Summary
Background: Mitral inflow velocity, deceleration time, and isovolumic relaxation time recorded by Doppler echocardiography have been widely used to evaluate left ventricular diastolic function but are affected by age, heart rate, loading conditions, and other factors. The diastolic mitral anulus velocity assessed by tissue Doppler echocardiography (TDE) was suggested to provide additional information about LV relaxation less affected by filling pressures.
Aim of this study: This study was designed to assess the clinical utility of mitral anulus velocity in the evaluation of left ventricular diastolic function.
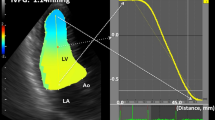
Patients and methods: Three groups of patients with a systolic ejection fraction > 45 % were separated: 10 normal volunteers (60 ± 10 y, CON group), 15 asymptomatic patients with known coronary artery disease (60 ± 11 y, CAD group) and 15 patients with longterm arterial hypertension and heart failure symptoms (58 ± 9 y, HYP group). The mitral inflow profile (E, A, E/A) was measured by pulsed Doppler, and the deceleration time (DT) and the isovolumic relaxation period (IVRT) were calculated. Systolic, early, and late diastolic velocities of the septal mitral anulus (ST, ET, AT, ET/AT) were assessed by pulsed TDE. All study subjects had invasive measurements of left ventricular end diastolic filling pressures during left heart catheterization.
Results: In the AH group, ET (6.9 ± 4.8 cm/s) and ET/AT (0.71 ± 0.28) were reduced compared to the CON group (11.7 ± 4.7 cm/s and 1.11 ± 0.36, p < 0.05, respectively) and the CAD group (8.9 ± 5.4 cm/s and 0.85 ± 0.26, respectively, p = ns). The groups did not differ with respect to the mitral E/A ratio, the deceleration time and the isovolumic relaxation time. LVED in the HYP group (16 ± 8 mm Hg) was elevated compared to the CON group (8 ± 3, p < 0.05) and the CAD group (12 ± 6 mm Hg, p = ns). No correlation was found between ET and LVED (r = 0.26). When the combination of mitral E/A ratio > 1 with LVED ≥ 15 mm Hg was classified as pseudonormalization, the pseudonormalization could be identified by a peak early diastolic mitral anulus velocity (ET) < 7 cm/s and an ET/AT ratio < 1 with a sensitivity of 77 % and a specificity of 88%.
Conclusions: The early diastolic mitral anulus velocity assessed by TDE (ET) is a preload-independent index of LV relaxation. TDE permits the detection of diastolic dysfunction in patients with a pseudonormal mitral inflow and elevated filling pressures.
Zusammenfassung
Hintergrund: Zur Analyse der linksventrikulären Relaxation werden die früh- und spätdiastolischen Geschwindigkeitsmaxima über der Mitralis (E, A) mit dem gepulsten Doppler abgeleitet sowie die Dauer der Dezelerations- und isovolumetrischen Relaxationszeit bestimmt. Alle genannten Parameter ändern sich jedoch in Abhängigkeit von Alter, Herzfrequenz und Lastbedingungen. Die Erfassung der diastolischen Exkursion des Mitralrings mittels Gewebedopplerechokardiographie (TDE) soll eine lastunabhängige Beurteilung der linksventrikulären, diastolischen Funktion ermöglichen.
Ziel der Studie: Ziel der vorliegenden Studie war die Erfassung der diagnostischen Wertigkeit der Mitralringexkusion in der Beurteilung der diastolischen, linksventrikulären Funktion.
Patienten und Methoden: Drei Gruppen von Patienten mit einer systolischen Ejektionsfraktion > 45 % wurden untersucht: 10 Kontrollprobanden (60 ± 10 J., KON-Gruppe), 15 asymptomatische Patienten mit koronarer Herzerkrankung (60 ± 11 J., KHK-Gruppe) und 15 Patienten mit langjähriger, arterieller Hypertonie und Symptomen der Herzinsuffizienz (58 ± 9 J., HYP-Gruppe). Das Mitraleinstromprofil (E, A, E/A) wurde mittels gepulstem Doppler gemessen und die Dezelerations- (DT) sowie isovolumetrische Relaxationszeit (IVRT) bestimmt. Systolische, früh- und spätdiastolische Geschwindigkeiten des medialen Mitralanulus (ST, ET, AT, ET/AT) wurden mittels gepulstem TDE abgeleitet. Bei allen Patienten wurde im Rahmen einer Linksherzkatheteruntersuchung der linksventrikuläre, enddiastolische Füllungsdruck (LVED) bestimmt.
Ergebnisse: In der HYP-Gruppe waren ET (6,9 ± 4,8 cm/s) und ET/AT (0,71 ± 0,28) im Vergleich zur KON-Gruppe (11,7 ± 4,7 cm/s bzw. 1,11 ± 0,36, p < 0,05) und zur KHK-Gruppe (8,9 ± 5,4 cm/s bzw. 0,85 ± 0,26, p = ns) vermindert. Die drei Gruppen unterschieden sich nicht hinsichtlich der mitralen E/A-Ratio, der Dezelerations- und isovolumetrischen Relaxationszeit. LVED war in der HYP-Gruppe (16 ± 8 mm Hg) höher als in der KON-Gruppe (8 ± 3, p < 0,05) und der KHK-Gruppe (12 ± 6 mm Hg, p = ns). Keine Korrelation wurde zwischen ET und LVED gefunden (r = 0,26). Wenn die Kombination aus mitraler E/A-Ratio > 1 und einem LVEDP ≥ 15 mm Hg als Pseudonormalisierung klassifiziert wurde, identifizierten eine frühdiastolische Mitralringexkursion (ET) < 7 cm/s und eine ET/AT-Ratio < 1 eine Pseudonormalisierung mit einer Sensitivität von 77 % und einer Spezifität von 88%.
Schlußfolgerung: Das mit TDE gemessene frühdiastolische Geschwindigkeitsmaximum des medialen Mitralanulus (ET) ist ein lastunabhängiger Index der linksventrikulären Relaxation. TDE identifiziert die diastolische Funktionsstörung bei Patienten mit pseudonormalem Mitraleinstromprofil und erhöhten Füllungsdrücken.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Eingegangen: 7. Januar 1999, Akzeptiert: 3. Februar 1999
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bruch, C., Marin, D., Kuntz, S. et al. Analyse der Mitralringexkursion mittels Gewebedopplerechokardiographie (Tissue Doppler echocardiography = TDE) Nichtinvasive Aufdeckung einer linksventrikulären, diastolischen Funktionsstörung. Z Kardiol 88, 353–362 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/s003920050297
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s003920050297