Abstract
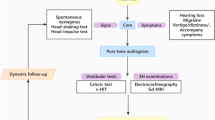
The aim of this study was to examine the efficacy of methylprednisolone in vestibular neuritis (VN) by objective and subjective measures. This prospective controlled randomized study was conducted at one tertiary hospital. Twenty-nine VN patients were randomized to either the steroid (n = 15) or the control (n = 14) group. The steroid group received methylprednisolone for 2 weeks, whereas control patients did not; both groups underwent regular vestibular exercises and were prescribed a Ginkgo biloba. Vestibular function tests including caloric test, video head impulse test (vHIT), and sensory organization test (SOT) were performed, and dizziness handicap index (DHI) was determined at enrollment; all tests were repeated at 1 and 6 months after enrollment. Both groups showed statistically significant improvements in caloric weakness and vHIT gain at 1- and 6-month follow-up evaluations compared to the initial examination; however, differences were not significant. The rates of normalization of canal paresis at 1 and 6 months were 50 and 64% in the control group and 33 and 60% in the steroid group, respectively, with no differences between the two groups. The rates of vHIT normalization at 1 and 6 months after treatment were 57 and 78% in the control group and 53 and 87% in the steroid group, respectively, with no differences between the two groups. Finally, there were no significant differences in the improvement of composite scores of SOT and the DHI scores between the two groups. In this prospective RCT, methylprednisolone had no additional benefit in patients with VN who underwent vestibular exercises and received a Ginkgo biloba.
Trial registration: Clinicaltrials.gov Identifier, NCT02098330; Trial title, The Efficacy of Steroid Therapy in Vestibular Neuritis.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Strupp M, Zingler VC, Arbusow V, Niklas D, Maag KP, Dieterich M, Bense S, Theil D, Jahn K, Brandt T (2004) Methylprednisolone, valacyclovir, or the combination for vestibular neuritis. N Engl J Med 351(4):354–361. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa033280
Baloh RW (2003) Clinical practice. Vestibular neuritis. N Engl J Med 348(11):1027–1032. doi:10.1056/NEJMcp021154
Murofushi T, Iwasaki S, Ushio M (2006) Recovery of vestibular evoked myogenic potentials after a vertigo attack due to vestibular neuritis. Acta Otolaryngol 126(4):364–367. doi:10.1080/00016480500417189
Okinaka Y, Sekitani T, Okazaki H, Miura M, Tahara T (1993) Progress of caloric response of vestibular neuronitis. Acta Otolaryngol Suppl 503:18–22
Shupak A, Issa A, Golz A, Margalit K, Braverman I (2008) Prednisone treatment for vestibular neuritis. Otol Neurotol 29(3):368–374. doi:10.1097/MAO.0b013e3181692804
Manzari L, Burgess AM, MacDougall HG, Curthoys IS (2013) Vestibular function after vestibular neuritis. Int J Audiol 52(10):713–718. doi:10.3109/14992027.2013.809485
Adour KK, Ruboyianes JM, Von Doersten PG, Byl FM, Trent CS, Quesenberry CP Jr, Hitchcock T (1996) Bell’s palsy treatment with acyclovir and prednisone compared with prednisone alone: a double-blind, randomized, controlled trial. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 105(5):371–378
Cope D, Bova R (2008) Steroids in otolaryngology. Laryngoscope 118(9):1556–1560. doi:10.1097/MLG.0b013e31817c0b4d
Fishman JM, Burgess C, Waddell A (2011) Corticosteroids for the treatment of idiopathic acute vestibular dysfunction (vestibular neuritis). Cochrane Database Syst Rev 5:Cd008607. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD008607.pub2
Kitahara T, Kondoh K, Morihana T, Okumura S, Horii A, Takeda N, Kubo T (2003) Steroid effects on vestibular compensation in human. Neurol Res 25(3):287–291. doi:10.1179/016164103101201364
MacDougall HG, Weber KP, McGarvie LA, Halmagyi GM, Curthoys IS (2009) The video head impulse test: diagnostic accuracy in peripheral vestibulopathy. Neurology 73(14):1134–1141. doi:10.1212/WNL.0b013e3181bacf85
Weber KP, Aw ST, Todd MJ, McGarvie LA, Curthoys IS, Halmagyi GM (2008) Head impulse test in unilateral vestibular loss: vestibulo-ocular reflex and catch-up saccades. Neurology 70(6):454–463. doi:10.1212/01.wnl.0000299117.48935.2e
Park HJ, Migliaccio AA, Della Santina CC, Minor LB, Carey JP (2005) Search-coil head-thrust and caloric tests in Meniere’s disease. Acta Otolaryngol 125(8):852–857
Yoo MH, Kim SH, Lee JY, Yang CJ, Lee HS, Park HJ (2016) Results of video head impulse and caloric tests in 36 patients with vestibular migraine and 23 patients with vestibular neuritis: a preliminary report. Clin Otolaryngol. doi:10.1111/coa.12556
Jung JH, Yoo MH, Song CI, Lee JR, Park HJ (2015) Prognostic significance of vestibulospinal abnormalities in patients with vestibular migraine. Otol Neurotol 36(2):282–288. doi:10.1097/mao.0000000000000656
Yang CJ, Lee JY, Kang BC, Lee HS, Yoo MH, Park HJ (2016) Quantitative analysis of gains and catch-up saccades of video-head impulse testing by age in normal subjects. Clin Otolaryngol. doi:10.1111/coa.12558
Jacobson GP, Newman CW (1990) The development of the dizziness handicap inventory. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 116(4):424–427
Karlberg ML, Magnusson M (2011) Treatment of acute vestibular neuronitis with glucocorticoids. Otol Neurotol 32(7):1140–1143. doi:10.1097/MAO.0b013e3182267e24
Goudakos JK, Markou KD, Psillas G, Vital V, Tsaligopoulos M (2014) Corticosteroids and vestibular exercises in vestibular neuritis. Single-blind randomized clinical trial. JAMA Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 140(5):434–440. doi:10.1001/jamaoto.2014.48
Goudakos JK, Markou KD, Franco-Vidal V, Vital V, Tsaligopoulos M, Darrouzet V (2010) Corticosteroids in the treatment of vestibular neuritis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Otol Neurotol 31(2):183–189. doi:10.1097/MAO.0b013e3181ca843d
Bartolomeo M, Biboulet R, Pierre G, Mondain M, Uziel A, Venail F (2014) Value of the video head impulse test in assessing vestibular deficits following vestibular neuritis. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 271(4):681–688. doi:10.1007/s00405-013-2451-y
Allum JH, Honegger F (2013) Relation between head impulse tests, rotating chair tests, and stance and gait posturography after an acute unilateral peripheral vestibular deficit. Otol Neurotol 34(6):980–989. doi:10.1097/MAO.0b013e31829ce5ec
Magliulo G, Iannella G, Gagliardi S, Re M (2015) A 1-year follow-up study with C-VEMPs, O-VEMPs and video head impulse testing in vestibular neuritis. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 272(11):3277–3281. doi:10.1007/s00405-014-3404-9
Nashner LM, Peters JF (1990) Dynamic posturography in the diagnosis and management of dizziness and balance disorders. Neurol Clin 8(2):331–349
Horak FB, Nashner LM, Diener HC (1990) Postural strategies associated with somatosensory and vestibular loss. Exp Brain Res 82(1):167–177
Batuecas-Caletrio A, Yanez-Gonzalez R, Sanchez-Blanco C, Perez PB, Gonzalez-Sanchez E, Sanchez LA, Kaski D (2015) Glucocorticoids improve acute dizziness symptoms following acute unilateral vestibulopathy. J Neurol. doi:10.1007/s00415-015-7918-x
Black FO, Shupert CL, Peterka RJ, Nashner LM (1989) Effects of unilateral loss of vestibular function on the vestibulo-ocular reflex and postural control. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 98(11):884–889
Goebel JA, Paige GD (1989) Dynamic posturography and caloric test results in patients with and without vertigo. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 100(6):553–558
Furman JM (1995) Role of posturography in the management of vestibular patients. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 112(1):8–15
Marioni G, Fermo S, Zanon D, Broi N, Staffieri A (2013) Early rehabilitation for unilateral peripheral vestibular disorders: a prospective, randomized investigation using computerized posturography. Eur Arch Oto-rhino-laryngol 270(2):425–435. doi:10.1007/s00405-012-1944-4
Nyabenda A, Briart C, Deggouj N, Gersdorff M (2004) Normative study and reliability of French version of the dizziness handicap inventory. Ann Readapt Med Phys 47(3):105–113. doi:10.1016/j.annrmp.2003.11.002
Zaitseva OV (2014) The role of tanakan in the improvement of the effectiveness of vestibular rehabilitation. Vestn Otorinolaringol 5:66–68
Hamann KF (2007) Special ginkgo extract in cases of vertigo: a systematic review of randomised, double-blind, placebo controlled clinical examinations. HNO 55(4):258–263. doi:10.1007/s00106-006-1440-5
Acknowledgements
This study was funded by a grant from the Korea Healthcare Technology R&D Project, Ministry of Health and Welfare, Republic of Korea (HI10C2020), which had no role in the design and conduct of the study; collection, management, analysis, and interpretation of the data; preparation, review, or approval of the manuscript; and decision to submit the manuscript for publication.
Funding
This study was funded by a grant from the Korea Healthcare Technology R&D Project, Ministry of Health and Welfare, Republic of Korea (HI10C2020).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that there were no conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yoo, M.H., Yang, C.J., Kim, S.A. et al. Efficacy of steroid therapy based on symptomatic and functional improvement in patients with vestibular neuritis: a prospective randomized controlled trial. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 274, 2443–2451 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-017-4556-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-017-4556-1