Abstract
Purpose
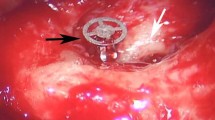
This study aimed to evaluate hearing results in patients with type 3 tympanoplasty using autologous cartilage grafts.
Methods
The study included patients treated with “stapes stabilizing cartilage graft” (SSCG) and Plastipore partial ossicular replacement prosthesis (PPORP) for hearing reconstruction. Hearing results and complications were assessed and postoperative audiological tests were performed at least 6 months after surgery.
Results
There were 18 patients (5 men, 13 women) in the SSCG group and 12 patients (5 men, 7 women) in the PPORP group. The air conduction threshold changed by 22.4 ± 7.5 dB in the SSCG group, and by 13.2 ± 12.9 dB in the PPORP group (p = 0.022), after hearing reconstruction. The air–bone gap (ABG) changed by 20.1 ± 8.3 dB in the SSCG group and by 16.3 ± 12.3 dB in the PPORP group. Although the change in ABG was greater in the SSCG group than in the PPORP group, the difference was not statistically significant (p > 0.05). No complications were recorded in the SSCG group, whereas two patients experienced a severe vertigo attack after surgery in the PPORP group, which lasted for approximately 2 weeks with conservative management. Extrusion was not encountered in the PPORP group, while extrusion of the titanium partial ossicular replacement prosthesis occurred in one patient in the SSCG group who underwent revision surgery.
Conclusions
Better hearing outcomes were obtained with SSCG than with PPORP. SSCG can be used as an alternative hearing reconstruction technique in cases of type 3 tympanoplasty.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Batti JS (2004) Ossicular discontinuity/fixation. In: Alper CM, Bluestone CD, Casselbrant ML, Dohar J, Mandel E (eds) Chapter 84. Advanced therapy of Otitis Media. BC Decker, pp 414–418
Kumar S, Yadav K, Ojha T, Sharma A, Singhal A, Gakhar S (2018) To evaluate and compare the result of ossiculoplasty using different types of graft materials and prosthesis in cases of ossicular discontinuity in chronic suppurative otitis media cases. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 70:15–21
Zollner F (1955) The principles of plastic surgery of the sound conducting apparatus. J Laryng 69:637
Frootko NJ (2008) Reconstruction of middle ear. Scott Brown’s otorhinolaryngology, head and neck surgery, 7th edn. Hodder Arnold, London
Mudhol RS, Naragund AI, Shruthi VS (2013) Ossiculoplasty: revisited. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 65:451–454
Glasscoc MG, Gulya A (2007) Glasscock-Shambangh surgery of the ear, 5th edn. Elsevier, Toronto
Luetje CM, Denninghoff JS (1987) Pericondrial attached double cartilage block: a better alternative to the PORP. Laryngoscope 97:1106–1108
Malafronte G, Filosa B, Mercone F (2008) A new double-cartilage block ossiculoplasty: long-term results. Otol Neurotol 29:531–533
Ayache D, Manac'h F, Teszler CB, Veyrat M, El-Bakkouri W, Corré A, Daval M (2017) Cartilage ossiculoplasty from stapes to tympanic membrane in one-stage intact canal wall tympanoplasty for cholesteatoma. J Int Adv Otol 13:171–175
Harvey SA, Lin SY (1999) Double cartilage block ossiculoplaty in chronic ear surgery. Laryngoscope 109:911–914
Nevoux J, Roger G, Chauvin P, Denoyelle F, Garabedian EN (2011) Cartilage shield tympanoplasty in children review of 268 consecutive cases. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 137:24–29
American Academy of Otolaryngology–Head and Neck Surgery Foundation Inc. (1995) Committee on hearing and equilibrium guidelines for the evaluation of results of treatment of conductive hearing loss. American Academy of Otolaryngology−Head and Neck Surgery Foundation, Inc. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 113:186–187
Wullstein H (1956) Theory and practice of tympanoplasty. Laryngoscope 66:1076–1093
Edizer DT, Durna YM, Hamit B, Demirhan H, Yigit O (2016) malleus to stapes bone cement rebridging ossiculoplasty: why don't we perform frequently? Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 125:445–451
Emir H, Kizilkaya KZ, Göcmen H, Uzunkulaoglu H, Tuzuner A, Bayiz U, Samim E (2009) Ossiculoplasty with intact stapes: analysis of hearing results according to the middle ear risk index. Acta Otolaryngol 129:1088–1094
Yu Z, Zhang L, Han D (2014) Long-term outcome of ossiculoplasty using autogenous mastoid cortical bone. J Laryngol Otol 128:866–870
Elsheikh MN, Elsherief H, Elsherief S (2006) Physiologic reestablishment of ossicular continuity during excision of retraction pockets: use of hydroxyapatite bone cement for rebridging the incus. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 132:196–199
Bayazit Y, Göksu N, Beder L (1999) Functional results of Plastipore prostheses for middle ear ossicular chain reconstruction. Laryngoscope 109:709–711
Baker AB, O'Connell BP, Nguyen SA, Lambert PR (2015) Ossiculoplasty with titanium prostheses in patients with intact s tapes: comparison of TORP versus PORP. Otol Neurotol 36:1676–1682
O’Connell BP, Rizk HG, Hutchinson T, Nguyen SA, Lambert PR (2016) Long-term outcomes of titanium ossiculoplasty in chronic otitis media. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 154:1084–1092
Woods O, El Fata F, Saliba I (2009) Ossicular reconstruction: incus versus universal titanium prosthesis. Auris Nasus Larynx 36:387–392
Yung MW (2003) Literature review of alloplastic materials in ossiculoplasty. J Laryngol Otol 117:431–436
Kim HH, Wiet RJ (2003) Preferred technique in ossiculoplasty. Oper Tech Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 14:243–246
Goldenberg RA (1992) Hydroxylapatite ossicular replacement prosthesis: a four-year experience. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 106:261–269
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Erdim, I., Sapmaz, E. Stapes stabilizing cartilage graft. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 277, 401–407 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-019-05721-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-019-05721-0