Abstract
Purpose
We aimed to study whether macronutrient intake could modify the association between ApoB Ins/Del and lipid profile, and serum leptin and ghrelin in type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) patients.
Methods
In this study, 700 T2DM patients were recruited. Anthropometric, biochemical and molecular data were collected, and Diet was assessed using a food frequency questionnaire. The interactions were tested using ANCOVA.
Results
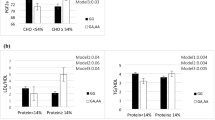
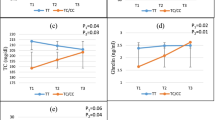
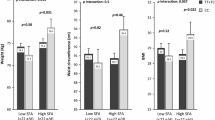
Del-allele carriers with high-MUFA and carbohydrate (≥ 12 and ≥ 54% of energy, respectively) had significantly higher TG (P = 0.04) and LDL-C (P = 0.02) compared to Ins/Ins homozygotes, and these were not significant in subjects with low-MUFA and -carbohydrate (< 12 and < 54%, respectively). A significant interaction was observed between ApoB Ins/Del and diet on TG in both unadjusted (P = 0.03) and adjusted models (model 2 and 3, P = 0.04 and P = 0.04, respectively), and on LDL-C only in adjusted models (model 2 and 3, P = 0.03 and P = 0.029, respectively). Besides, Del-allele carriers with protein, SFA, MUFA and n-3PUFA of ≥ 14, 9, 12 and 0.6%, respectively, had a significant increase in their serum leptin than Ins/Ins homozygotes (P < 0.05). However, these associations were not significant between the two genetic groups in subjects with low intakes of protein, SFA, MUFA and n-3PUFA. Moreover, Del-allele carriers with low carbohydrate (< 54%) had significantly higher leptin and ghrelin than Ins/Ins homozygotes (P < 0.05), however, in high-carbohydrate group, leptin and ghrelin were not significantly lower.
Conclusions
These findings indicate that the interaction between ApoB Ins/Del and dietary intake of MUFA, SFA, n-3PUFA, carbohydrate and protein could modulate the serum levels of TG, LDL-C, leptin and ghrelin in T2DM patients.

Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ApoB:
-
Apolipoprotein B
- T2DM:
-
Type 2 diabetes mellitus
- ANCOVA:
-
Analysis of covariance
- HDL-c:
-
High-density lipoprotein cholesterol
- LDL-c:
-
Low density lipoprotein cholesterol
- TG:
-
Triglyceride
- TC:
-
Total cholesterol
- SFA:
-
Saturated fatty acid
- MUFA:
-
Monounsaturated fatty acid
- PUFA:
-
Polyunsaturated fatty acid
References
da Rocha Fernandes J, Ogurtsova K, Linnenkamp U, Guariguata L, Seuring T, Zhang P, Cavan D, Makaroff LE (2016) IDF Diabetes Atlas estimates of 2014 global health expenditures on diabetes. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 117:48–54
Ogurtsova K, da Rocha Fernandes JD, Huang Y, Linnenkamp U, Guariguata L, Cho NH, Cavan D, Shaw JE, Makaroff LE (2017) IDF Diabetes Atlas: Global estimates for the prevalence of diabetes for 2015 and 2040. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 128:40–50
Gadi R, Samaha FF (2007) Dyslipidemia in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Curr Diabetes Rep 7(3):228–234
Taskinen MR (2002) Diabetic dyslipidemia. Atherosclerosis Suppl 31 3(1):47–51
Ho JS, Cannaday JJ, Barlow CE, Mitchell TL, Cooper KH, FitzGerald SJ (2008) Relation of the number of metabolic syndrome risk factors with all-cause and cardiovascular mortality. Am J Cardiol 102(6):689–692
Scaglione R, Argano C, Chiara TD, Licata G (2004) Obesity and cardiovascular risk: the new public health problem of worldwide proportions. Expert Rev Cardiovasc Ther 2(2):203–212
Ordovas JM, Corella D (2004) Nutritional genomics. Annu Rev Genom Hum Genet 5:71–118
Tan SY, Batterham M, Tapsell L (2011) Increased intake of dietary polyunsaturated fat does not promote whole body or preferential abdominal fat mass loss in overweight adults. Obes Facts 4(5):352–357
Moussavi N, Gavino V, Receveur O (2008) Is obesity related to the type of dietary fatty acids? An ecological study. Public Health Nutr 11(11):1149–1155
Fontani G, Corradeschi F, Felici A, Alfatti F, Bugarini R, Fiaschi AI, Cerretani D, Montorfano G, Rizzo AM, Berra B (2005) Blood profiles, body fat and mood state in healthy subjects on different diets supplemented with Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids. Eur J Clin Investig 35(8):499–507
Lottenberg AM, da Silva Afonso M, Lavrador MS, Machado RM, Nakandakare ER (2012) The role of dietary fatty acids in the pathology of metabolic syndrome. J Nutr Biochem 30 23(9):1027–1040
Flock MR, Fleming JA, Kris-Etherton PM (2014) Macronutrient replacement options for saturated fat: effects on cardiovascular health. Curr Opin Lipidol 25(1):67–74
Chasman DI, Paré G, Zee RY, Parker AN, Cook NR, Buring JE, Kwiatkowski DJ, Rose LM, Smith JD, Williams PT, Rieder MJ (2008) Genetic loci associated with plasma concentration of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol, triglycerides, apolipoprotein A1, and Apolipoprotein B among 6382 white women in genome-wide analysis with replication. Circ Cardiovasc Genet 1(1):21–30
Johansen CT, Kathiresan S, Hegele RA (2011) Genetic determinants of plasma triglycerides. J Lipid Res 52(2):189–206
Blackhart BD, Ludwig EM, Pierotti VR, Caiati L, Onasch MA, Wallis SC, Powell L, Pease R, Knott TJ, Chu ML (1986) Structure of the human apolipoprotein B gene. J Biol Chem 261(33):15364–15367
Whitfield AJ, Barrett PH, Van Bockxmeer FM, Burnett JR (2004) Lipid disorders and mutations in the APOB gene. Clin Chem 50(10):1725–1732
Xiao D, Huang K, Chen Q, Huang B, Liu W, Peng Y, Chen M, Huang D, Zou T, Yang J (2015) Four Apolipoprotein B gene polymorphisms and the risk for coronary artery disease: a meta-analysis of 47 studies. Genes Genom 37(7):621–632
Tsunoda K, Harihara S, Tanabe Y, Dashnyam B (2012) Polymorphism of the apolipoprotein B gene and association with plasma lipid and lipoprotein levels in the Mongolian Buryat. Biochem Genet 50(3–4):249–268
Rebhi L, Omezzine A, Kchock K, Belkahla R, Ben Hadjmbarek I, Rejeb J, Rejeb B, Nabli N, Bibi N, Massoud A, Abdelaziz T, Boughzala A, Bouslama E A (2008) 5′ ins/del and 3′ VNTR polymorphisms in the apolipoprotein B gene in relation to lipids and coronary artery disease. Clin Chem Lab Med 46:329–334
Machado MO, Hirata MH, Bertolami MC, Hirata RDC (2001) Apo B gene haplotype is associated with lipid profile of higher risk for coronary heart disease in Caucasian Brazilian men. J Clin Lab Anal 15:19–24
Saha N, Tay JSH, Heng CK, Humphries SE (1993) DNA polymorphisms of the apolipoprotein B gene are associated with obesity and serum lipids in healthy Indians in Singapore. Clin Genet 44:113–120
Lamia R, Asma O, Slim K, JihÈne R, Imen B, Ibtihel BH, Kaouther K, Radhia B, Nabila BR, Naoufel N, Ahmed BA (2012) Association of four apolipoprotein B polymorphisms with lipid profile and stenosis in Tunisian coronary patients. J Genet 91(1):75–79
Renges HH, Wile DB, McKeigue PM, Marmot MG, Humphries SE (1991) Apolipoprotein B gene polymorphisms are associated with lipid levels in men of South Asian descent. Atherosclerosis 91(3):267–275
Hixson JE, McMahan CA, McGill HC, Strong JP (1992) Apo B insertion/deletion polymorphisms are associated with atherosclerosis in young black but not young white males. Pathobiological Determinants of Atherosclerosis in Youth (PDAY) Research Group. Arteriosclerosis Vasc Biol 12(9):1023–1029
Cavalli SA, Hirata MH, Salazar LA, Diament J, Forti N, Giannini SD, Nakandakare ER, Bertolami MC, Hirata RD (2000) Apolipoprotein B gene polymorphisms: prevalence and impact on serum lipid concentrations in hypercholesterolemic individuals from Brazil. Clin Chim Acta 302(1):189–203
Glisic S, Prljic J, Radovanovic N, Alavantic D (1997) Study of apoB gene signal peptide insertion:deletion polymorphism in a healthy Serbian population: no association with serum lipid levels. Clin Chim Acta 263:57–65
Jemaa R, Mebazaa A, Fumeron F (2004) Apolipoprotein B signal peptide polymorphism and plasma LDL-cholesterol response to low-calorie diet. Int J Obes 28(7):902–905
Humphries SE, Talmud PJ, Cox C, Sutherland W, Mann J (1996) Genetic factors affecting the consistency and magnitude of changes in plasma cholesterol in response to dietary challenge. QJM 89(9):671–680
Loffreda S, Yang SQ, Lin HZ, Karp CL, Brengman ML, Wang DJ, Klein AS, Bulkley GB, Bao C, Noble PW, Lane MD (1998) Leptin regulates proinflammatory immune responses. FASEB J 12(1):57–65
Li WG, Gavrila D, Liu X, Wang L, Gunnlaugsson S, Stoll LL, McCormick ML, Sigmund CD, Tang C, Weintraub NL (2004) Ghrelin inhibits proinflammatory responses and nuclear factor-κB activation in human endothelial cells. Circulation 109(18):2221–2226
Schreyer SA, Vick C, Lystig TC, Mystkowski P, LeBoeuf RC (2002) LDL receptor but not apolipoprotein E deficiency increases diet-induced obesity and diabetes in mice. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 282(1):E207-14
Rafiee M, Sotoideh G, Djalali M, Alvandi E, Eshraghian M, Sojoudi F, Koohdani F (2016) Dietary ω-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid intake modulates impact of insertion/deletion polymorphism of ApoB gene on obesity risk in type 2 diabetic patients. Nutrition 32:1110–1115
Basiri MG, Sotoudeh G, Alvandi E, Djalali M, Eshraghian MR, Noorshahi N, Koohdani F (2015) APOA2–256T>C polymorphism interacts with saturated fatty acids intake to affect anthropometric and hormonal variables in type 2 diabetic patients. Genes Nutr 10(3):1–7
Consultation WE. Waist Circumference and Waist-Hip Ratio (2008) Report of a WHO expert consultation. World Health Organization, Geneva, pp 8–11
Aadahl M, Jørgensen TO (2003) Validation of a new self-report instrument for measuring physical activity. Med Sci Sports Exerc 35(7):1196–1202
Kelishadi R, Rabiei K, Khosravi A, Famouri F, Sadeghi M, Rouhafza H (2001) Assessment of physical activity of adolescents in Isfahan. J Shahrekord Univ Med Sci 3:27–33
Ainsworth BE, Haskell WL, Leon AS, Jacobs DR Jr, Montoye HJ, Sallis JF, Paffenbarger RS Jr (1993) Compendium of physical activities: classification of energy costs of human physical activities. Med Sci Sports Exerc 25(1):71–80
Esmaillzadeh A, Mirmiran PA, Azizi F (2005) Whole-grain consumption and the metabolic syndrome: a favorable association in Tehranian adults. Eur J Clin Nutr 59(3):353–362
Willett W (1998) Food frequency methods. In: Willett W (ed) Nutritional epidemiology, 2th edn. Oxford University Press, Oxford, pp 74–100
Subar AF (2004) Developing dietary assessment tools. J Am Diet Assoc 104:769–770
Ghaffarpour M, houshiar-Rad A, Kianfar H (1999) The manual for household measures, cooking yields factors and edible portion of food. Keshavarzi, Tehran
Miller SA, Dykes DD, Polesky HF (1988) A simple salting out procedure for extracting DNA from human nucleated cells. Nucleic Acids Res 16(3):1215
Boekholdt SM, Peters RJ, Fountoulaki K, Kastelein JJ, Sijbrands EJ (2003) Molecular variation at the apolipoprotein B gene locus in relation to lipids and cardiovascular disease: a systematic meta-analysis. Hum Genet 113(5):417–425
Fenech M (2015) Nutrigenomics and nutrigenetics: the new paradigm for optimising health and preventing disease. J Nutr Sci Vitaminol 61(Supplement):S209
Seo T, Oelkers PM, Giattina MR, Worgall TS, Sturley SL, Deckelbaum RJ (2001) Differential modulation of ACAT1 and ACAT2 transcription and activity by long chain free fatty acids in cultured cells. Biochemistry 40(15):4756–4762
Willner EL, Tow B, Buhman KK, Wilson M, Sanan DA, Rudel LL, Farese RV (2003) Deficiency of acyl CoA: cholesterol acyltransferase 2 prevents atherosclerosis in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci 100(3):1262–1267
Herz J, Goldstein JL, Strickland DK, Ho YK, Brown MS (1991) 39-kDa protein modulates binding of ligands to low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein/alpha 2-macroglobulin receptor. J Biol Chem 266(31):21232–21238
Miyazaki M, Kim YC, Ntambi JM (2001) A lipogenic diet in mice with a disruption of the stearoyl-CoA desaturase 1 gene reveals a stringent requirement of endogenous monounsaturated fatty acids for triglyceride synthesis. J Lipid Res 42(7):1018–1024
Kallel A, Feki M, Elasmi M, Souissi M (2007) Apolipoprotein B signal peptide polymorphism: distribution and influence on lipid parameters in Tunisian population. Physiol Res 56(4):411
Miyazaki M, Dobrzyn A, Man WC, Chu K, Sampath H, Kim HJ, Ntambi JM (2004) Stearoyl-CoA desaturase 1 gene expression is necessary for fructose-mediated induction of lipogenic gene expression by sterol regulatory element-binding protein-1c-dependent and-independent mechanisms. J Biol Chem 279(24):25164–25171
Chen ZY, Cunnane SC (1992) Preferential retention of linoleic acid-enriched triacylglycerols in liver and serum during fasting. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 263(2):R233-9
Biddinger SB, Miyazaki M, Boucher J, Ntambi JM, Kahn CR (2006) Leptin suppresses stearoyl-CoA desaturase 1 by mechanisms independent of insulin and sterol regulatory element–binding protein-1c. Diabetes 55(7):2032–2041
Ntambi JM, Miyazaki M, Stoehr JP, Lan H, Kendziorski CM, Yandell BS, Song Y, Cohen P, Friedman JM, Attie AD (2002) Loss of stearoyl–CoA desaturase-1 function protects mice against adiposity. Proc Natl Acad Sci 99(17):11482–11486
Obici S, Feng Z, Morgan K, Stein D, Karkanias G, Rossetti L (2002) Central administration of oleic acid inhibits glucose production and food intake. Diabetes 51(2):271–275
Peyron-Caso E, Taverna M, Guerre-Millo M, Véronèse A, Pacher N, Slama G, Rizkalla SW (2002) Dietary (n-3) polyunsaturated fatty acids up-regulate plasma leptin in insulin-resistant rats. J Nutr 132(8):2235–2240
Carvalheira JB, Siloto RM, Ignacchitti I, Brenelli SL, Carvalho CR, Leite A, Velloso LA, Gontijo JA, Saad MJ (2001) Insulin modulates leptin-induced STAT3 activation in rat hypothalamus. Febs Lett 500(3):119–124
Liu Q, Zhang J, Zerbinatti C, Zhan Y, Kolber BJ, Herz J, Muglia LJ, Bu G (2011) Lipoprotein receptor LRP1 regulates leptin signaling and energy homeostasis in the adult central nervous system. PLoS Biol 9(1):e1000575
Havel PJ, Townsend R, Chaump L, Teff K (1999) High-fat meals reduce 24-h circulating leptin concentrations in women. Diabetes 48(2):334–341
Havel PJ (2004) Update on adipocyte hormones regulation of energy balance and carbohydrate/lipid metabolism. Diabetes 53:S143–S151
Misra M, Miller KK, Almazan C, Ramaswamy K, Aggarwal A, Herzog DB, Neubauer G, Breu J, Klibanski A (2004) Hormonal and body composition predictors of soluble leptin receptor, leptin, and free leptin index in adolescent girls with anorexia nervosa and controls and relation to insulin sensitivity. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 89(7):3486–3495
Monteleone P, Bencivenga R, Longobardi N, Serritella C, Maj M (2003) Differential responses of circulating ghrelin to high-fat or high-carbohydrate meal in healthy women. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 88(11):5510–5514
Lee CC, Lee RP, Subeq YM, Wang CH, Fang TC, Hsu BG (2008) Fasting serum total ghrelin level inversely correlates with metabolic syndrome in hemodialysis patients. Arch Med Res 39(8):785–790
Acknowledgements
This research was funded and supported by the Tehran University of Medical Sciences (Research Project 91-03-161-19322). The authors thank the participants in this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rafiee, M., Sotoudeh, G., Djalali, M. et al. The interaction between apolipoprotein B insertion/deletion polymorphism and macronutrient intake on lipid profile and serum leptin and ghrelin levels in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients. Eur J Nutr 58, 1055–1065 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00394-018-1621-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00394-018-1621-5