Abstract
Purpose
To compare the immunohistochemical expression of matrix metalloproteinases-2, -7, -9 and -26 and tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases-1 and -2 in pleomorphic adenomas and adenoid cystic carcinomas of the minor salivary glands.
Methods
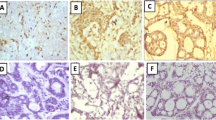
Twenty cases of pleomorphic adenomas and 20 cases of adenoid cystic carcinomas were evaluated for the immunohistochemical expression of matrix metalloproteinases-2, -7, -9, and -26 and tissue inhibitors-1 and -2 in tumor parenchyma.
Results
Most pleomorphic adenomas and adenoid cystic carcinomas showed high expression of matrix metalloproteinases and tissue inhibitors, predominantly located in the tumor cells. There was no statistically significant difference in the expression of the metalloproteinases-2 (p = 0.359), -7 (p = 0.081), and -26 (p = 0 553), as well as the tissue inhibitors-1 (p = 0.657), and -2 (p = 0.248) between the parenchyma of the studied tumors. Only matrix metalloproteinase-9 showed a significant difference in expression between the two tumors, with adenoid cystic carcinoma showing a more intense staining for this gelatinase (p = 0.041).
Conclusions
The expression of the studied metalloproteinases suggests the involvement of these enzymes in the tissue remodeling process in pleomorphic adenomas and adenoid cystic carcinomas, but only MMP-9, significantly expressed in the adenoid cystic carcinomas, appears to be involved in the process of invasiveness and more aggressive behavior of these tumors. Additionally, results point that TIMPs-1 and -2 may have more complex functions besides metalloproteinase inhibition, which may be related to the pathogenesis and biological behavior of salivary gland tumors.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barnes L, Eveson JW, Reichart P, Sidransky D (2005) World health organization classification of tumors: pathology & genetics—head and neck tumors, 3 edn. IARC Press, Lyon
Sung MW, Kim KH, Kim JW et al (2003) Clinicopathologic predictors and impact of distant metastasis from adenoid cystic carcinoma of the head and neck. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 129(11):1193–1197. https://doi.org/10.1001/archotol.129.11.1193.
El-Naggar AK et al (2017) WHO classification of head and neck tumors, 4 edn. IARC Press, Lyon
Bobbio A, Copelli C, Ampollini L et al (2008) Lung metastasis resection of adenoid cystic carcinoma of salivary glands. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg 33(5):790–793. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejcts.2007.12.057
Nagase H, Visse R, Murphy G (2006) Structure and function of matrix metalloproteinases and TIMPs. Cardiovasc Res 69(3):562–573. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cardiores.2005.12.002
Barros SSLV, Henriques ÁCG, Pereira KMA et al (2011) Immunohistochemical expression of matrix metalloproteinases in squamous cell carcinoma of the tongue and lower lip. Arch Oral Biol 56(8):752–760. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.archoralbio.2010.11.022
Souza Freitas V, de Andrade Santos PP, Almeida Freitas RD et al (2011) Mast cells and matrix metalloproteinase 9 expression in actinic cheilitis and lip squamous cell carcinoma. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 112(3):342–348. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tripleo.2011.02.032.
Kayano K, Shimada T, Shinomiya T et al (2004) Activation of pro-MMP-2 mediated by MT1-MMP in human salivary gland carcinomas: possible regulation of pro-MMP-2 activation by TIMP-2. J Pathol 202(4):403–411. https://doi.org/10.1002/path.1541
Wang Y, Irie T, Aida T, Tachikawa T (2005) Expression of TIMP-1 and -2 in different growth patterns of adenoid cystic carcinoma. Oral Oncol 41(8):821–827. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oraloncology.2005.04.009
Nagel H, Laskawi R, Wahlers A, Hemmerlein B (2004) Expression of matrix metalloproteinases MMP-2, MMP-9 and their tissue inhibitors TIMP-1, -2, and -3 in benign and malignant tumours of the salivary gland. Histopathology 44(3):222–231
Hu JA, Xu JY, Li YN et al (2005) Expression of MMP-2 and E-CD in salivary mucoepidermoid carcinoma and its correlation with infiltration, metastasis and prognosis. Zhejiang Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban 34(5):421–426
Chen Y, Tian K, Geng N et al (2005) The expression of matrix metalloproteinases and their tissue inhibitors in pleomorphic adenoma]. Zhonghua Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi 40(1):58–61
Lipari L, Mauro A, Gallina S, Tortorici S, Buscemi M, Tete S, Gerbino A (2012) Expression of gelatinases (Mmp-2, Mmp-9) and cyclooxygenases (Cox1, Cox-2) in some benign salivary gland tumors. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol 25(1):107–115. https://doi.org/10.1177/039463201202500113
Mardani M, Andisheh-Tadbir A, Khademi B et al (2014) Serum level of matrix metalloproteinase-9 in patients with salivary gland tumor. J Dent Shiraz Univ Med Sci 15(4):199–203
Tang YL, Liu X, Gao SY et al (2015) WIP1 stimulates migration and invasion of salivary adenoid cystic carcinoma by inducing MMP-9 and VEGF-C. Oncotarget 6(11):9031–9044. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.3320
Kolude B, Akinyele A, Ahmed L et al (2015) Stoichiometric expression of MMP-2/TIMP-2 in benign and malignant tumours of the salivary gland. Tumor Biol 36:2351–2357. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-014-2842-8
Zhao L, Jiang L, Du P et al (2016) Expression of SKA1 and MMP-9 in primary salivary adenoid cystic carcinoma: Correlation with tumor progression and patient prognosis. Acta Otolaryngol 136(6):575–579. https://doi.org/10.3109/00016489.2016.1142117
Luukkaa H, Klemi P, Hirsimaki P et al (2010) Matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-7 in salivary gland cancer. Acta Oncol 49(1):85–90. https://doi.org/10.3109/02841860903287197 (a)
Daa T, Kashima K, Kondo Y et al (2008) Aberrant methylation in promoter regions of cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor genes in adenoid cystic carcinoma of the salivary gland. APMIS 116(1):21–26. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0463.2008.00773.x
Polette M, Nawrocki-Raby B, Gilles C et al (2004) Tumour invasion and matrix metalloproteinases. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 49(3):179–186. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.critrevonc.2003.10.008
Li M, Yamamoto H, Adachi Y et al (2006) Role of matrix metalloproteinase-7 (matrilysin) in human cancer invasion, apoptosis, growth, and angiogenesis. Exp Biol Med (Maywood) 231(1):20–27
Zhang CY, Mao L, Li L et al (2007) Promoter methylation as a common mechanism for inactivating E-cadherin in human salivary gland adenoid cystic carcinoma. Cancer 110(1):87–95. https://doi.org/10.1002/cncr.22758
Wang R, Geng N, Zhou Y et al (2015) Aberrant Wnt-1/beta-catenin signaling and WIF-1 deficiency are important events which promote tumor cell invasion and metastasis in salivary gland adenoid cystic carcinoma. Bio-Med Mater Eng 26(1): S2145-153. https://doi.org/10.3233/BME-151520
Bourboulia D, Stetler-Stevenson WG (2010) Matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) and tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases (TIMPs): positive and negative regulators in tumor cell adhesion. Semin Cancer Biol 20(3):161–168. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semcancer.2010.05.002
Tian K, Chen Y, Geng N et al (2005) Relationship of the disturbed balance between matrix metalloproteinases and their tissue inhibitors and the invasion of malignant salivary gland tumours. Hua xi kou qiang yi xue za zhi 23(4):273–276
Luukkaa H, Klemi P, Leivo I et al (2010) Expression of matrix metalloproteinase-1, -7, -9, -13, Ki-67, and HER-2 in epithelial-myoepithelial salivary gland cancer. Head Neck 32(8):1019–1027. https://doi.org/10.1002/hed.21277(b)
Verma RP, Hansch C (2007) Matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs): chemical-biological functions and (Q)SARs. Bioorg Med Chem 15(6):2223–2268. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmc.2007.01.011
Monaghan H, MacWhinnie N, Williams AR (2007) The role of matrix metalloproteinases-2, -7 and -9 and beta-catenin in high grade endometrial carcinoma. Histopathology 50(3):348–357. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2559.2007.02612.x
Kerkela E, Saarialho-Kere U (2003) Matrix metalloproteinases in tumor progression: focus on basal and squamous cell skin cancer. Exp Dermatol 12(2):109–125
Kuula H, Salo T, Pirila E et al (2008) Human beta-defensin-1 and -2 and matrix metalloproteinase-25 and -26 expression in chronic and aggressive periodontitis and in peri-implantitis. Arch Oral Biol 53(2):175–186. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.archoralbio.2007.09.010
Uria JA, Lopez-Otin C (2000) Matrilysin-2, a new matrix metalloproteinase expressed in human tumors and showing the minimal domain organization required for secretion, latency, and activity. Cancer Res 60(17):4745–4751
Luukkaa H, Klemi P, Hirsimaki P et al (2008) Matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-1, -9 and -13 as prognostic factors in salivary gland cancer. Acta Otolaryngol 128(4):482–490. https://doi.org/10.1080/00016480801922895
Zhang X, Wang Y, Yamamoto G, Tachikawa T (2009) Expression of matrix metalloproteinases MMP-2, MMP-9 and their tissue inhibitors TIMP-1 and TIMP-2 in the epithelium and stroma of salivary gland pleomorphic adenomas. Histopathology 55(3):250–260. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2559.2009.03355.x
Raitz R, Martins MD, Araujo VC (2003) A study of the extracellular matrix in salivary gland tumors. J Oral Pathol Med 32(5):290–296
Bento PM, Freitas RA, Pinto LP, Souza LB (2006) Tenascin and fibronectin in pleomorphic adenoma of the salivary gland. J Appl Oral Sci 14(3):198–202
de Vicente JC, Lequerica-Fernandez P, Lopez-Arranz JS et al (2008) Expression of matrix metalloproteinase-9 in high-grade salivary gland carcinomas is associated with their metastatic potential. Laryngoscope 118(2):247–251. https://doi.org/10.1097/MLG.0b013e318158f754
Funding
Supported by CNPq-Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (Grant no. 307539/2010-5). Jean Nunes dos Santos, Cassiano Francisco Weege Nonaka, Leão Pereira Pinto and Lelia Batista de Souza are research fellows at CNPq, Brazil.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
None of the authors has any conflict of interest, financial or otherwise.
Ethical approval
This study was approved by the UFRN Research Ethics Committee, Natal, Brazil (No. 203/2008).
Patient consent
Not required.
Statement of agreement
Certify that all authors (Valéria Souza Freitas; Jean Nunes dos Santos; Pedro Paulo de Andrade Santos; Cassiano Francisco Weege Nonaka; Leão Pereira Pinto and Lélia Batista de Souza) have viewed and agreed to the manuscript submitted.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Souza Freitas, V., dos Santos, J.N., de Andrade Santos, P.P. et al. Expression of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs-2, -7, -9, and -26) and tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases (TIMPs-1 and -2) in pleomorphic adenomas and adenoid cystic carcinomas. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 275, 3075–3082 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-018-5176-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-018-5176-0