Abstract
Purpose
To investigate the effect of two extracts obtained from Agaricus bisporus on the mRNA expression of cholesterol-related genes. One of the extracts contained ergosterol and other fungal sterols (SFE) and the other contained β-glucans and fungal sterols (EβG).
Methods
Firstly, the dietary mixed micelles (DMMs) generated after in vitro digestion of standards and SFE were applied to Caco2 cells. Then, the lower compartment after a Caco2-transport experiment was applied to HepG2 cells. The mRNA expression was assessed in both cell lines by low-density arrays (LDA). Mice received the extracts, ergosterol or control drugs after 4 weeks of a high-cholesterol diet. The lipid profile of plasma, liver and feces was determined. LDA assays were performed in liver and intestines.
Results
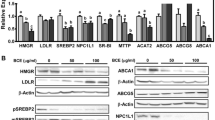
The DMM fraction of SFE up-regulated the LDLR mRNA expression in Caco2 cells. The lower compartment after Caco2-transport experiments up-regulated LDLR and modulated several other lipid-related genes in HepG2 cells. In mice, SFE decreased TC/HDL ratio and reduced hepatic triglycerides paralleled with down-regulation of Dgat1 expression, while EβG did it without transcriptional changes. Addition of SFE or ergosterol induced in jejunum a similar transcriptional response to simvastatin and ezetimibe; they all down-regulated Srebf2 and Nr1h4 (FXR) genes.
Conclusion
Ergosterol-containing extracts from A. bisporus lowered hepatic triglyceride and modify the mRNA expression of cholesterol-related genes although the transcriptional regulation was unrelated to changes in plasma lipid profile. These extracts may be useful limiting hepatic steatosis and as bioactive ingredients to design novel functional foods preventing lifestyle-related diseases such as non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CH+ERG-lard:
-
Lard enriched with cholesterol and ergosterol
- CH-Lard:
-
Lard enriched with cholesterol
- CH+SFE-lard:
-
Lard enriched with cholesterol and the SFE extract
- DMM:
-
Dietary mixed micelles
- EβG extract:
-
Extract containing ergosterol and β-glucans
- FXR:
-
Farnesoid X receptor
- HDL:
-
High-density lipoprotein
- LDA:
-
Low-density array
- LDL:
-
Low-density lipoprotein
- LXR:
-
Liver X receptor
- SFE extract:
-
Extract obtained by supercritical fluid extraction
- SREBP:
-
Sterol regulatory element-binding protein
References
Gil-Ramirez A, Soler-Rivas C (2014) The use of edible mushroom extracts as bioactive ingredients to design novel functional foods with hypocholesterolemic activities. In: Pesti G (ed) Cultivation, antioxidant properties and health benefits. Nova Publishers, New York, pp 43–73
Jeong SC, Jeong YT, Yang BK, Islam R, Koyyalamudi SR, Pang G, Cho KY, Song CH (2010) White button mushroom (Agaricus bisporus) lowers blood glucose and cholesterol levels in diabetic and hypercholesterolemic rats. Nutr Res 30(1):49–56
Calpe-Berdiel L, Escolà-Gil JC, Blanco-Vaca F (2009) New insights into the molecular actions of plant sterols and stanols in cholesterol metabolism. Atherosclerosis 203:18–31
Lammert F, Wang DQH (2005) New insights into the genetic regulation of intestinal cholesterol absorption. Gastroenterol J 129:718–734
Gil-Ramírez A, Ruiz-Rodríguez A, Marín FR, Reglero G, Soler-Rivas C (2014) Effect of ergosterol-enriched extracts obtained from Agaricus bisporus on cholesterol absorption using an in vitro digestion model. J Funct Foods 11:589–597
Kaneko E, Matsuda M, Yamada Y, Tachibana Y, Shimomura I, Makishima M (2003) Induction of intestinal ATP-binding cassette transporters by a phytosterol-derived liver X receptor agonist. J Biol Chem 278(19):36098
Matsubara T, Li F, Gonzalez FJ (2013) FXR signaling in the enterohepatic system. Moll Cell Endocrinol 368(1–2):17–29
Miyata M, Hata T, Yamazoe Y, Yoshinari K (2014) SREBP-2 negatively regulates FXR-dependent transcription of FGF19 in human intestinal cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 443(2):477–482
Jesch ED, Seo JM, Carr TP, Lee JY (2009) Sitosterol reduces messenger RNA and protein expression levels of Niemann-Pick C1-like 1 in FHs 74 Int cells. Nutr Res 29:859–866
Gil-Ramírez A, Aldars-García L, Palanisamy M, Jiverdeanu RM, Ruiz-Rodríguez A, Marín FR, Reglero G, Soler-Rivas C (2013) Sterol enriched fractions obtained from Agaricus bisporus fruiting bodies and by-products by compressed fluid technologies (PLE and SFE). Innov Food Sci Emerg Technol 18:101–107
Van de Steeg E, Kleemann R, Jansen HT, van Duyvenvoorde W, Offerman EH, Wortelboer HM, Degroot J (2013) Combined analysis of pharmacokinetic and efficacy data of preclinical studies with statins markedly improves translation of drug efficacy to human trials. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 347:635–644
Lei YF, Chen JL, Wei H, Xiong CM, Zhang YH, Ruan JL (2011) Hypolipidemic and anti-inflammatory properties of Abacopterin A from Abacopteris penangiana in high-fat diet-induced hyperlipidemia mice. Food Chem Toxicol 49:3206–3210
Qin YW, Ye P, He JQ, Sheng L, Wang LY, Du J (2010) Simvastatin inhibited cardiac hypertrophy and fibrosis in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice fed a “Western-style diet” by increasing PPAR α and γ expression and reducing TC, MMP-9, and Cat S levels. Acta Pharmacol Sin 31:1350–1358
Zúñiga S, Molina H, Azocar L, Amigo L, Nervi F, Pimentel F, Jarufe N, Arrese M, Lammert F, Miquel JF (2008) Ezetimibe prevents cholesterol gallstone formation in mice. Liver Int 28:935–947
Wang HH, Portincasa P, Mendez-Sanchez N, Uribe M, Wang DQ (2008) Effect of ezetimibe on the prevention and dissolution of cholesterol gallstones. Gastroenterology 134:2101–2110
Muraoka T, Aoki K, Iwasaki T, Shinoda K, Nakamura A, Aburatani H, Mori S, Tokuyama K, Kubota N, Kadowaki T, Terauchi Y (2011) Ezetimibe decreases SREBP-1c expression in liver and reverses hepatic insulin resistance in mice fed a high-fat diet. Metabolism 60:617–628
Palanisamy M, Aldars-García L, Gil-Ramírez A, Ruiz-Rodríguez A, Marín FR, Reglero G, Soler-Rivas C (2014) Pressurized water extraction of β-glucan enriched fractions with bile acids-binding capacities obtained from edible mushrooms. Biotechnol Progr 30:391–400
Nitschke J, Altenbach HJ, Malolepszy T, Mölleken H (2011) A new method for the quantification of chitin and chitosan in edible mushrooms. Carbohydr Res 346:1307–1310
Vandesompele J, De Preter K, Pattyn F, Poppe B, Van Roy N, De Paepe A, Speleman F (2002) Accurate normalization of real-time quantitative RT-PCR data by geometric averaging of multiple internal control genes. Genome Biol 3(7):1–12
Pfaffl MW (2001) A new mathematical model for relative quantification in real-time RT–PCR. Nucleic Acids Res 29(9):e45
Fukushima M, Nakano M, Morii Y, Ohashi T, Fujiwara Y, Sonoyama K (2010) Hepatic LDL receptor mRNA in rats is increased by dietary mushroom (Agaricus bisporus) fiber and sugar beet fiber. J Nutr 130:2151–2156
Ikemoto S, Takahashi M, Tsunoda N, Maruyama K, Itakura H, Kawanaka K, Tabata I, Higuchi M, Tange T, Yamamoto TT, Ezaki O (1997) Cholate inhibits high-fat diet-induced hyperglycemia and obesity with acyl-CoA synthetase mRNA decrease. Am J Physiol 273:E37–E45
Duan L-P, Wang HH, Wang DQ-H (2004) Cholesterol absorption is mainly regulated by the jejunal and ileal ATP-binding cassette sterol efflux transporters Abcg5 and Abcg8 in mice. J Lipid Res 45(7):1312–1323
Field FJ, Born E, Mathur SN (1997) Effect of micellar β-sitosterol on cholesterol metabolism in CaCo-2 cells. J Lipid Res 38:348–360
Plat J, Mensink RP (2002) Increased intestinal ABCA1 expression contributes to the decrease in cholesterol absorption after plant stanol consumption. FASEB J 16(10):1248–1253
Field FJ, Born E, Mathur SN (2004) LXR/RXR ligand activation enhances basolateral efflux of β-sitosterol in CaCo-2 cells. J Lipid Res 45:905–913
Petruzzelli M, Groen AK, van Erpecum KJ, Vrins C, van der Velde AE, Portincasa P, Palasciano G, van Berge Henegouwen GP, Lo Sasso G, Morgano A, Moschetta A (2009) Micellar lipid composition profoundly affects LXR-dependent cholesterol transport across CaCo2 cells. FEBS Lett 583:1274–1280
EFSA Panel on Dietetic Products, Nutrition and Allergies (NDA) (2010) Scientific Opinion on the substantiation of health claims related to plant sterols and plant stanols and maintenance of normal blood cholesterol concentrations (ID 549, 550, 567, 713, 1234, 1235, 1466, 1634, 1984, 2909, 3140), and maintenance of normal prostate size and normal urination (ID 714, 1467, 1635) pursuant to Article 13(1) of Regulation (EC) No 1924/2006. EFSA J 8:1813–1834. Available online: www.efsa.europa.eu/en/publications/efsajournal.htm
Reagan-Shaw S, Nihal M, Ahmad N (2008) Dose translation from animal to human studies revisited. FASEB J 22:659–661
Verbraecken J, Van de Heyning P, De Backer W, Van Gaal L (2006) Body surface area in normal-weight, overweight, and obese adults. A comparison study. Metabolism 5:515–524
EFSA Panel on Dietetic Products, Nutrition and Allergies (NDA) (2008) Scientific opinion of the panel on dietetic products nutrition and allergies on a request from Unilever PLC/NV on plant sterols and lower/reduced blood cholesterol, reduced the risk of (coronary) heart disease. EFSA J 781:1–12. Available online: www.efsa.europa.eu/en/publications/efsajournal.htm
Plat J, Mensink RP (2001) Effects of plant stanol esters on LDL receptor protein expression and on LDL receptor and HMG-CoA reductase mRNA expression in mononuclear blood cells of healthy men and women. FASEB J 16(2):258–260
Calpe-Berdiel L, Escolΰ-Gil JC, Ribas V, Navarro-Sastre A, Garcιs-Garcιs J, Blanco-Vaca F (2005) Changes in intestinal and liver global gene expression in response to a phytosterol-enriched diet. Atherosclerosis 181(1):75–85
Fukushima M, Ohashi T, Fujiwara Y, Sonoyama K, Nakano M (2001) Cholesterol-lowering effects of maitake (Grifola frondosa) fiber, shiitake (Lentinus edodes) fiber, and enokitake (Flammulina velutipes) fiber in rats. Exp Biol Med 226:758–765
Gil-Ramirez A, Soler-Rivas C (2014) The use of edible mushroom extracts as bioactive ingredients to design novel functional foods with hypocholesterolemic activities. In: GrégoirePesti (ed) Mushrooms: cultivation, antioxidant properties and health benefits. Nova Science Publishers, Inc. Hauppauge, NY, pp 43–73
Bobek P, Ozdín L, Kuniak L (1997) Effect of oyster mushroom and isolated β-glucan on lipid peroxidation and on the activities of antioxidative enzymes in rats fed the cholesterol diet. J Nut Biochem 8:469–471
Carter SJ, Roberts MB, Salter J, Eaton CB (2010) Relationship between Mediterranean Diet Score and atherothrombotic risk: findings from the Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES III), 1988–1994. Atherosclerosis 210:630–636
Carter B, Taylor O, Prendergast D, Zimmerman T, Von Furstenberg R, Moore D, Karpen S (2007) Stigmasterol, a soy lipid–derived phytosterol, is an antagonist of the bile acid Nnuclear receptor FXR. Pediatr Res 62(3):301–306
Yang C, Yu L, Li W, Xu F, Cohen JC, Hobbs HH (2004) Disruption of cholesterol homeostasis by plant sterols. J Clin Invest 114(6):813–822
Yang C, McDonald JG, Patel A, Zhang Y, Umetani M, Xu F, Westover EJ, Covey DF, Mangelsdorf DJ, Cohen JC, Hobbs HH (2006) Sterol intermediates from cholesterol biosynthetic pathway as liver X receptor ligands. J BiolChem 281(38):27816–27826
Cui J, Huang L, Zhao A, Lew J-L, Yu J, Sahoo S, Meinke PT, Royo I, Pelαez F, Wright SD (2003) Guggulsterone is a farnesoid X receptor antagonist in coactivator association assays but acts to enhance transcription of bile salt export pump. J BiolChem 278(12):10214–10220
Garcia-Calvo M, Lisnock J, Bull HG, Hawes BE, Burnett DA, Braun MP, Crona JH, Davis HR, Dean DC, Detmers PA, Graziano MP, Hughes M, MacIntyre DE, Ogawa A, O’Neill KA, Iyer SPN, Shevell DE, Smith MM, Tang YS, Makarewicz AM, Ujjainwalla F, Altmann SW, Chapman KT, Thornberry NA (2005) The target of ezetimibe is Niemann-Pick C1-Like 1 (NPC1L1). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102(23):8132–8137
Watanabe M, Houten SM, Wang L, Moschetta A, Mangelsdorf DJ, Heyman RA, Moore DD, Auwerx J (2004) Bile acids lower triglyceride levels via a pathway involving FXR, SHP, and SREBP-1c. J Clin Invest 113:1408–1418
Kanaya N, Kubo M, Liu Z, Chu P, Wang C, Yuan YC, Chen S (2011) Protective effects of white button mushroom (Agaricus bisporus) against hepatic steatosis in ovariectomized mice as a model of postmenopausal women. PLoS ONE 6:e26654
Inoue N, Inafuku M, Shirouchi B, Nagao K, Yanagita T (2013) Effect of Mukitake mushroom (Panellus serotinus) on the pathogenesis of lipid abnormalities in obese, diabetic ob/ob mice. Lipids Health Dis 12:18
Inafuku M, Nagao K, Nomura S, Shirouchi B, Inoue N, Nagamori N, Nakayama H, Toda T, Yanagita T (2012) Protective effects of fractional extracts from Panellus serotinus on non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in obese, diabetic db/db mice. Br J Nutr 107:639–646
Volger OL, van der Boom H, de Wit ECM, van Duyvenvoorde W, Hornstra G, Plat J, Havekes LM, Mensink RP, Princen HMG (2001) Dietary plant stanol esters reduce VLDL cholesterol secretion and bile saturation in apolipoprotein E*3-Leiden transgenic mice. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 21(6):1046–1052
Igel M, Giesa U, Lόtjohann D, von Bergmann K (2003) Comparison of the intestinal uptake of cholesterol, plant sterols, and stanols in mice. J Lipid Res 44(3):533–538
Acknowledgments
The research was supported by AGL2010-21537 national R+D program from the Spanish Ministry of Science and Innovation and ALIBIRD-C M S2009/AGR-1469 regional program from the Community of Madrid (Spain). CTICH (Centro Tecnológico de Investigación del Champiñón de La Rioja, Autol, Spain) is also acknowledged for the cultivation and supplying of the mushrooms fruiting bodies and Maria Navarro-Rubio for her technical assistance.
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Alicia Gil-Ramírez and Víctor Caz have equally contributed.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gil-Ramírez, A., Caz, V., Martin-Hernandez, R. et al. Modulation of cholesterol-related gene expression by ergosterol and ergosterol-enriched extracts obtained from Agaricus bisporus . Eur J Nutr 55, 1041–1057 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00394-015-0918-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00394-015-0918-x