Abstract
Introduction
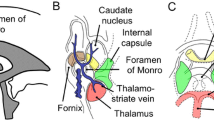
Endoscopic treatment for occlusive hydrocephalus requires knowledge of individual ventricular and vascular anatomies of the ventricular system.
Methods
We studied the feasibility of virtual neuroendoscopy (VNE) based on 3-D ultrasonography (3-D US) for the identification of parenchymal and vascular anatomical landmarks of the third ventricle and its impact on the surgical planning of endoscopic third ventriculostomy (ETV) in paediatric patients. 3-D US was performed through the anterior fontanel in four infants with hydrocephalus.
Results
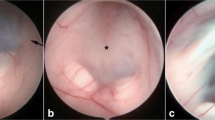
Virtual neuroendoscopy revealed the size of the foramen of Monro, anatomical landmarks of the floor of the third ventricle crucial for correct fenestration during ETV, but not the premesencephalic cistern. The basilar bifurcation was identified in relation to the floor of the third ventricle by VNE (power-Doppler ultrasonography) and confirmed intraoperatively after ETV.
Conclusion
3-D US-based VNE reveals detailed anatomical information on the ventricular system including the foramen of Monro and the floor of the third ventricle. Within the premesencephalic cistern vascular anatomy can be visualized, but not non-vascular structures.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Auer LM, Auer DP (1998) Virtual endoscopy for planning and simulation of minimally invasive neurosurgery. Neurosurgery 43:529–537
Burtscher J, Dessl A, Maurer H, Seiwald M, Felber S (1999) Virtual neuroendoscopy, a comparative magnetic resonance and anatomical study. Minim Invasive Neurosurg 42:113–117
Burtscher J, Dessl A, Bale R, Eisner W, Auer A, Twerdy K, Felber S (2000) Virtual endoscopy for planning endoscopic third ventriculostomy procedures. Pediatr Neurosurg 32:77–82
Buxton N, Macarthur D, Mallucci C, Punt J, Vloeberghs M (1998) Neuroendoscopic third ventriculostomy in patients less than 1 year old. Pediatr Neurosurg 29:73–76
Buxton N, Macarthur D, Mallucci C, Punt J, Vloeberghs M (1998) Neuroendoscopy in the premature population. Childs Nerv Syst 14:649–652
Cartmill M, Vloeberghs M (1999) The use of transendoscopic Doppler ultrasonography as a safety-enhancing measure during neuroendoscopic third ventriculostomy. Eur J Pediatr Surg 9 [Suppl 1]:50–51
Cartmill M, Jaspan T, McConachie N, Vloeberghs M (2001) Neuroendoscopic third ventriculostomy in dysmorphic brains. Childs Nerv Syst 17:391–394
Cinalli G, Sainte-Rose C, Chumas P, Zerah M, Brunelle F, Lot G, Pierre-Kahn A, Rénier D (1999) Failure of third ventriculostomy in the treatment of aqueductal stenosis in children. J Neurosurg 90:448–454
Erbe E, Kriete A, Jödicke A, Deinsberger W, Böker D-K (1996) 3D-ultrasonography and image matching for detection of brain shift during intracranial surgery. In: Computer assisted radiology CAR 1996. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Gronningsaeter A, Unsgard G, Ommedal S, Angelsen BA (1996) Ultrasound-guided neurosurgery: a feasibility study in the 3–30 MHz frequency range. Br J Neurosurg 10:161–168
Hata N, Dohi T, Iseki H, Takakura K (1997) Development of a frameless and armless stereotactic neuronavigation system with ultrasonographic registration. Neurosurgery 41:608–613
Hopf NJ, Grunert P, Freis G, Resch KDM, Perneczky A (1999) Endoscopic third ventriculostomy: outcome analysis of 100 consecutive procedures. Neurosurgery 44:795–806
Javadpour M, Mallucci C, Brodbelt A, Golash A, May P (2001) The impact of endoscopic third ventriculostomy on the management of newly diagnosed hydrocephalus in infants. Pediatr Neurosurg 35:131–135
Jödicke A, Deinsberger W, Erbe H, Kriete A, Böker DK (1998) Intraoperative three-dimensional ultrasonography: an approach to register brain shift using multidimensional image processing. Minim Invasive Neurosurg 41:13–19
Jones RF, Stening WA, Brydon M (1990) Endoscopic third ventriculostomy. Neurosurgery 26:86–92
Koivukangas J, Ylitalo J, Alasaarela E, Tauriainen A (1986) Three-dimensional ultrasound imaging of brain for neurosurgery. Ann Clin Res 18:65–72
Levy ML (1998) Special editorial commentary: virtual endoscopic simulations in neurosurgery: technical considerations and methodology. Neurosurgery 43:538–548
Levy ML, Chen CT, Amar AP, Yamada S, Togo K, Iizuka Y (1999) Virtual endoscopic environments in modern neurosurgical practice. Neurosurg Focus 6:Article 11
Lewis AI, Larson JJ, Crone KR (1995) Endoscopic treatment of complex hydrocephalus. In: Cohen AR (eds) Cranial endoscopy. Lippincott-Raven, Philadelphia, pp 168–175
McLaughlin MR, Wahlig JB, Kaufmann AM, Albright AL (1997) Traumatic basilar aneurysm after third ventriculostomy: case report. Neurosurgery 43:647–648
Riegel T, Alberti O, Shiratori V, Hellwig D, Bertalanffy H (2000) Relationships of virtual reality neuroendoscopic simulations to actual imaging. Minim Invasive Neurosurg 43:176–180
Sainte-Rose C (1992) Third ventriculostomy. In: Manwaring KH, Crone KR (eds) Neuroendoscopy. Liebert, New York, pp 47–62
Schmidt RH (1999) Use of a microvascular Doppler probe to avoid basilar artery injury during endoscopic third ventriculostomy: technical note. J Neurosurg 90:156–159
Shigematsu Y, Korogi Y, Hirai T, Okuda T, Ikushima I, Sugahara T, Liang L, Ge Y, Takahashi M (1998) Virtual MRI endoscopy of the intracranial cerebrospinal fluid spaces. Neuroradiology 40:644–650
Trobaugh JW, Trobaugh DJ, Richard WD (1994) Three-dimensional imaging with stereotactic ultrasonography. Comput Med Imaging Graph 18:315–323
Vandertop PW (1998) Traumatic basilar aneurysm after third ventriculostomy: case report. Neurosurgery 43:647–648
Vloeberghs M, Cartmill M (1999) Improved safety of neuroendoscopic third ventriculostomy by using an operative Doppler ultrasound probe. Neurosurg Focus 6:Article 13
Yuh EL, Jeffrey RB Jr, Birdwell RL, Chen BH, Napel S (1999) Virtual endoscopy using perspective volume-rendered three-dimensional sonographic data: technique and clinical applications. Am J Roentgenol 172:1193–1197
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The authors have no financial interest in the systems used in this study
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jödicke, A., Berthold, L.D., Scharbrodt, W. et al. Endoscopic surgical anatomy of the paediatric third ventricle studied using virtual neuroendoscopy based on 3-D ultrasonography. Childs Nerv Syst 19, 325–331 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-003-0748-7
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-003-0748-7