Abstract
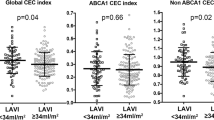
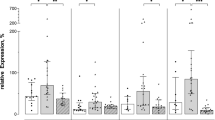
Increased morbidity and mortality in atrial fibrillation (AF) are related to the pro-fibrotic, pro-thrombotic, and pro-inflammatory processes that underpin the disease. High-density lipoproteins (HDL) have anti-inflammatory, anti-oxidative, and anti-thrombotic properties. Functional impairment of HDL may, therefore, associate with AF initiation or progression. We studied indices of HDL quality and quantity of AF patients and healthy controls, including HDL-particle number, HDL cholesterol, apolipoprotein (apo) A–I levels, serum amyloid A (SAA) content and HDL-cholesterol efflux capacity, and paraoxonase activity of apoB-depleted serum. Serum samples were collected from AF patients (n = 91) before catheter ablation and from age- and sex-matched control subjects (n = 54). HDL-cholesterol efflux capacity was assessed in a validated assay using [3H]-cholesterol-labeled J774 macrophages. Lecithin–cholesterol acyltransferase (LCAT) and paraoxonase activities were assessed using fluorometric assays, SAA levels were determined by ELISA, and total and subclass HDL-particle number was assessed by nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. ApoA-I levels were determined by immunoturbidimetry. HDL-cholesterol efflux capacity, HDL-particle number, apoA-I levels, and LCAT activity were markedly reduced in AF patients when compared to healthy individuals (all p < 0.001), whereas HDL-associated paraoxonase activity and SAA content were not altered (p = 0.578, p = 0.681). Notably, cholesterol efflux capacity, HDL-particle number, apoA-I levels as well as LCAT activity recovered following restoration of sinus rhythm (all p < 0.001). We identified marked alterations in HDL function, HDL maturation, and HDL-particle number in AF patients. Assessing HDL-particle number and function in AF may be used as a surrogate marker of AF onset and progression and may help identifying patients at high risk.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alonso A, Yin X, Roetker NS, Magnani JW, Kronmal RA, Ellinor PT, Chen LY, Lubitz SA, McClelland RL, McManus DD, Soliman EZ, Huxley RR, Nazarian S, Szklo M, Heckbert SR, Benjamin EJ (2014) Blood lipids and the incidence of atrial fibrillation: the multi-ethnic study of atherosclerosis and the Framingham Heart Study. J Am Heart Assoc. https://doi.org/10.1161/jaha.114.001211
Artl A, Marsche G, Lestavel S, Sattler W, Malle E (2000) Role of serum amyloid A during metabolism of acute-phase HDL by macrophages. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 20:763–772
Barter PJ, Nicholls S, Rye K-A, Anantharamaiah GM, Navab M, Fogelman AM (2004) Antiinflammatory properties of HDL. Circ Res. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.res.0000146094.59640.13
Bauer L, Kern S, Rogacev KS, Emrich IE, Zawada A, Fliser D, Heinemann A, Heine GH, Marsche G (2017) HDL cholesterol efflux capacity and cardiovascular events in patients with chronic kidney disease. J Am Coll Cardiol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacc.2016.10.054
Benjamin EJ, Wolf PA, D’Agostino RB, Silbershatz H, Kannel WB, Levy D (1998) Impact of atrial fibrillation on the risk of death: the Framingham Heart Study. Circulation 98:946–952
Besler C, Heinrich K, Rohrer L, Doerries C, Riwanto M, Shih DM, Chroni A, Yonekawa K, Stein S, Schaefer N, Mueller M, Akhmedov A, Daniil G, Manes C, Templin C, Wyss C, Maier W, Tanner FC, Matter CM, Corti R, Furlong C, Lusis AJ, Eckardstein A, Fogelman AM, Lüscher TF, Landmesser U (2011) Mechanisms underlying adverse effects of HDL on eNOS-activating pathways in patients with coronary artery disease. J Clin Investig. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci42946
Bhattacharyya T, Nicholls SJ, Topol EJ, Zhang R, Yang X, Schmitt D, Fu X, Shao M, Brennan DM, Ellis SG, Brennan M-L, Allayee H, Lusis AJ, Hazen SL (2008) Relationship of paraoxonase 1 (PON1) gene polymorphisms and functional activity with systemic oxidative stress and cardiovascular risk. JAMA. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.299.11.1265
Birner-Gruenberger R, Schittmayer M, Holzer M, Marsche G (2014) Understanding high-density lipoprotein function in disease: recent advances in proteomics unravel the complexity of its composition and biology. Prog Lipid Res. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plipres.2014.07.003
Büttner P, Schumacher K, Dinov B, Zeynalova S, Sommer P, Bollmann A, Husser D, Hindricks G, Kornej J (2018) Role of NT-proANP and NT-proBNP in patients with atrial fibrillation. Heart Rhythm. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hrthm.2018.03.021
Curcic S, Holzer M, Pasterk L, Knuplez E, Eichmann TO, Frank S, Zimmermann R, Schicho R, Heinemann A, Marsche G (2017) Secretory phospholipase A2 modified HDL rapidly and potently suppresses platelet activation. Sci Rep. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-08136-1
Di Biase L, Mohanty P, Mohanty S, Santangeli P, Trivedi C, Lakkireddy D, Reddy M, Jais P, Themistoclakis S, Dello Russo A, Casella M, Pelargonio G, Narducci ML, Schweikert R, Neuzil P, Sanchez J, Horton R, Beheiry S, Hongo R, Hao S, Rossillo A, Forleo G, Tondo C, Burkhardt JD, Haissaguerre M, Natale A (2016) Ablation versus amiodarone for treatment of persistent atrial fibrillation in patients with congestive heart failure and an implanted device: results from the AATAC multicenter randomized trial. Circulation. https://doi.org/10.1161/circulationaha.115.019406
Francone OL, Gurakar A, Fielding C (1989) Distribution and functions of lecithin: cholesterol acyltransferase and cholesteryl ester transfer protein in plasma lipoproteins. Evidence for a functional unit containing these activities together with apolipoproteins A-I and D that catalyzes the esterification and transfer of cell-derived cholesterol. J Biol Chem 264:7066–7072
Holzer M, Schilcher G, Curcic S, Trieb M, Ljubojevic S, Stojakovic T, Scharnagl H, Kopecky CM, Rosenkranz AR, Heinemann A, Marsche G (2015) Dialysis modalities and HDL composition and function. J Am Soc Nephrol. https://doi.org/10.1681/asn.2014030309
Holzer M, Trieb M, Konya V, Wadsack C, Heinemann A, Marsche G (2013) Aging affects high-density lipoprotein composition and function. Biochim Biophys Acta. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbalip.2013.06.004
Hopkins PN, Pottala JV, Nanjee MN (2015) A comparative study of four independent methods to measure LDL particle concentration. Atherosclerosis. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2015.08.042
Issac TT, Dokainish H, Lakkis NM (2007) Role of inflammation in initiation and perpetuation of atrial fibrillation: a systematic review of the published data. J Am Coll Cardiol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacc.2007.06.054
Khera AV, Cuchel M, de la Llera-Moya M, Rodrigues A, Burke MF, Jafri K, French BC, Phillips JA, Mucksavage ML, Wilensky RL, Mohler ER, Rothblat GH, Rader DJ (2011) Cholesterol efflux capacity, high-density lipoprotein function, and atherosclerosis. N Engl J Med. https://doi.org/10.1056/nejmoa1001689
Kirchhof P, Benussi S, Kotecha D, Ahlsson A, Atar D, Casadei B, Castella M, Diener H-C, Heidbuchel H, Hendriks J, Hindricks G, Manolis AS, Oldgren J, Popescu BA, Schotten U, van Putte B, Vardas P (2016) 2016 ESC guidelines for the management of atrial fibrillation developed in collaboration with EACTS. Eur Heart J. https://doi.org/10.1093/eurheartj/ehw210
Korantzopoulos P, Kolettis TM, Galaris D, Goudevenos JA (2007) The role of oxidative stress in the pathogenesis and perpetuation of atrial fibrillation. Int J Cardiol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijcard.2006.04.026
Mackey RH, Greenland P, Goff DC, Lloyd-Jones D, Sibley CT, Mora S (2012) High-density lipoprotein cholesterol and particle concentrations, carotid atherosclerosis, and coronary events: MESA (multi-ethnic study of atherosclerosis). J Am Coll Cardiol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacc.2012.03.060
Marrouche NF, Brachmann J, Andresen D, Siebels J, Boersma L, Jordaens L, Merkely B, Pokushalov E, Sanders P, Proff J, Schunkert H, Christ H, Vogt J, Bänsch D (2018) Catheter ablation for atrial fibrillation with heart failure. N Engl J Med. https://doi.org/10.1056/nejmoa1707855
Mineo C, Deguchi H, Griffin JH, Shaul PW (2006) Endothelial and antithrombotic actions of HDL. Circ Res. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.res.0000225982.01988.93
Mora S, Otvos JD, Rifai N, Rosenson RS, Buring JE, Ridker PM (2009) Lipoprotein particle profiles by nuclear magnetic resonance compared with standard lipids and apolipoproteins in predicting incident cardiovascular disease in women. Circulation. https://doi.org/10.1161/circulationaha.108.816181
Navab M, Yu R, Gharavi N, Huang W, Ezra N, Lotfizadeh A, Anantharamaiah GM, Alipour N, van Lenten BJ, Reddy ST, Marelli D (2007) High-density lipoprotein: antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. Curr Atheroscler Rep 9:244–248
Potočnjak I, Degoricija V, Trbušić M, Pregartner G, Berghold A, Marsche G, Frank S (2017) Serum concentration of HDL particles predicts mortality in acute heart failure patients. Sci Rep. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep46642
Rohatgi A, Khera A, Berry JD, Givens EG, Ayers CR, Wedin KE, Neeland IJ, Yuhanna IS, Rader DR, de Lemos James A, Shaul PW (2014) HDL cholesterol efflux capacity and incident cardiovascular events. N Engl J Med. https://doi.org/10.1056/nejmoa1409065
Sattler K, Gräler M, Keul P, Weske S, Reimann C-M, Jindrová H, Kleinbongard P, Sabbadini R, Bröcker-Preuss M, Erbel R, Heusch G, Levkau B (2015) Defects of high-density lipoproteins in coronary artery disease caused by low sphingosine-1-phosphate content: correction by sphingosine-1-phosphate-loading. J Am Coll Cardiol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacc.2015.07.057
Sattler KJE, Elbasan S, Keul P, Elter-Schulz M, Bode C, Gräler MH, Bröcker-Preuss M, Budde T, Erbel R, Heusch G, Levkau B (2010) Sphingosine 1-phosphate levels in plasma and HDL are altered in coronary artery disease. Basic Res Cardiol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00395-010-0112-5
Spieker LE, Sudano I, Hürlimann D, Lerch PG, Lang MG, Binggeli C, Corti R, Ruschitzka F, Lüscher TF, Noll G (2002) High-density lipoprotein restores endothelial function in hypercholesterolemic men. Circulation 105:1399–1402
Tang WHW, Wu Y, Mann S, Pepoy M, Shrestha K, Borowski AG, Hazen SL (2011) Diminished antioxidant activity of high-density lipoprotein-associated proteins in systolic heart failure. Circ Heart Fail. https://doi.org/10.1161/circheartfailure.110.958348
Theilmeier G, Schmidt C, Herrmann J, Keul P, Schäfers M, Herrgott I, Mersmann J, Larmann J, Hermann S, Stypmann J, Schober O, Hildebrand R, Schulz R, Heusch G, Haude M, von Wnuck Lipinski K, Herzog C, Schmitz M, Erbel R, Chun J, Levkau B (2006) High-density lipoproteins and their constituent, sphingosine-1-phosphate, directly protect the heart against ischemia/reperfusion injury in vivo via the S1P3 lysophospholipid receptor. Circulation. https://doi.org/10.1161/circulationaha.105.607135
Trieb M, Horvath A, Birner-Gruenberger R, Spindelboeck W, Stadlbauer V, Taschler U, Curcic S, Stauber RE, Holzer M, Pasterk L, Heinemann A, Marsche G (2016) Liver disease alters high-density lipoprotein composition, metabolism and function. Biochim Biophys Acta. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbalip.2016.04.013
Trieb M, Wolf P, Knuplez E, Weger W, Schuster C, Peinhaupt M, Holzer M, Trakaki A, Eichmann T, Lass A, Wadsack C, Schuligoi R, Heinemann A, Marsche G (2019) Abnormal composition and function of high-density lipoproteins in atopic dermatitis patients. Allergy. https://doi.org/10.1111/all.13620
Wilson PW, Garrison RJ, Castelli WP, Feinleib M, McNamara PM, Kannel WB (1980) Prevalence of coronary heart disease in the Framingham Offspring Study: role of lipoprotein cholesterols. Am J Cardiol 46:649–654
Zewinger S, Drechsler C, Kleber ME, Dressel A, Riffel J, Triem S, Lehmann M, Kopecky C, Säemann MD, Lepper PM, Silbernagel G, Scharnagl H, Ritsch A, Thorand B, las de Heras Gala T, Wagenpfeil S, Koenig W, Peters A, Laufs U, Wanner C, Fliser D, Speer T, März W (2015) Serum amyloid A: high-density lipoproteins interaction and cardiovascular risk. Eur Heart J. https://doi.org/10.1093/eurheartj/ehv352
Funding
This work was supported by the Austrian Science Fund FWF (FWF W1241, DK-MOLIN, and P22976-B18 to GM). PB and DH were supported by the Volkswagen Foundation Germany through the Lichtenberg professorship program to DH (#84901)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Trieb, M., Kornej, J., Knuplez, E. et al. Atrial fibrillation is associated with alterations in HDL function, metabolism, and particle number. Basic Res Cardiol 114, 27 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00395-019-0735-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00395-019-0735-0