Abstract
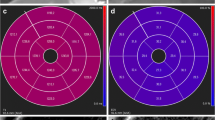
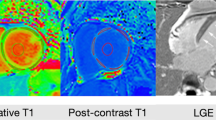
The extracellular volume fraction (ECV) by T1 mapping can quantify diffuse myocardial fibrosis, and useful as a non-invasive marker for risk stratification for patients with non-ischemic dilated cardiomyopathy (NIDCM). Prolonged QRS interval on electrocardiogram is related to worse clinical outcome for heart failure patients. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the prognostic value of the combination of ECV and QRS duration for NIDCM patients. A total of 60 NIDCM patients (mean age 61 ± 12 years, mean left ventricular ejection fraction 37 ± 10%, mean QRS duration 110 ± 19 ms) were enrolled. Using a 1.5-T MR scanner and 32-channel cardiac coils, the mean ECV value of six myocardial segments at the mid-ventricular level was measured by the modified look-locker inversion recovery method. Adverse events were defined as follows: cardiac death; recurrent hospitalization due to heart failure. Patients were allocated into three groups based on ECV value and QRS duration (group 1: ECV ≦ 0.30 and QRS ≦ 120 ms; group 2: ECV > 0.30 or QRS > 120 ms; group 3: ECV > 0.30 and QRS > 120 ms). During a median follow-up duration of 370 days, 7 of 60 (12%) NIDCM patients experienced adverse events. NIDCM patients with events had longer QRS duration (134 ± 31 ms vs. 106 ± 14 ms, p = 0.01) and higher ECV (0.34 ± 0.07 vs 0.29 ± 0.05, p = 0.026) compared with those without events. On Kaplan–Meier curve analysis, significant difference was found between group 1 and group 3 (p < 0.001, log-rank test). No significant difference was found between group 1 and group 2 (p = 0.053), group 2 and group 3 (p = 0.115). The area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC) for predicting adverse events was 0.778 (95% confidence interval CI 0.612–0.939) for ECV, 0.792 (95% CI 0.539–0.924) for QRS duration, 0.822 (95% CI 0.688–0.966) for combination of ECV and QRS duration. NIDCM patients with high ECV and prolonged QRS duration had significantly worse prognosis compared to those with normal ECV and normal QRS duration. The combination of ECV and QRS duration could be useful as a non-invasive method for better risk stratification for patients with NIDCM.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AUC:
-
Area under the curve
- CMR:
-
Cardiovascular magnetic resonance
- ECV:
-
Extracellular volume
- EF:
-
Ejection fraction
- LGE:
-
Late gadolinium enhancement
- LV:
-
Left ventricular
- MRI:
-
Magnetic resonance imaging
- NIDCM:
-
Non-ischemic dilated cardiomyopathy
- ROC:
-
Receiver operating characteristics
References
Kuruvilla S, Adenaw N, Katwal AB, Lipinski MJ, Kramer CM, Salerno M (2014) Late gadolinium enhancement on cardiac magnetic resonance predicts adverse cardiovascular outcomes in nonischemic cardiomyopathy: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Circ Cardiovasc Imaging 7(2):250–258
Di Marco A, Anguera I, Schmitt M, Klem I, Neilan TG, White JA, Sramko M, Masci PG, Barison A, Mckenna P, Mordi I, Haugaa KH, Leyva F, Rodriguez Capitan J, Satoh H, Nabeta T, Dallaglio PD, Campbell NG, Sabate X, Cequier A (2017) Late gadolinium enhancement and the risk for ventricular arrhythmias or sudden death in dilated cardiomyopathy: systematic review and meta-analysis. JACC Heart Fail 5(1):28–38
Lund LH, Jurga J, Edner M, Benson L, Dahlstrom U, Linde C, Alehagen U (2013) Prevalence, correlates, and prognostic significance of QRS prolongation in heart failure with reduced and preserved ejection fraction. Eur Heart J 34(7):529–539
Hombach V, Merkle N, Torzewski J, Kraus JM, Kunze M, Zimmermann O, Kestler HA, Wöhrle J (2009) Electrocardiographic and cardiac magnetic resonance imaging parameters as predictors of a worse outcome in patients with idiopathic dilated cardiomyopathy. Eur Heart J 30(16):2011–2018
Marume K, Noguchi T, Tateishi E, Morita Y, Kamakura T, Ishibashi K, Noda T, Miura H, Nishimura K, Nakai M, Yamada N, Tsujita K, Anzai T, Kusano K, Ogawa H, Yasuda S (2018) Mortality and sudden cardiac death risk stratification using the noninvasive combination of wide QRS duration and late gadolinium enhancement in idiopathic dilated cardiomyopathy. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol 11(4):e006233
Iles LM, Ellims AH, Llewellyn H, Hare JL, Kaye DM, McLean CA, Taylor AJ (2015) Histological validation of cardiac magnetic resonance analysis of regional and diffuse interstitial myocardial fibrosis. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging 6(1):14–22
Aus dem Siepen F, Buss SJ, Messroghli D, Andre F, Lossnitzer D, Seitz S, Keller M, Schnabel PA, Giannitsis E, Korosoglou G, Katus HA, Steen H (2015) T1 mapping in dilated cardiomyopathy with cardiac magnetic resonance: quantification of diffuse myocardial fibrosis and comparison with endomyocardial biopsy. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging 16(2):210–216
Coelho-Filho OR, Shah RV, Mitchell R, Neilan TG, Moreno H Jr, Simonson B, Kwong R, Rosenzweig A, Das S, Jerosch-Herold M (2013) Quantification of cardiomyocyte hypertrophy by cardiac magnetic resonance: implications for early cardiac remodeling. Circulation 128(11):1225–1233
Messroghli DR, Nordmeyer S, Dietrich T, Dirsch O, Kaschina E, Savvatis K, O h-Ici D, Klein C, Berger F, Kuehne T (2011) Assessment of diffuse myocardial fibrosis in rats using small-animal Look-Locker inversion recovery T1 mapping. Circ Cardiovasc Imaging 4(6):636–640
Semelka RC, Tomei E, Wagner S, Mayo J, Kondo C, Suzuki J, Caputo GR, Higgins CB (1990) Normal left ventricular dimensions and function: interstudy reproducibility of measurements with cine MR imaging. Radiology 174(3 Pt 1):763–768
Wong TC, Piehler K, Meier CG, Testa SM, Klock AM, Aneizi AA, Shakesprere J, Kellman P, Shroff SG, Schwartzman DS, Mulukutla SR, Simon MA, Schelbert EB (2012) Association between extracellular matrix expansion quantified by cardiovascular magnetic resonance and short-term mortality. Circulation 126(10):1206–1216
Gulati A, Jabbour A, Ismail TF, Guha K, Khwaja J, Raza S, Morarji K, Brown TD, Ismail NA, Dweck MR, Di Pietro E, Roughton M, Wage R, Daryani Y, O'Hanlon R, Sheppard MN, Alpendurada F, Lyon AR, Cook SA, Cowie MR, Assomull RG, Pennell DJ, Prasad SK (2013) Association of fibrosis with mortality and sudden cardiac death in patients with nonischemic dilated cardiomyopathy. JAMA 309(9):896–908
Puntmann VO, Peker E, Chandrashekhar Y, Nagel E (2016) T1 mapping in characterizing myocardial disease: a comprehensive review. Circ Res 119(2):277–299
Mewton N, Liu CY, Croisille P, Bluemke D, Lima JA (2011) Assessment of myocardial fibrosis with cardiovascular magnetic resonance. J Am Coll Cardiol 57(8):891–903
Messroghli DR, Moon JC, Ferreira VM, Grosse-Wortmann L, He T, Kellman P, Mascherbauer J, Nezafat R, Salerno M, Schelbert EB, Taylor AJ, Thompson R, Ugander M, van Heeswijk RB, Friedrich MG (2017) Clinical recommendations for cardiovascular magnetic resonance mapping of T1, T2, T2* and extracellular volume: a consensus statement by the Society for Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance (SCMR) endorsed by the European Association for Cardiovascular Imaging (EACVI). J Cardiovasc Magn Reson 19(1):75
aus dem Siepen F, Buss SJ, Messroghli D, Andre F, Lossnitzer D, Seitz S, Keller M, Schnabel PA, Giannitsis E, Korosoglou G, Katus HA, Steen H (2015) T1 mapping in dilated cardiomyopathy with cardiac magnetic resonance: quantification of diffuse myocardial fibrosis and comparison with endomyocardial biopsy. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging 16(2):210–216
Puntmann VO, Carr-White G, Jabbour A, Yu CY, Gebker R, Kelle S, Hinojar R, Doltra A, Varma N, Child N, Rogers T, Suna G, Arroyo Ucar E, Goodman B, Khan S, Dabir D, Herrmann E, Zeiher AM, Nagel E (2016) T1-mapping and outcome in nonischemic cardiomyopathy: all-cause mortality and heart failure. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging 9(1):40–50
Vita T, Gräni C, Abbasi SA, Neilan TG, Rowin E, Kaneko K, Coelho-Filho O, Watanabe E, Mongeon FP, Farhad H, Rassi CH, Choi YL, Cheng K, Givertz MM, Blankstein R, Steigner M, Aghayev A, Jerosch-Herold M, Kwong RY (2019) Comparing CMR mapping methods and myocardial patterns toward heart failure outcomes in nonischemic dilated cardiomyopathy. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging 12(8 Pt 2):1659–1669
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to John Martin for his English proofreading.
Funding
Research Grant, MSD Life Science Foundation, Public Interest Incorporated Foundation. Research Grant, Japan Society for the Promotion of Science: Grant-in-Aid for Early-Career Scientists.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest directly relevant to the content of this article.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kodama, S., Kato, S., Hayakawa, K. et al. Combination of extracellular volume fraction by cardiac magnetic resonance imaging and QRS duration for the risk stratification for patients with non-ischemic dilated cardiomyopathy. Heart Vessels 35, 1439–1445 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00380-020-01618-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00380-020-01618-9