Abstract
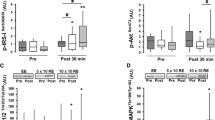
We analysed the effects of resistance exercise upon the phosphorylation state of proteins associated with adaptive processes from the Akt/PKB (protein kinase B) and the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathways. Nine healthy young men (21.7 ± 0.55 year) performed 10 sets of 10 leg extensions at 80% of their 1-RM (repetition maximum). Muscle biopsies were taken from the vastus lateralis at rest, within the first 30 s after exercise and at 24 h post-exercise. Immediately post exercise, the phosphorylation states of Akt/PKB on Thr308 and Ser473 and 4E-BP1 on Thr37/46 (eukaryotic initiation factor 4E-binding protein 1) were decreased (−60 to −90%, P < 0.05). Conversely, the phosphorylation of p70s6k (p70 ribosomal S6 kinase) on Thr421/Ser424 was increased more than 20-fold (P < 0.05), and this was associated with a 10- to 50-fold increase in the phosphorylation of p38 and ERK1/2 (extracellular signal-regulated kinase) (P < 0.05). Twenty-four hours post-exercise the phosphorylation state of Akt/PKB on Thr308 was depressed, whereas the phosphorylation of p70s6k on Thr421/Ser424 and sarcoplasmic ERK1/2 were elevated. The present results indicate that high-intensity resistance exercise in the fasted state inhibits Akt/PKB and 4E-BP1 whilst concomitantly augmenting MAPK signalling and p70s6k on Thr421/Ser424.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blomstrand E, Eliasson J, Karlsson HK, Kohnke R (2006) Branched-chain amino acids activate key enzymes in protein synthesis after physical exercise. J Nutr 136:269S–273S
Bolster DR, Crozier SJ, Kimball SR, Jefferson LS (2002) AMP-activated protein kinase suppresses protein synthesis in rat skeletal muscle through down-regulated mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) signaling. J Biol Chem 277:23977–23980
Brozinick JT Jr, Birnbaum MJ (1998) Insulin, but not contraction, activates Akt/PKB in isolated rat skeletal muscle. J Biol Chem 273:14679–14682
Burnett PE, Barrow RK, Cohen NA, Snyder SH, Sabatini DM (1998) RAFT1 phosphorylation of the translational regulators p70 S6 kinase and 4E-BP1. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:1432–1437
Chan MH, McGee SL, Watt MJ, Hargreaves M, Febbraio MA (2004) Altering dietary nutrient intake that reduces glycogen content leads to phosphorylation of nuclear p38 MAP kinase in human skeletal muscle: association with IL-6 gene transcription during contraction. FASEB J 18:1785–1787
Coffey VG, Zhong Z, Shield A, Canny BJ, Chibalin AV, Zierath JR, Hawley JA (2006) Early signaling responses to divergent exercise stimuli in skeletal muscle from well-trained humans. FASEB J 20:190–192
Creer A, Gallagher P, Slivka D, Jemiolo B, Fink W, Trappe S (2005) Influence of muscle glycogen availability on ERK1/2 and Akt signaling after resistance exercise in human skeletal muscle. J Appl Physiol 99:950–956
Cuthbertson DJ, Babraj J, Smith K, Wilkes E, Fedele MJ, Esser K, Rennie M (2006) Anabolic signaling and protein synthesis in human skeletal muscle after dynamic shortening or lengthening exercise. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 290:E731–E738
Deldicque L, Theisen D, Francaux M (2005) Regulation of mTOR by amino acids and resistance exercise in skeletal muscle. Eur J Appl Physiol 94:1–10
Deldicque L, Atherton P, Patel R, Theisen D, Nielens H, Rennie MJ, Francaux M (2008) Effects of resistance exercise with and without creatine supplementation on gene expression and cell signaling in human skeletal muscle. J Appl Physiol 104:371–378
Deshmukh A, Coffey VG, Zhong Z, Chibalin AV, Hawley JA, Zierath JR (2006) Exercise-induced phosphorylation of the novel Akt substrates AS160 and filamin A in human skeletal muscle. Diabetes 55:1776–1782
Dreyer HC, Fujita S, Cadenas JG, Chinkes DL, Volpi E, Rasmussen BB (2006) Resistance exercise increases AMPK activity and reduces 4E-BP1 phosphorylation and protein synthesis in human skeletal muscle. J Physiol 576:613–624
Eliasson J, Elfegoun T, Nilsson J, Kohnke R, Ekblom B, Blomstrand E (2006) Maximal lengthening contractions increase p70 S6 kinase phosphorylation in human skeletal muscle in the absence of nutritional supply. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 291:E1197–E1205
Farooq A, Zhou MM (2004) Structure and regulation of MAPK phosphatases. Cell Signal 16:769–779
Gingras AC, Gygi SP, Raught B, Polakiewicz RD, Abraham RT, Hoekstra MF, Aebersold R, Sonenberg N (1999) Regulation of 4E-BP1 phosphorylation: a novel two-step mechanism. Genes Dev 13:1422–1437
Holz MK, Ballif BA, Gygi SP, Blenis J (2005) mTOR and S6K1 mediate assembly of the translation preinitiation complex through dynamic protein interchange and ordered phosphorylation events. Cell 123:569–580
Horman S, Browne G, Krause U, Patel J, Vertommen D, Bertrand L, Lavoinne A, Hue L, Proud C, Rider M (2002) Activation of AMP-activated protein kinase leads to the phosphorylation of elongation factor 2 and an inhibition of protein synthesis. Curr Biol 12:1419–1423
Iijima Y, Laser M, Shiraishi H, Willey CD, Sundaravadivel B, Xu L, McDermott PJ, Kuppuswamy D (2002) c-Raf/MEK/ERK pathway controls protein kinase C-mediated p70S6K activation in adult cardiac muscle cells. J Biol Chem 277:23065–23075
Karlsson HK, Nilsson PA, Nilsson J, Chibalin AV, Zierath JR, Blomstrand E (2004) Branched-chain amino acids increase p70S6k phosphorylation in human skeletal muscle after resistance exercise. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 287:E1–E7
Koopman R, Zorenc AH, Gransier RJ, Cameron-Smith D, van Loon LJ (2006) Increase in S6K1 phosphorylation in human skeletal muscle following resistance exercise occurs mainly in type II muscle fibers. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 290:E1245–E1252
Long YC, Widegren U, Zierath JR (2004) Exercise-induced mitogen-activated protein kinase signalling in skeletal muscle. Proc Nutr Soc 63:227–232
Louis M, Poortmans JR, Francaux M, Berre J, Boisseau N, Brassine E, Cuthbertson DJ, Smith K, Babraj JA, Waddell T, Rennie MJ (2003) No effect of creatine supplementation on human myofibrillar and sarcoplasmic protein synthesis after resistance exercise. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 285:E1089–E1094
McGee SL, Hargreaves M (2004) Exercise and myocyte enhancer factor 2 regulation in human skeletal muscle. Diabetes 53:1208–1214
Mukhopadhyay NK, Price DJ, Kyriakis JM, Pelech S, Sanghera J, Avruch J (1992) An array of insulin-activated, proline-directed serine/threonine protein kinases phosphorylate the p70 S6 kinase. J Biol Chem 267:3325–3335
Phillips SM, Tipton KD, Aarsland A, Wolf SE, Wolfe RR (1997) Mixed muscle protein synthesis and breakdown after resistance exercise in humans. Am J Physiol 273:E99–E107
Rennie MJ, Tipton KD (2000) Protein and amino acid metabolism during and after exercise and the effects of nutrition. Annu Rev Nutr 20:457–483
Rose AJ, Broholm C, Kiillerich K, Finn SG, Proud CG, Rider MH, Richter EA, Kiens B (2005) Exercise rapidly increases eukaryotic elongation factor 2 phosphorylation in skeletal muscle of men. J Physiol 569:223–228
Sorichter S, Koller A, Haid C, Wicke K, Judmaier W, Werner P, Raas E (1995) Light concentric exercise and heavy eccentric muscle loading: effects on CK, MRI and markers of inflammation. Int J Sports Med 16:288–292
Terzis G, Georgiadis G, Stratakos G, Vogiatzis I, Kavouras S, Manta P, Mascher H, Blomstrand E (2008) Resistance exercise-induced increase in muscle mass correlates with p70S6 kinase phosphorylation in human subjects. Eur J Appl Physiol 102:145–152
Wang X, Flynn A, Waskiewicz AJ, Webb BL, Vries RG, Baines IA, Cooper JA, Proud CG (1998) The phosphorylation of eukaryotic initiation factor eIF4E in response to phorbol esters, cell stresses, and cytokines is mediated by distinct MAP kinase pathways. J Biol Chem 273:9373–9377
Wang L, Gout I, Proud CG (2001) Cross-talk between the ERK and p70 S6 kinase (S6K) signaling pathways. MEK-dependent activation of S6K2 in cardiomyocytes. J Biol Chem 276:32670–32677
Weng QP, Kozlowski M, Belham C, Zhang A, Comb MJ, Avruch J (1998) Regulation of the p70 S6 kinase by phosphorylation in vivo. Analysis using site-specific anti-phosphopeptide antibodies. J Biol Chem 273:16621–16629
Widegren U, Jiang XJ, Krook A, Chibalin AV, Bjornholm M, Tally M, Roth RA, Henriksson J, Wallberg-henriksson H, Zierath JR (1998) Divergent effects of exercise on metabolic and mitogenic signaling pathways in human skeletal muscle. FASEB J 12:1379–1389
Widegren U, Ryder JW, Zierath JR (2001) Mitogen-activated protein kinase signal transduction in skeletal muscle: effects of exercise and muscle contraction. Acta Physiol Scand 172:227–238
Williamson D, Gallagher P, Harber M, Hollon C, Trappe S (2003) Mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway activation: effects of age and acute exercise on human skeletal muscle. J Physiol 547:977–987
Wojtaszewski JF, Nielsen P, Kiens B, Richter EA (2001) Regulation of glycogen synthase kinase-3 in human skeletal muscle: effects of food intake and bicycle exercise. Diabetes 50:265–269
Wolfe RR (2000) Protein supplements and exercise. Am J Clin Nutr 72:551S–557S
Wretman C, Lionikas A, Widegren U, Lannergren J, Westerblad H, Henriksson J (2001) Effects of concentric and eccentric contractions on phosphorylation of MAPK(erk1/2) and MAPK(p38) in isolated rat skeletal muscle. J Physiol 535:155–164
Yu M, Blomstrand E, Chibalin AV, Krook A, Zierath JR (2001) Marathon running increases ERK1/2 and p38 MAP kinase signalling to downstream targets in human skeletal muscle. J Physiol 536:273–282
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants to MJ Rennie from UK Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council (BB/X510697/1 and BB/C516779/1), US National Institute of Health AR 49869, and the EC EXEGENESIS program and to M Francaux from the Fonds de la Recherche Scientifique Medicale (3.4574.03).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Deldicque, L., Atherton, P., Patel, R. et al. Decrease in Akt/PKB signalling in human skeletal muscle by resistance exercise. Eur J Appl Physiol 104, 57–65 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-008-0786-7
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-008-0786-7