Abstract
Purpose
The purpose of this study was to investigate the autophagy associated with apoptosis in hepatic damage in the short bowel syndrome rat model.
Methods
SD rats underwent jugular vein catheterization for continuous total parenteral nutrition (TPN) and 90% small bowel resection. Animals were divided into two groups: TPN plus SBS (Control group) or TPN plus SBS plus intravenous administration of HGF (HGF group). On day 7, the rats were harvested, and hepatocellular injury was evaluated.
Results
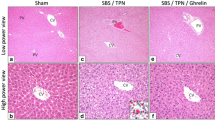
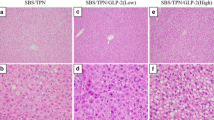
In an SBS rat model, hepatic steatosis and lobular inflammation were histologically suppressed in the HGF group (p < 0.01). The expression of tumor necrosis factor-α in the HGF group tend to be higher than that in the control group (p = 0.13). The gene expression of transforming Growth Factor-β in the HGF group was suppressed compared to the control group (p < 0.01). HGF treatment may have an antiapoptotic effect via the intrinsic pathway by caspase 9. Protein expressions of Rubicon (p = 0.03) and p62 (p < 0.01) in the HGF group were found to have increased compared to those in the control group.
Conclusion
The inhibitory effect of HGF on hepatic steatosis remains unclear, and further studies focusing on the mechanisms of fat accumulation are needed.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- IFALD:
-
Intestinal failure-associated liver disease
- SBS:
-
Short bowel syndrome
- NAFLD:
-
Nonalcoholic fatty liver diseases
- HGF:
-
Hepatocyte growth factor
- TPN:
-
Total parenteral nutrition
- IL6:
-
Interleukin-6
- TNFα:
-
Tumor necrosis factor-α
- TGFβ:
-
Transforming growth factor-β
- BAX:
-
Bcl-2-associated X protein
References
Thatch KA, Schwartz MZ, Yoo EY, Mendelson KG, Duke DS (2008) Modulation of the inflammatory response and apoptosis using epidermal growth factor and hepatocyte growth factor in a liver injury model: a potential approach to the management and treatment of cholestatic liver disease. J Pediatr Surg 43(12):2169–2173
Sugimoto T, Yamashita S, Ishigami M, Sakai N, Hirano K, Tahara M, Matsumoto K, Nakamura T, Matsuzawa Y (2002) Decreased microsomal triglyceride transfer protein activity contributes to initiation of alcoholic liver steatosis in rats. J Hepatol 36(2):157–162
Kosone T, Takagi H, Horiguchi N, Ariyama Y, Otsuka T, Sohara N, Kakizaki S, Sato K, Mori M (2007) HGF ameliorates a high-fat diet-induced fatty liver. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 293(1):G204-210
Matsukubo M, Yano K, Kaji T, Sugita K, Onishi S, Harumatsu T, Nagano A, Matsui M, Murakami M, Yamada K, Yamada W, Muto M, Kumagai K, Ido A, Ieiri S (2021) The administration of hepatocyte growth factor prevents total parenteral nutrition-induced hepatocellular injury in a rat model. Pediatr Surg Int 37(3):353–361
Yano K, Kaji T, Onishi S, Machigashira S, Nagai T, Harumatsu T, Yamada K, Yamada W, Muto M, Nakame K, Mukai M, Ieiri S (2019) Novel effect of glucagon-like peptide-2 for hepatocellular injury in a parenterally fed rat model of short bowel syndrome. Pediatr Surg Int 35(12):1345–1351
Yano K, Sugita K, Muto M, Matsukubo M, Onishi S, Kedoin C, Matsui M, Murakami M, Harumatsu T, Yamada K, Yamada W, Kumagai K, Ido A, Kaji T, Ieiri S (2022) The preventive effect of recombinant human hepatocyte growth factor for hepatic steatosis in a rat model of short bowel syndrome. J Pediatr Surg 57(7):1286–1292
Sugita K, Kaji T, Yano K, Matsukubo M, Nagano A, Matsui M, Murakami M, Harumatsu T, Onishi S, Yamada K, Yamada W, Muto M, Kumagai K, Ido A, Ieiri S (2021) The protective effects of hepatocyte growth factor on the intestinal mucosal atrophy induced by total parenteral nutrition in a rat model. Pediatr Surg Int 37(12):1743–1753
Nabeshima A, Yamada S, Guo X, Tanimoto A, Wang KY, Shimajiri S, Kimura S, Tasaki T, Noguchi H, Kitada S, Watanabe T, Fujii J, Kohno K, Sasaguri Y (2013) Peroxiredoxin 4 protects against nonalcoholic steatohepatitis and type 2 diabetes in a nongenetic mouse model. Antioxid Redox Signal 19(17):1983–1998
Nishikoba N, Kumagai K, Kanmura S, Nakamura Y, Ono M, Eguchi H, Kamibayashiyama T, Oda K, Mawatari S, Tanoue S, Hashimoto S, Tsubouchi H, Ido A (2020) HGF-MET signaling shifts m1 macrophages toward an M2-like phenotype through PI3K-mediated induction of arginase-1 expression. Front Immunol 11:2135
Kanda Y (2013) Investigation of the freely available easy-to-use software “EZR” for medical statistics. Bone Marrow Transplant 48(3):452–458
Katz MS, Thatch KA, Schwartz MZ (2010) Dose variation of hepatocyte growth factor and its effects on an animal model of TPN-induced liver injury. J Surg Res 163(2):294–298
Gao M, Fan S, Goldberg ID, Laterra J, Kitsis RN, Rosen EM (2001) Hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor blocks the mitochondrial pathway of apoptosis signaling in breast cancer cells. J Biol Chem 276(50):47257–47265
Puche JE, Saiman Y, Friedman SL (2013) Hepatic stellate cells and liver fibrosis. Compr Physiol 3(4):1473–1492
Narmada BC, Chia SM, Tucker-Kellogg L, Yu H (2013) HGF regulates the activation of TGF-beta1 in rat hepatocytes and hepatic stellate cells. J Cell Physiol 228(2):393–401
Tanaka S, Hikita H, Tatsumi T, Sakamori R, Nozaki Y, Sakane S, Shiode Y, Nakabori T, Saito Y, Hiramatsu N, Tabata K, Kawabata T, Hamasaki M, Eguchi H, Nagano H, Yoshimori T, Takehara T (2016) Rubicon inhibits autophagy and accelerates hepatocyte apoptosis and lipid accumulation in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in mice. Hepatology 64(6):1994–2014
Moumen A, Patane S, Porras A, Dono R, Maina F (2007) Met acts on Mdm2 via mTOR to signal cell survival during development. Development 134(7):1443–1451
Gallo S, Gatti S, Sala V, Albano R, Costelli P, Casanova E, Comoglio PM, Crepaldi T (2014) Agonist antibodies activating the Met receptor protect cardiomyoblasts from cobalt chloride-induced apoptosis and autophagy. Cell Death Dis 5(4):e1185
Bagias G, Misiakos EP, Charalampopoulos A, Zavras N, Sakellariou S, Schizas D, Sukhotnik I, Giamarelos E, Pikoulis E (2023) The effect of hepatocyte growth factor on intestinal adaption in an experimental model of short bowel syndrome. Pediatr Surg Int 39(1):80
Schwartz MZ, Kato Y, Yu D, Lukish JR (2000) Growth-factor enhancement of compromised gut function following massive small-bowel resection. Pediatr Surg Int 16(3):174–175
Kato Y, Yu D, Schwartz MZ (1998) Enhancement of intestinal adaptation by hepatocyte growth factor. J Pediatr Surg 33(2):235–239
Kato Y, Yu D, Schwartz MZ (1998) Hepatocyte growth factor up-regulates SGLT1 and GLUT5 gene expression after massive small bowel resection. J Pediatr Surg 33(1):13–15
Kato Y, Yu D, Lukish JR, Schwartz MZ (1997) Hepatocyte growth factor enhances intestinal mucosal cell function and mass in vivo. J Pediatr Surg 32(7):991–994
Fafalios A, Ma J, Tan X, Stoops J, Luo J, Defrances MC, Zarnegar R (2011) A hepatocyte growth factor receptor (Met)-insulin receptor hybrid governs hepatic glucose metabolism. Nat Med 17(12):1577–1584
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Laboratory Animal Science Research Support Center Institute for Research Promotion, Kagoshima University. We thank Mr. Brian Quinn for his comments and assistance with this manuscript. We thank Tomomi Kamibayashiyama, a technician at our institution, for her help with the rat’s management, histopathological measurement, biological measurement, western blot, and RT-PCR analyses. We thank Orie Iwaya, a technician at the Department of Pathology, Graduate School of Medical and Dental Science, for her help with histopathological staining. This study was supported by Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS: 23K08031, 22K07848, 22K07894, 22K08719, 22K08736, 22K08757, 21K07867, 21K08623) and a Grant from the Kawano Masanori Memorial Foundation for Promotion of Pediatrics.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
KS, KY, and MM designed the study. KS, KY, SO, and TK performed experiments. YI, MO, and LT supported histopathological assessment. MM, TH, and KS analyzed the data and created the Figure. MM, KK, AI, and TK provided conceptual advice. KS wrote the manuscript in consultation with SI.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest in association with the present study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Sugita, K., Yano, K., Matsukubo, M. et al. Potential mechanisms underlying the effect of hepatocyte growth factor on liver injury in short bowel syndrome model rats. Pediatr Surg Int 40, 8 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00383-023-05593-w
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00383-023-05593-w