Abstract
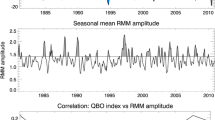
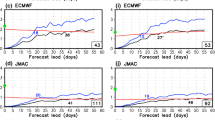
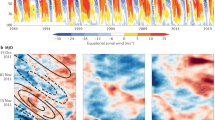
Recent studies have shown that the Madden-Julian Oscillation (MJO) is significantly modulated by the stratospheric Quasi-Biennial Oscillation (QBO). In general, boreal winter MJO becomes more active during the easterly phase of the QBO (EQBO) than during the westerly phase (WQBO). Based on this finding, here we examine the possible impacts of the QBO on MJO prediction skill in the operational models that participated in the WCRP/WWRP subseasonal-to-seasonal (S2S) prediction project. All models show a higher MJO prediction skill during EQBO winters than during WQBO winters. For the bivariate anomaly correlation coefficient of 0.5, the MJO prediction skill during EQBO winters is enhanced by up to 10 days. This enhancement is insensitive to the initial MJO amplitude, indicating that the improved MJO prediction skill is not simply the result of a stronger MJO. Instead, a longer persistence of the MJO during EQBO winters likely induces a higher prediction skill by having a higher prediction limit.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baggnett CF, Barnes EA, Maloney ED, Mundhenk BD (2017) Advancing atmospheric river forecasts into subseasonal-to-seasonal time scales. Geophys Res Lett 44:7528–7536. https://doi.org/10.1002/2017GL074434
Dee DP, Uppala SM, Simmons AJ et al (2011) The ERA-Interim reanalysis: configuration and performance of the data assimilation system. Q J R Meteorol Soc 137:553–597. https://doi.org/10.1002/qj.828
Ferreira RN, Schubert WH, Hack JJ (1996) Dynamical aspects of twin tropical cyclones associated with the Madden-Julian oscillation. J Atmos Sci 53:929–945. https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0469(1996)053%3C0929:DAOTTC%3E2.0.CO;2
Geller MA, Zhou T, Shindell D et al (2016) Modeling the QBO-Improvements resulting from higher model vertical resolution. J Adv Model Earth Syst 8:1092–1105. https://doi.org/10.1002/2016MS000699
Gonzalez AO, Jiang X (2017) Winter mean lower tropospheric moisture over the Maritime Continent as a climate model diagnostic metric for the propagation of the Madden-Julian oscillation. Geophys Res Lett 44:2588–2596. https://doi.org/10.1002/2016GL072430
Gottschalck J, Wheeler M, Weickmann K et al (2010) A frame for assessing operational Madden-Julian Oscillation forecasts: a clivar MJO working group project. Bull Am Meteorol Soc 91:1247–1258. https://doi.org/10.1175/2010BAMS2816.1
Grise KM, Son S-W, Gyakum JR (2013) Intraseasonal and interannual variability in North American storm tracks and its relationship to equatorial Pacific variability. Mon Weather Rev 141:3610–3625. https://doi.org/10.1175/MWR-D-12-00322.1
Hendon HH, Abhik S (2018) Differences in vertical structure of the Madden-Julian Oscillation associated with the quasi-biennial oscillation. Geophys Res Lett 45:4419–4428. https://doi.org/10.1029/2018GL077207
Jeong J-H, Ho C-H, Kim B-M, Kwon W-T (2005) Influence of the Madden-Julian Oscillation on wintertime surface air temperature and cold surges in east Asia. J Geophys Res Atmos 110:D11104. https://doi.org/10.1029/2004JD005408
Keen RA (1982) The role of cross-equatorial tropical cyclone pairs in the Southern Oscillation. Mon Weather Rev 110:1405–1416. https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0493(1982)110<1405TROCET>2.0.CO;2
Kiladis GN, Dias J, Straub KH, Wheeler MC, Tulich SN, Kikuchi K, Weickmann KM, Ventrice MJ (2014) A comparison of OLR and circulation-based indices for tracking the MJO. Mon Weather Rev 142:1697–1715. https://doi.org/10.1175/MWR-D-13-00301.1
Kim H-M (2017) The impact of the mean moisture bias on the key physics of MJO propagation in the ECMWF reforecast. J Geophys Res Atmos 122:7772–7784. https://doi.org/10.1002/2017JD027005
Kim H-K, Seo K-H (2016) Cluster analysis of tropical cyclone tracks over the western North Pacific using a Self-Organizing Map. J Clim 29:3731–3751. https://doi.org/10.1175/JCLI-D-15-0380.1
Kim J, Grise KM, Son S-W (2013) Thermal characteristics of the cold-point tropopause region in CMIP5 models. J Geophys Res Atmos 118:8827–8841. https://doi.org/10.1002/jgrd.50649
Kim H-M, Webster PJ, Toma VE, Kim D (2014) Predictability and prediction skill of the MJO in two operational forecasting systems. J Clim 27:5364–5378. https://doi.org/10.1175/JCLI-D-13-00480.1
L’Huereux ML, Higgins RW (2008) Boreal winter links between the Madden-Julian Oscillation and the Arctic Oscillation. J Clim 21:3040–3050. https://doi.org/10.1175/2007JCLI1955.1
Liebmann B, Smith CA (1996) Description of a complete (interpolated) outgoing longwave radiation dataset. Bull Am Meteorol Soc 77:1275–1277
Lim Y, Son S-W, Kim D (2018) MJO prediction skill of the Subseasonal-to-Seasonal Prediction models. J Clim 31:4075–4094. https://doi.org/10.1175/JCLI-D-17-0545.1
Lin H, Brunet G (2009) The influence of the Madden-Julian Oscillation on Canadian winter-time surface air temperature. Mon Weather Rev 137:2250–2262. https://doi.org/10.1175/2009MWR2831.1
Lin H, Brunet G (2011) Impact of the North Atlantic Oscillation on the forecast skill of the Madden-Julian Oscillation. Geophys Res Lett 38:L02802. https://doi.org/10.1029/2010GL046131
Lin H, Brunet G, Derome J (2008) Forecast skill of the Madden-Julian Oscillation in two Canadian atmospheric models. Mon Weather Rev 136:4130–4149. https://doi.org/10.1175/2008MWR2459.1
Liu C, Tian B, Li K-F, Manney GL, Livesey NJ, Yung YL, Waliser DE (2014) Northern Hemisphere mid-winter vortex-displacement and vortex-split stratospheric sudden warmings: influence of the Madden-Julian Oscillation and Quasi-Biennial Oscillation. J Geophys Res Atmos 119:12599–12620. https://doi.org/10.1002/2014JD021876
Madden RA, Julian PR (1971) Detection of a 40–50 Day Oscillation in the Zonal wind in the Tropical Pacific. J Atmos Sci 28:702–708. https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0469(1971)028%3C0702:DOADOI%3E2.0.CO;2
Madden RA, Julian PR (1972) Description of global-scale circulation cells in the tropics with a 40–50 day period. J Atmos Sci 29:1109–1123. https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0469(1972)029%3C1109:DOGSCC%3E2.0.CO;2
Marshall AG, Hendon HH, Son S-W, Lim Y (2017) Impact of the quasi-biennial oscillation on predictability of the Madden-Julian oscillation. Clim Dyn 49:1365–1377. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-016-3392-0
Nishimoto E, Yoden S (2017) Influence of the Stratospheric Quasi-Biennial Oscillation on the Madden–Julian Oscillation during Austral Summer. J Atmos Sci 74:1105–1125. https://doi.org/10.1175/JAS-D-16-0205.1
Rashid HA, Hendon HH, Wheeler MC, Alves O (2011) Prediction of the Madden–Julian Oscillation with the POAMA dynamical prediction system. Clim Dyn 36:649–661. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-010-0754-x
Salby ML, Hendon HH (1994) Intraseasonal behavior of clouds, temperature, and motion in the Tropics. J Atmos Sci 51:2207–2224. https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0469(1994)051%3C2207:IBOCTA%3E2.0.CO;2
Schmidt H, Rast S, Bunzel F et al (2013) Response of the middle atmosphere to anthropogenic and natural forcings in the CMIP5 simulations with the Max Planck Institute Earth system model. J Adv Model Earth Syst 5:98–116. https://doi.org/10.1002/jame.20014
Seo K-H, Lee H-J (2017) Mechanisms for a PNA-Like Teleconnection Pattern in Response to the MJO. J Atmos Sci 74:1767–1781. https://doi.org/10.1175/JAS-D-16-0343.1
Seo K-H, Lee H-J, Frierson DMW (2016) Unraveling the teleconnection mechanisms that induce wintertime temperature anomalies over the Northern Hemisphere continents in response to the MJO. J Atmos Sci 73:3557–3571. https://doi.org/10.1175/JAS-D-16-0036.1
Son S-W, Lim Y, Yoo C, Hendon HH, Kim J (2017) Stratospheric control of the Madden–Julian Oscillation. J Clim 30:1909–1922. https://doi.org/10.1175/JCLI-D-16-0620.1
Straub KH (2013) MJO initiation in the real-time multivariate MJO index. J Clim 26:1130–1151. https://doi.org/10.1175/JCLI-D-12-00074.1
Vitart F (2017) Madden-Julian Oscillation prediction and teleconnections in the S2S database. Q J R Meteorol Soc 143:2210–2220. https://doi.org/10.1002/qj.3079
Vitart F, Ardilouze C, Bonet A et al (2017) The Sub-seasonal to Seasonal (S2S) prediction project database. Bull Am Meteorol Soc 98:163–173. https://doi.org/10.1175/BAMS-D-16-0017.1
Wang J, Kim H-M, Chang EKM, Son S-W (2018) Modulation of the MJO and North Pacific Storm Track relationship by the QBO. J Geophys Res Atmos 123:3976–3992. https://doi.org/10.1029/2017JD027977
Wheeler MC, Hendon HH (2004) An all-season real-time multivariate MJO index: development of an index for monitoring and prediction. Mon Weather Rev 132:1917–1932. https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0493(2004)132%3C1917:AARMMI%3E2.0.CO;2
Xiang B, Zhao M, Jiang X, Lin S-J, Li T, Fu X, Vecchi G (2015) The 3–4-week MJO prediction skill in a GFDL coupled model. J Clim 28:5351–5364. https://doi.org/10.1175/JCLI-D-15-0102.1
Yoo C, Son S-W (2016) Modulation of the boreal wintertime Madden-Julian Oscillation by the stratospheric quasi-biennial oscillation. Geophys Res Lett 43:1392–1398. https://doi.org/10.1002/2016GL067762
Zhang C (2005) Madden-Julian Oscillation. Rev Geophys 43:RG2003. https://doi.org/10.1029/2004RG000158
Zhang C, Zhang B (2018) QBO-MJO connection. J Geophys Res Atmos 123:2957–2967. https://doi.org/10.1002/2017JD028171
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by the Korea Meteorological Institute under Grant KMI 2018-01011. We thank the operational centers for supplying their model output through the S2S database. We also appreciate the three anonymous reviewers for their constructive comments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lim, Y., Son, SW., Marshall, A.G. et al. Influence of the QBO on MJO prediction skill in the subseasonal-to-seasonal prediction models. Clim Dyn 53, 1681–1695 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-019-04719-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-019-04719-y