Abstract
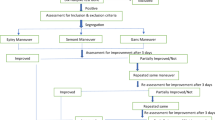
Although several researchers have tried various canalith repositioning procedures for lateral canalolithiasis, a standard treatment has not been established. We adopt 120° rotation, which is anatomically appropriate because the principle of cure may be the fixing of pathological debris to the dark cells of the utricle. The aims of this study were to clarify the efficacy rate of the affected-ear-up 120° maneuver and to elucidate the appearance rate of lying-down nystagmus in patients with lateral canalolithiasis. The subjects were 31 patients (26 females, 5 males) who revealed transient direction-changing geotropic positional nystagmus. After determining the involved side, we performed the canalith repositioning procedure immediately. To perform this maneuver: (1) Place the patient in the supine position. (2) Rotate the head toward the healthy side until facing downward 120° from supine. (3) Sit up. (4) Ask the patient to remain upright with the chin down until going to bed. Twenty-nine patients (94%) became symptom free by only one maneuver. However, one patient converted to ipsilateral posterior cupulolithiasis, and another required a second maneuver. Lying-down nystagmus was found in 29 patients (94%), the transient type in 23 (74%), and the persistent type in 6 (19%). The direction of transient (not persistent) lying-down nystagmus was mostly toward the healthy side. These results suggest that the affected-ear-up 120° maneuver is effective and that lying-down nystagmus appears at a high rate.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dix MR, Hallpike CS (1952) The pathology, symptomatology and diagnosis of certain common disorders of the vestibular system. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 61:987–1016
Imai T, Takeda N, Ito M et al (2009) 3D analysis of benign positional nystagmus due to cupulolithiasis in posterior semicircular canal. Acta Otolaryngol 129:1044–1049
Ichijo H (2013) Cupulolithiasis of the posterior semicircular canal. Am J Otolaryngol 34:458–463
Cupulolithiasis (heavy cupula) of the left posterior semicircular canal. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=D3qpATkJp2s. Accessed 5 July 2017
Baloh RW, Yue Q, Jacobson KM et al (1995) Persistent direction-changing positional nystagmus: another variant of benign positional nystagmus? Neurology 45:1297–1301
Bisdorff AR, Debatisse D (2001) Localizing signs in positional vertigo due to lateral canal cupulolithiasis. Neurology 57:1085–1088
Hiruma K, Numata T (2004) Positional nystagmus showing neutral points. ORL J 66:46–50
Ichijo H (2012) Persistent direction-changing geotropic positional nystagmus. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 269:747–751
Kim CH, Kim MB, Ban JH (2014) Persistent geotropic direction-changing positional nystagmus with a null plane: the light cupula. Laryngoscope 124:15–19
Seo T, Shiraishi K, Kobayashi T et al (2016) Clinical course of persistent geotropic direction-changing positional nystagmus with neutral position-Light cupula. Acta Otolaryngol 136:34–37
McClure JA (1985) Horizontal canal BPV. J Otolaryngol 14:30–35
Baloh RW, Jacobson K, Honrubia V (1993) Horizontal semicircular canal variant of benign positional vertigo. Neurology 43:2542–2549
Epley JM (1995) Positional vertigo related to semicircular canalithiasis. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 112:154–161
Lempert T, Tiel-Wilck K (1996) A positional maneuver for treatment of horizontal-canal benign positional vertigo. Laryngoscope 106:476–478
Escher A, Ruffieux C, Maire R (2007) Efficacy of the barbecue manoeuvre in benign paroxysmal vertigo of the horizontal canal. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 264:1239–1241
Ichijo H (2013) Asymmetry of positioning nystagmus in posterior canalolithiasis. Acta Otolaryngol 133:159–164
Koo JW, Moon IJ, Shim WS et al (2006) Value of lying-down nystagmus in the lateralization of horizontal semicircular canal benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Otol Neurotol 27:367–371
Ichijo H (2016) Neutral position of persistent direction-changing positional nystagmus. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 273:311–316
Yamane H, Imoto T, Nakai Y et al (1984) Otoconia degradation. Acta Otolaryngol Suppl 406:263–270
Harada Y, Takumida M (1990) Functional aspects of the vestibular dark cells in the guinea pig: morphological investigation using ruthenium red staining technique. Auris Nasus Larynx 17:77–85
Ichijo H (2011) Positional nystagmus of horizontal canalolithiasis. Acta Otolaryngol 131:46–51
Ichijo H (2017) Onset time of benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Acta Otolaryngol 137:144–148
Shigeno K (2015) Positional treatments for lateral semicircular canal benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Equilib Res 74:191–198
Curious positional nystagmus. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=IJMkkW6DOMQ&t=6s. Accessed 5 July 2017
Appiani GC, Catania G, Gagliardi M et al (2005) Repositioning maneuver for the treatment of the apogeotropic variant of horizontal canal benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Otol Neurotol 26:257–260
House MG, Honrubia V (2003) Theoretical models for the mechanisms of benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Audiol Neurootol 8:91–99
Otsuka K, Suzuki M, Furuya M (2003) Model experiment of benign paroxysmal positional vertigo mechanism using the whole membranous labyrinth. Acta Otolaryngol 123:515–518
Valli P, Botta L, Zucca G et al (2008) Simulation of cupulolithiasis and canalolithiasis by an animal model. J Vestib Res 18:89–96
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr. Kazunori Futai for preparing some of the figures.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
We declare that we have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Funding
None.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ichijo, H. Affected-ear-up 120° maneuver for treatment of lateral semicircular canal benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 274, 3351–3357 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-017-4663-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-017-4663-z