Abstract
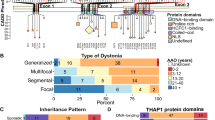
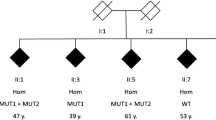
Complex regional pain syndrome type 1 (CRPS-1) is a chronic pain disorder that in some patients is associated with fixed dystonia. The pathogenesis of CRPS and its relation to dystonia remain poorly understood. Several genes (so-called DYT genes) identified in other causes of dystonia play a role in mechanisms that have been implicated in CRPS. Because different mutations in the same gene can result in diverse phenotypes, we sequenced all coding exons of the DYT1, DYT5a, DYT5b, DYT6, DYT11, DYT12, and DYT16 genes in 44 CRPS patients with fixed dystonia to investigate whether high-penetrant causal mutations play a role in CRPS. No such mutations were identified, indicating that these genes do not seem to play a major role in CRPS.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albert J, Ott H (1983) Three brothers with algodystrophy of the hip. Ann Rheum Dis 42:421–424
Ali ZA, Bursill CA, Douglas G, McNeill E, Papaspyridonos M, Tatham AL, Bendall JK, Akhtar AM, Alp NJ, Greaves DR, Channon KM (2008) CCR2-mediated antiinflammatory effects of endothelial tetrahydrobiopterin inhibit vascular injury-induced accelerated atherosclerosis. Circulation 118:S71–S77
Beck G, Brinkkoetter P, Hanusch C, Schulte J, van Ackern K, van der Woude FJ, Yard BA (2004) Clinical review: immunomodulatory effects of dopamine in general inflammation. Crit Care 8:485–491
Birklein F, Schmelz M (2008) Neuropeptides, neurogenic inflammation and complex regional pain syndrome (CRPS). Neurosci Lett 437:199–202
Blanco-Arias P, Einholm AP, Mamsa H, Concheiro C, Gutierrez-de-Teran H, Romero J, Toustrup-Jensen MS, Carracedo A, Jen JC, Vilsen B, Sobrido MJ (2009) A C-terminal mutation of ATP1A3 underscores the crucial role of sodium affinity in the pathophysiology of rapid-onset dystonia-parkinsonism. Hum Mol Genet 18:2370–2377
Bruscas IC, Beltran Audera CH, Jimenez ZF (2004) Polytopic and recurrent reflex sympathetic dystrophy in lower limbs in two siblings. An Med Int 21:183–184
Camargos S, Scholz S, Simon-Sanchez J, Paisan-Ruiz C, Lewis P, Hernandez D, Ding J, Gibbs JR, Cookson MR, Bras J, Guerreiro R, Oliveira CR, Lees A, Hardy J, Cardoso F, Singleton AB (2008) DYT16, a novel young-onset dystonia-parkinsonism disorder: identification of a segregating mutation in the stress-response protein PRKRA. Lancet Neurol 7:207–215
Cayrol C, Lacroix C, Mathe C, Ecochard V, Ceribelli M, Loreau E, Lazar V, Dessen P, Mantovani R, Aguilar L, Girard JP (2007) The THAP-zinc finger protein THAP1 regulates endothelial cell proliferation through modulation of pRB/E2F cell-cycle target genes. Blood 109:584–594
Chan P, Gonzalez-Maeso J, Ruf F, Bishop DF, Hof PR, Sealfon SC (2005) Epsilon-sarcoglycan immunoreactivity and mRNA expression in mouse brain. J Comp Neurol 482:50–73
de Carvalho Aguiar P, Sweadner KJ, Penniston JT, Zaremba J, Liu L, Caton M, Linazasoro G, Borg M, Tijssen MA, Bressman SB, Dobyns WB, Brashear A, Ozelius LJ (2004) Mutations in the Na+/K+-ATPase alpha3 gene ATP1A3 are associated with rapid-onset dystonia parkinsonism. Neuron 43:169–175
de Rooij AM, de Mos M, Sturkenboom MC, Marinus J, van den Maagdenberg AM, van Hilten JJ (2009a) Familial occurrence of complex regional pain syndrome. Eur J Pain 13:171–177
de Rooij AM, Florencia Gosso M, Haasnoot GW, Marinus J, Verduijn W, Claas FH, van den Maagdenberg AM, van Hilten JJ (2009b) HLA-B62 and HLA-DQ8 are associated with complex regional pain syndrome with fixed dystonia. Pain 145:82–85
de Rooij AM, Perez RS, Huygen FJ, Eijs FV, Kleef MV, Bauer MC, van Hilten JJ, Marinus J (2009c) Spontaneous onset of complex regional pain syndrome. Eur J Pain PMID 19793666
Drummond PD, Finch PM (2006) Sensory changes in the forehead of patients with complex regional pain syndrome. Pain 123:83–89
Eisenberg E, Shtahl S, Geller R, Reznick AZ, Sharf O, Ravbinovich M, Erenreich A, Nagler RM (2008) Serum and salivary oxidative analysis in complex regional pain syndrome. Pain 138:226–232
Erdmann MW, Wynn-Jones CH (1992) ‘Familial’ reflex sympathetic dystrophy syndrome and amputation. Injury 23:136–138
Fahn S (1988) Concept and classification of dystonia. Adv Neurol 50:1–8
Fuchs T, Gavarini S, Saunders-Pullman R, Raymond D, Ehrlich ME, Bressman SB, Ozelius LJ (2009) Mutations in the THAP1 gene are responsible for DYT6 primary torsion dystonia. Nat Genet 41:286–288
Galer BS, Henderson J, Perander J, Jensen MP (2000) Course of symptoms and quality of life measurement in complex regional pain syndrome: a pilot survey. J Pain Symptom Manage 20:286–292
Granata A, Schiavo G, Warner TT (2009) TorsinA and dystonia: from nuclear envelope to synapse. J Neurochem 109:1596–1609
Grima B, Lamouroux A, Boni C, Julien JF, Javoy-Agid F, Mallet J (1987) A single human gene encoding multiple tyrosine hydroxylases with different predicted functional characteristics. Nature 326:707–711
Harden RN, Bruehl S, Galer BS, Saltz S, Bertram M, Backonja M, Gayles R, Rudin N, Bhugra MK, Stanton-Hicks M (1999) Complex regional pain syndrome: are the IASP diagnostic criteria valid and sufficiently comprehensive? Pain 83:211–219
Huhne K, Leis S, Schmelz M, Rautenstrauss B, Birklein F (2004) A polymorphic locus in the intron 16 of the human angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) gene is not correlated with complex regional pain syndrome I (CRPS I). Eur J Pain 8:221–225
Huygen FJ, De Bruijn AG, De Bruin MT, Groeneweg JG, Klein J, Zijlstra FJ (2002) Evidence for local inflammation in complex regional pain syndrome type 1. Mediators Inflamm 11:47–51
Ichinose H, Ohye T, Takahashi E, Seki N, Hori T, Segawa M, Nomura Y, Endo K, Tanaka H, Tsuji S et al (1994) Hereditary progressive dystonia with marked diurnal fluctuation caused by mutations in the GTP cyclohydrolase I gene. Nat Genet 8:236–242
Kaji R, Goto S, Tamiya G, Ando S, Makino S, Lee LV (2005) Molecular dissection and anatomical basis of dystonia: X-linked recessive dystonia-parkinsonism (DYT3). J Med Invest 52(suppl):280–283
Kemler MA, van de Vusse AC, van den Berg-Loonen EM, Barendse GA, van Kleef M, Weber WE (1999) HLA-DQ1 associated with reflex sympathetic dystrophy. Neurology 53:1350–1351
Kuner R, Teismann P, Trutzel A, Naim J, Richter A, Schmidt N, Bach A, Ferger B, Schneider A (2004) TorsinA, the gene linked to early-onset dystonia, is upregulated by the dopaminergic toxin MPTP in mice. Neurosci Lett 355:126–130
Kuo MF, Paulus W, Nitsche MA (2008) Boosting focally-induced brain plasticity by dopamine. Cereb Cortex 18:648–651
Lee HY, Xu Y, Huang Y, Ahn AH, Auburger GW, Pandolfo M, Kwiecinski H, Grimes DA, Lang AE, Nielsen JE, Averyanov Y, Servidei S, Friedman A, Van Bogaert P, Abramowicz MJ, Bruno MK, Sorensen BF, Tang L, Fu YH, Ptacek LJ (2004) The gene for paroxysmal non-kinesigenic dyskinesia encodes an enzyme in a stress response pathway. Hum Mol Genet 13:3161–3170
Ludecke B, Dworniczak B, Bartholome K (1995) A point mutation in the tyrosine hydroxylase gene associated with Segawa’s syndrome. Hum Genet 95:123–125
Maihofner C, Handwerker HO, Neundorfer B, Birklein F (2003) Patterns of cortical reorganization in complex regional pain syndrome. Neurology 61:1707–1715
Mailis A, Wade J (1994) Profile of Caucasian women with possible genetic predisposition to reflex sympathetic dystrophy: a pilot study. Clin J Pain 10:210–217
Merskey H, Bogduk N (1994) Complex Regional Pain Syndrome, Type I. In: Merskey H, Bogduk N (eds) Classification of chronic pain: descriptions of chronic pain syndromes and definitions of pain terms. IASP Press, Seattle, pp 41–42
Miller SA, Dykes DD, Polesky HF (1988) A simple salting out procedure for extracting DNA from human nucleated cells. Nucleic Acids Res 16:1215
Muller U (2009) The monogenic primary dystonias. Brain 132:2005–2025
Navarro X, Vivo M, Valero-Cabre A (2007) Neural plasticity after peripheral nerve injury and regeneration. Prog Neurobiol 82:163–201
Nishiyama A, Endo T, Takeda S, Imamura M (2004) Identification and characterization of epsilon-sarcoglycans in the central nervous system. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 125:1–12
Ozelius LJ, Hewett JW, Page CE, Bressman SB, Kramer PL, Shalish C, de Leon D, Brin MF, Raymond D, Corey DP, Fahn S, Risch NJ, Buckler AJ, Gusella JF, Breakefield XO (1997) The early-onset torsion dystonia gene (DYT1) encodes an ATP-binding protein. Nat Genet 17:40–48
Patel CV, Handy I, Goldsmith T, Patel RC (2000) PACT, a stress-modulated cellular activator of interferon-induced double-stranded RNA-activated protein kinase, PKR. J Biol Chem 275:37993–37998
Rainier S, Thomas D, Tokarz D, Ming L, Bui M, Plein E, Zhao X, Lemons R, Albin R, Delaney C, Alvarado D, Fink JK (2004) Myofibrillogenesis regulator 1 gene mutations cause paroxysmal dystonic choreoathetosis. Arch Neurol 61:1025–1029
Roussigne M, Cayrol C, Clouaire T, Amalric F, Girard JP (2003) THAP1 is a nuclear proapoptotic factor that links prostate-apoptosis-response-4 (Par-4) to PML nuclear bodies. Oncogene 22:2432–2442
Schwartzman RJ, Kerrigan J (1990) The movement disorder of reflex sympathetic dystrophy. Neurology 40:57–61
Tegeder I, Costigan M, Griffin RS, Abele A, Belfer I, Schmidt H, Ehnert C, Nejim J, Marian C, Scholz J, Wu T, Allchorne A, Diatchenko L, Binshtok AM, Goldman D, Adolph J, Sama S, Atlas SJ, Carlezon WA, Parsegian A, Lotsch J, Fillingim RB, Maixner W, Geisslinger G, Max MB, Woolf CJ (2006) GTP cyclohydrolase and tetrahydrobiopterin regulate pain sensitivity and persistence. Nat Med 12:1269–1277
van der Laan L, ter Laak HJ, Gabreels-Festen A, Gabreels F, Goris RJ (1998) Complex regional pain syndrome type I (RSD): pathology of skeletal muscle and peripheral nerve. Neurology 51:20–25
van Hilten JJ, van de Beek WJ, Roep BO (2000) Multifocal or generalized tonic dystonia of complex regional pain syndrome: a distinct clinical entity associated with HLA-DR13. Ann Neurol 48:113–116
van Rijn MA, Marinus J, Putter H, van Hilten JJ (2007) Onset and progression of dystonia in complex regional pain syndrome. Pain 130:287–293
Vaneker M, van der Laan L, Allebes WA, Gorsi RJ (2002) Genetic factors associated with complex regional pain syndrome 1: HLA DRB and TNF alpha promotor gene polymorphism. Disabil Med 2:69–74
Veldman PH, Reynen HM, Arntz IE, Goris RJ (1993) Signs and symptoms of reflex sympathetic dystrophy: prospective study of 829 patients. Lancet 342:1012–1016
Weber YG, Storch A, Wuttke TV, Brockmann K, Kempfle J, Maljevic S, Margari L, Kamm C, Schneider SA, Huber SM, Pekrun A, Roebling R, Seebohm G, Koka S, Lang C, Kraft E, Blazevic D, Salvo-Vargas A, Fauler M, Mottaghy FM, Munchau A, Edwards MJ, Presicci A, Margari F, Gasser T, Lang F, Bhatia KP, Lehmann-Horn F, Lerche H (2008) GLUT1 mutations are a cause of paroxysmal exertion-induced dyskinesias and induce hemolytic anemia by a cation leak. J Clin Invest 118:2157–2168
Wood PB (2008) Role of central dopamine in pain and analgesia. Expert Rev Neurother 8:781–797
Zimprich A, Grabowski M, Asmus F, Naumann M, Berg D, Bertram M, Scheidtmann K, Kern P, Winkelmann J, Muller-Myhsok B, Riedel L, Bauer M, Muller T, Castro M, Meitinger T, Strom TM, Gasser T (2001) Mutations in the gene encoding epsilon-sarcoglycan cause myoclonus-dystonia syndrome. Nat Genet 29:66–69
Acknowledgments
This study is part of Trauma RElated Neuronal Dysfunction (TREND), a Dutch Consortium that integrates research on epidemiology, assessment technology, pharmacotherapeutics, biomarkers and genetics on Complex Regional Pain Syndrome type 1. The consortium aims to develop concepts on disease mechanisms that occur in response to tissue injury, its assessment and treatment. TREND is supported by a government grant (BSIK03016).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
M. F. Gosso and A. M. de Rooij contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gosso, M.F., de Rooij, A.M., Alsina-Sanchis, E. et al. Systematic mutation analysis of seven dystonia genes in complex regional pain syndrome with fixed dystonia. J Neurol 257, 820–824 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-009-5426-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-009-5426-6