Terra R, Carneiro LSF, Rodrigues VD, Nascimento OJM, Deslandes AC, Laks J (2018) Effect of exercise on inflammatory profile of older persons: systematic review and meta-analyses. J Phys Act Health 15:64–71
Moylan JS, Reid MB (2007) Oxidative stress, chronic disease, and muscle wasting. Muscle Nerve 35:411–429
Nikolaidis M (2017) The effects of resistance exercise on muscle damage, position sense, and blood redox status in young and elderly individuals. Geriatrics 2(3):20
Nikolaidis MG, Kyparos A, Spanou C, Paschalis V, Theodorou AA, Panayiotou G, Grivas GV, Zafeiridis A, Dipla K, Vrabas IS (2013) Aging is not a barrier to muscle and redox adaptations: applying the repeated eccentric exercise model. Exp Gerontol 48:734–743
Nikolaidis MG, Margaritelis NV, Paschalis V et al (2015) Common questions and tentative answers on how to assess oxidative stress after antioxidant supplementation and exercise. In: Lamprecht M (ed) Antioxidants in sport nutrition, chap 14. CRC Press/Taylor & Francis, Boca Raton (FL)
Nikolaidis MG, Paschalis V, Giakas G, Fatouros IG, Koutedakis Y, Kouretas D, Jamurtas AZ (2007) Decreased blood oxidative stress after repeated muscle-damaging exercise. Med Sci Sports Exer 39:1080–1089
Nordin TC, Done AJ, Traustadottir T (2014) Acute exercise increases resistance to oxidative stress in young but not older adults. Age 36:9727
Park KS, Lee MG (2015) Effects of unaccustomed downhill running on muscle damage, oxidative stress, and leukocyte apoptosis. J Exerc Nutr Biochem 19:55–63
Paulsen G, Mikkelsen UR, Raastad T, Peake JM (2012) Leucocytes, cytokines and satellite cells: what role do they play in muscle damage and regeneration following eccentric exercise? Exerc Immunol Rev 18:42–97
Penailillo L, Blazevich A, Numazawa H, Nosaka K (2013) Metabolic and muscle damage profiles of concentric versus repeated eccentric cycling. Med Sci Sports Exer 45:1773–1781
Penailillo L, Blazevich AJ, Nosaka K (2017) Factors contributing to lower metabolic demand of eccentric compared with concentric cycling. J Appl Physiol 123:884–893
Pokora I, Kempa K, Chrapusta SJ, Langfort J (2014) Effects of downhill and uphill exercises of equivalent submaximal intensities on selected blood cytokine levels and blood creatine kinase activity. Biol sport 31:173–178
Powers SK, Nelson WB, Hudson MB (2011) Exercise-induced oxidative stress in humans: cause and consequences. Free Radic Biol Med 51:942–950
Powers SK, Radak Z, Ji LL (2016) Exercise-induced oxidative stress: past, present and future. J Physiol 594:5081–5092
Sacheck JM, Milbury PE, Cannon JG, Roubenoff R, Blumberg JB (2003) Effect of vitamin E and eccentric exercise on selected biomarkers of oxidative stress in young and elderly men. Free Radic Biol Med 34:1575–1588
Spirlandeli AL, Deminice R, Jordao AA (2014) Plasma malondialdehyde as biomarker of lipid peroxidation: effects of acute exercise. Int J Sports Med 35:14–18
Theodorou AA, Panayiotou G, Paschalis V, Nikolaidis MG, Kyparos A, Mademli L, Grivas GV, Vrabas IS (2013) Stair descending exercise increases muscle strength in elderly males with chronic heart failure. BMC Res Notes 6:87
Toft AD, Jensen LB, Bruunsgaard H, Ibfelt T, Halkjaer-Kristensen J, Febbraio M, Pedersen BK (2002) Cytokine response to eccentric exercise in young and elderly humans. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 283:C289–295
Vincent KR, Vincent HK, Braith RW, Lennon SL, Lowenthal DT (2002) Resistance exercise training attenuates exercise-induced lipid peroxidation in the elderly. Eur J Appl Physiol 87:416–423
Webb R, Hughes MG, Thomas AW, Morris K (2017) The ability of exercise-associated oxidative stress to trigger redox-sensitive signalling responses. Antioxidants (Basel, Switzerland) 6:63
Woods JA, Wilund KR, Martin SA, Kistler BM (2012) Exercise, inflammation and aging. Aging Dis 3:130–140
Acknowledgements
This work was funded by research Grants awarded to L.P. (#11150293) by CONICYT of Chile.
Funding
This work was funded by a research Grant (Fondo Nacional de Desarrollo Científico y Tecnológico) awarded to L.P. (#11150293) by CONICYT of Chile.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
LP and KN conceived and designed the research. RG and KM conducted the experiments. HZ and DV contributed the biochemical analyses. RG and LP analysed the data. RG wrote the manuscript. All authors read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There were no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by Michalis G. Nikolaidis.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
González-Bartholin, R., Mackay, K., Valladares, D. et al. Changes in oxidative stress, inflammation and muscle damage markers following eccentric versus concentric cycling in older adults. Eur J Appl Physiol 119, 2301–2312 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-019-04213-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-019-04213-7