Abstract
Purpose
Tonsillectomy is still one of the most common surgical procedures worldwide performed by otorhinolaryngologists. This single-blind randomized study aimed to compare cold dissection tonsillectomy, coblation tonsillectomy, and harmonic scalpel tonsillectomy in pediatric patients in respect of intraoperative blood loss, operating time, and postoperative pain and bleeding.
Methods
This single-blind randomized clinical trial evaluated 82 pediatric patients aged 3–16 years (mean age: 7.23 ± 3.26 years) applied with tonsillectomy between April 2017 and March 2020. Harmonic scalpel tonsillectomy was applied to 33 (40.2%) patients, the cold knife technique to 25 (30.5%), and coblation tonsillectomy to 24 (29.3%).
Results
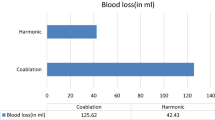
There was no statistically significant difference between the three techniques in respect of postoperative pain levels and post-tonsillectomy bleeding rates. The intraoperative bleeding rate and mean operating time were determined to be significantly lower in the harmonic scalpel group (p < 0.05).
Conclusion
Harmonic scalpel tonsillectomy is associated with a shorter operating time and lower intraoperative bleeding rates and similar postoperative pain score and postoperative bleeding rates compared with coblation tonsillectomy and cold dissection tonsillectomy. Harmonic scalpel tonsillectomy is a fast, safe, and effective method for tonsillectomy in children.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dutta NN, Bordoloi BM (2002) Tonsillectomy using harmonic scalpel. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 54:74–76. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02911016
Temple RH, Timms MS (2001) Paediatric coblation tonsillectomy. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 61:195–198. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0165-5876(01)00553-5
Verma R, Verma RR, Verma RR (2017) Tonsillectomy-comparative study of various techniques and changing trend. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 69:549–558. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-017-1190-6
Wındfuhr JP, Chen YS, Remmert S (2005) Hemorrhage following tonsillectomy and adenoidectomy in 15,218 patients. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 132:281–286. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.otohns.2004.09.007
McClelland L, Jones NS (2005) Historical article Tonsillectomy: haemorrhaging ideas. J Laryngol Otol 119:753–758. https://doi.org/10.1258/002221505774481336
Roje Z, Racic G, Zoran D, Pisac VP, Timms M (2009) Postoperative morbidity and histopathologic characteristics of tonsillar tissue following coblation tonsillectomy in children: a prospective randomized single-blind study. Coll Antropol 33:293–298
Paramasivan VK, Arumugam SV, Kameswaran M (2012) Randomised comparative study of adenotonsillectomy by conventional and coblation method for children with obstructive sleep apnoea. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 76:816–821. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijporl.2012.02.049
Bellosa A, Chidambaram A, Morar P, Timms MS (2003) Coblation tonsillectomy versus dissection tonsillectomy: postoperative hemorrhage. Laryngoscope 113:2010–2013. https://doi.org/10.1097/00005537-200311000-00029
Shakeel M, Trinidade A, Al-Adhami A, Kubba H (2010) Pediatric Tonsillectomy Cold Steel vs Harmonic Scalpel. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 143:116–117. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.otohns.2010.06.215
Collison PJ, Weiner R (2004) Harmonic scalpel versus conventional tonsillectomy: a double blind clinical trial. Ear Nose Throat J 83:707–710
Basu S, Sengupta A, Dubey AB, Sengupta A (2019) Harmonic scalpel versus coblation tonsillectomy a comparative study. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 71:498–503. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-019-01679-x
Oko MO, Ganly I, Loughran S, Clement WA, Young D, Geddes NK (2005) A prospective randomized single-blind trial comparing ultrasonic scalpel tonsillectomy with tonsillectomy by blunt dissection in a pediatric age group. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 133:579–584. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.otohns.2005.08.002
Parsons SP, Cordes SR, Comer B (2006) Comparison of posttonsillectomy pain using the ultrasonic scalpel, coblator, and electrocautery. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 134:106–113. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.otohns.2005.09.027
Mitic S, Tvinnereim M, Lie E, Saltyte BJ (2007) A pilot randomized controlled trial of coblation tonsillectomy versus dissection tonsillectomy with bipolar diathermy haemostasis. Clin Otolaryngol 32:261–267. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2273.2007.01468.x
Chimona T, Proimos E, Mamoulakis C, Tzanakakis M, Skoulakis CE, Papadakis CE (2008) Multiparametric comparison of cold knife tonsillectomy, radiofrequency excision and thermal welding tonsillectomy in children. Int J Otorhinolaryngol 72:1431–1436
Pajic-Penavic I, Danic D, Mrzljak-Vucinic N, Matic I, Vukonic-Arar Z, Dikanovic M (2013) Postoperative quality of life after two different methods of tonsillectomy. Wien Klin Wochenschr 125:524–528. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00508-013-0411-6
Zhang LY, Zhong L, David M, Cervin A (2017) Tonsillectomy or tonsillotomy? A systematic review for paediatric sleepdisordered breathing. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 103:41–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijporl.2017.10.008
Sathe N, Chinnadurai S, McPheeters M, Francis D (2017) Comparative Effectiveness of Partial Versus Total Tonsillectomy in Children: A Systematic Review. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 156:456–463. https://doi.org/10.1177/0194599816683916
Funding
No funding was received for this work from any organizations. There is no financial disclosure.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Each of the authors has contributed to read and approved this manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical standard
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Subasi, B., Oghan, F., Tasli, H. et al. Comparison of three tonsillectomy techniques in children. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 278, 2011–2015 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-020-06299-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-020-06299-8